Working with csv files in Python (original) (raw)
Python is one of the important fields for data scientists and many programmers to handle a variety of data. CSV (Comma-Separated Values) is one of the prevalent and accessible file formats for storing and exchanging tabular data.
In article explains What is CSV. Working with CSV files in Python, Reading, and Writing to a CSV file, and Storing Emails in CSV files .
Table of Content
- What is a CSV File?
- Working with CSV files in Python
- Reading a CSV file
- Reading CSV Files Into a Dictionary With csv
- Writing to a CSV file
- Writing a dictionary to a CSV file
- Reading CSV Files With Pandas
- Writing CSV Files with Pandas
- Storing Emails in CSV files
What is a CSV File?
CSV (Comma Separated Values) is a simple file format used to store tabular data, such as a spreadsheet or database. A CSV file stores tabular data (numbers and text) in plain text. Each line of the file is a data record. Each record consists of one or more fields, separated by commas. The use of the comma as a field separator is the source of the name for this file format. For working CSV files in Python, there is an inbuilt module called CSV.
Working with CSV files in Python
Below are some operations that we perform while working with Python CSV files in Python
- Reading a CSV file
- Reading CSV Files Into a Dictionary With
csv - Writing to a CSV file
- Writing a dictionary to a CSV file
- Reading CSV Files With P
andas - Writing CSV Files With P
andas - Storing email in CSV file
Reading a CSV file
Reading from a CSV file is done using the reader object. The CSV file is opened as a text file with Python’s built-in open() function, which returns a file object. In this example, we first open the CSV file in READ mode, file object is converted to csv.reader object and further operation takes place. Code and detailed explanation is given below.
Python `
importing csv module
import csv
csv file name
filename = "aapl.csv"
initializing the titles and rows list
fields = [] rows = []
reading csv file
with open(filename, 'r') as csvfile: # creating a csv reader object csvreader = csv.reader(csvfile)
# extracting field names through first row
fields = next(csvreader)
# extracting each data row one by one
for row in csvreader:
rows.append(row)
# get total number of rows
print("Total no. of rows: %d" % (csvreader.line_num))printing the field names
print('Field names are:' + ', '.join(field for field in fields))
printing first 5 rows
print('\nFirst 5 rows are:\n') for row in rows[:5]: # parsing each column of a row for col in row: print("%10s" % col, end=" "), print('\n')
`
Output:
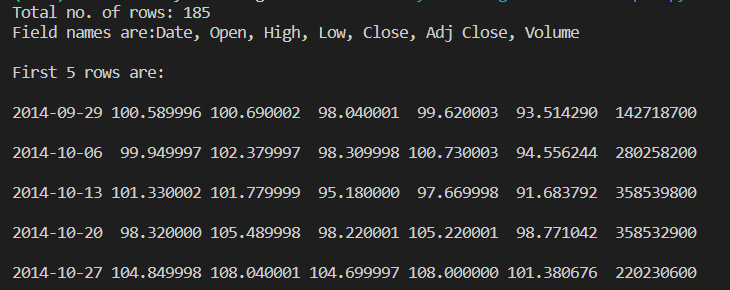
The above example uses a CSV file aapl.csv which can be downloaded from here .
Run this program with the aapl.csv file in the same directory.
- Let us try to understand this piece of code.
with open(filename, 'r') as csvfile:
csvreader = csv.reader(csvfile)
- Here, we first open the CSV file in READ mode. The file object is named as csvfile . The file object is converted to csv.reader object. We save the csv.reader object as csvreader.
fields = csvreader.next()
- csvreader is an iterable object. Hence, .next() method returns the current row and advances the iterator to the next row. Since, the first row of our csv file contains the headers (or field names), we save them in a list called fields .
for row in csvreader:
rows.append(row)
- Now, we iterate through the remaining rows using a for loop. Each row is appended to a list called rows . If you try to print each row, one can find that a row is nothing but a list containing all the field values.
print("Total no. of rows: %d"%(csvreader.line_num))
- csvreader.line_num is nothing but a counter which returns the number of rows that have been iterated.
Reading CSV Files Into a Dictionary With csv
We can read a CSV file into a dictionary using the csv module in Python and the csv.DictReader class. Here’s an example:
Suppose, we have a employees.csv file and content inside it will be:
name,department,birthday_month
John Smith,HR,July
Alice Johnson,IT,October
Bob Williams,Finance,January
In this example, csv.DictReader reads each row of the CSV file as a dictionary where the keys are the column headers, and the values are the corresponding values in each row. The dictionaries are then appended to a list ( data_list in this case).
Python `
import csv
Open the CSV file for reading
with open('employees.csv', mode='r') as file: # Create a CSV reader with DictReader csv_reader = csv.DictReader(file)
# Initialize an empty list to store the dictionaries
data_list = []
# Iterate through each row in the CSV file
for row in csv_reader:
# Append each row (as a dictionary) to the list
data_list.append(row)Print the list of dictionaries
for data in data_list: print(data)
`
Output:
{'name': 'John Smith', 'department': 'HR', 'birthday_month': 'July'}
{'name': 'Alice Johnson', 'department': 'IT', 'birthday_month': 'October'}
{'name': 'Bob Williams', 'department': 'Finance', 'birthday_month': 'January'}
Writing to a CSV file
To write to a CSV file, we first open the CSV file in WRITE mode. The file object is converted to csv.writer object and further operations takes place. Code and detailed explanation is given below.
Python `
importing the csv module
import csv
field names
fields = ['Name', 'Branch', 'Year', 'CGPA']
data rows of csv file
rows = [['Nikhil', 'COE', '2', '9.0'], ['Sanchit', 'COE', '2', '9.1'], ['Aditya', 'IT', '2', '9.3'], ['Sagar', 'SE', '1', '9.5'], ['Prateek', 'MCE', '3', '7.8'], ['Sahil', 'EP', '2', '9.1']]
name of csv file
filename = "university_records.csv"
writing to csv file
with open(filename, 'w') as csvfile: # creating a csv writer object csvwriter = csv.writer(csvfile) # writing the fields csvwriter.writerow(fields) # writing the data rows csvwriter.writerows(rows)
`
Let us try to understand the above code in pieces.
- fields and rows have been already defined. fields is a list containing all the field names. rows is a list of lists. Each row is a list containing the field values of that row.
with open(filename, 'w') as csvfile:
csvwriter = csv.writer(csvfile)
- Here, we first open the CSV file in WRITE mode. The file object is named as csvfile . The file object is converted to csv.writer object. We save the csv.writer object as csvwriter .
csvwriter.writerow(fields)
- Now we use writerow method to write the first row which is nothing but the field names.
csvwriter.writerows(rows)
- We use writerows method to write multiple rows at once.
Writing a dictionary to a CSV file
To write a dictionary to a CSV file, the file object (csvfile) is converted to a DictWriter object. Detailed example with explanation and code is given below.
Python `
importing the csv module
import csv
my data rows as dictionary objects
mydict = [{'branch': 'COE', 'cgpa': '9.0', 'name': 'Nikhil', 'year': '2'}, {'branch': 'COE', 'cgpa': '9.1', 'name': 'Sanchit', 'year': '2'}, {'branch': 'IT', 'cgpa': '9.3', 'name': 'Aditya', 'year': '2'}, {'branch': 'SE', 'cgpa': '9.5', 'name': 'Sagar', 'year': '1'}, {'branch': 'MCE', 'cgpa': '7.8', 'name': 'Prateek', 'year': '3'}, {'branch': 'EP', 'cgpa': '9.1', 'name': 'Sahil', 'year': '2'}]
field names
fields = ['name', 'branch', 'year', 'cgpa']
name of csv file
filename = "university_records.csv"
writing to csv file
with open(filename, 'w') as csvfile: # creating a csv dict writer object writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fields)
# writing headers (field names)
writer.writeheader()
# writing data rows
writer.writerows(mydict)`
In this example, we write a dictionary mydict to a CSV file.
with open(filename, 'w') as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames = fields)
- Here, the file object ( csvfile ) is converted to a DictWriter object. Here, we specify the fieldnames as an argument.
writer.writeheader()
- writeheader method simply writes the first row of your csv file using the pre-specified fieldnames.
writer.writerows(mydict)
- writerows method simply writes all the rows but in each row, it writes only the values(not keys).
So, in the end, our CSV file looks like this:

csv file
Consider that a CSV file looks like this in plain text:

university record
- We notice that the delimiter is not a comma but a semi-colon. Also, the rows are separated by two newlines instead of one. In such cases, we can specify the delimiter and line terminator.
Reading CSV Files With P andas
We can read a Python CSV files with Pandas using the pandas.read_csv( ) function. Here’s an example:
Suppose, we have a employees.csv file and content inside it will be:
name,department,birthday_month
John Smith,HR,July
Alice Johnson,IT,October
Bob Williams,Finance,January
In this example, pd.read_csv() reads the CSV file into a Pandas DataFrame. The resulting DataFrame can be used for various data manipulation and analysis tasks.
Python `
import pandas as pd
Read the CSV file into a DataFrame
df = pd.read_csv('employees.csv')
Display the DataFrame
print(df)
`
Output:
name department birthday_month 0 John Smith HR July
1 Alice Johnson IT October
2 Bob Williams Finance January
We can access specific columns, filter data, and perform various operations using pandas DataFrame functionality. For example, if we want to access the “name” column, we can use df['name'].
Python `
Access the 'name' column
names = df['name'] print(names)
`
Output :
0 John Smith
1 Alice Johnson
2 Bob Williams
Name: name, dtype: object
Writing CSV Files with Pandas
We can use Pandas to write CSV files. It can done by using pd.DataFrame() function. In this example, the Pandas library is used to convert a list of dictionaries ( mydict ) into a DataFrame, representing tabular data. The DataFrame is then written to a Python CSV file named “output.csv” using the to_csv method, creating a structured and readable data file for further analysis or sharing.
Python `
import pandas as pd
mydict = [ {'branch': 'COE', 'cgpa': '9.0', 'name': 'Nikhil', 'year': '2'}, {'branch': 'COE', 'cgpa': '9.1', 'name': 'Sanchit', 'year': '2'}, {'branch': 'IT', 'cgpa': '9.3', 'name': 'Aditya', 'year': '2'}, {'branch': 'SE', 'cgpa': '9.5', 'name': 'Sagar', 'year': '1'}, {'branch': 'MCE', 'cgpa': '7.8', 'name': 'Prateek', 'year': '3'}, {'branch': 'EP', 'cgpa': '9.1', 'name': 'Sahil', 'year': '2'} ]
Create a DataFrame from the list of dictionaries
df = pd.DataFrame(mydict)
Write the DataFrame to a CSV file
df.to_csv('output.csv', index=False)
`
Output CSV File:
branch,cgpa,name,year
COE,9.0,Nikhil,2
COE,9.1,Sanchit,2
IT,9.3,Aditya,2
SE,9.5,Sagar,1
MCE,7.8,Prateek,3
EP,9.1,Sahil,2
Storing Emails in CSV files
Here we are importing the csv module and then simply using the same concept of storing the emails in the form of comma-separated entity also with their names. We’re opening the file open() function and specifying that we need that as a csv file and then writing the each column into the csv file using writer object.
Python `
importing the csv module
import csv
field names
fields = ['Name', 'Email']
data rows of csv file
rows = [ ['Nikhil', 'nikhil.gfg@gmail.com'], ['Sanchit', 'sanchit.gfg@gmail.com'], ['Aditya', 'aditya.gfg@gmail.com'], ['Sagar', 'sagar.gfg@gmail.com'], ['Prateek', 'prateek.gfg@gmail.com'], ['Sahil', 'sahil.gfg@gmail.com']]
name of csv file
filename = "email_records.csv"
writing to csv file
with open(filename, 'w') as csvfile: # creating a csv writer object csvwriter = csv.writer(csvfile)
# writing the fields
csvwriter.writerow(fields)
# writing the data rows
csvwriter.writerows(rows)`
Output:

Emails in csv