Permutations of given String (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 10 Apr, 2025
Given a **string s, the task is to **return all permutations of a given string in lexicographically sorted order.
**Note: A permutation is the rearrangement of all the elements of a string. Duplicate arrangement can exist.
**Examples:
**Input: s = "ABC"
**Output: "ABC", "ACB", "BAC", "BCA", "CAB", "CBA"**Input: s = "XY"
**Output: "XY", "YX"**Input: s = "AAA"
**Output: "AAA", "AAA", "AAA", "AAA", "AAA", "AAA"
The idea is to use backtracking to generate all possible permutations of given **string s. To do so, first **initialize an array of string **ans[] to *store all the permutations. Start from the 0 th index and for each index i*, **swap the value s[i] with all the elements in its right i.e. from i+1 to n-1, and recur to the index i + 1. If the index i is equal to **n, store the resultant **string in **ans[], else keep operating similarly for all other indices. Thereafter, **swap back the values to original values to initiate **backtracking. At last **sort the array ans[].
**illustration:
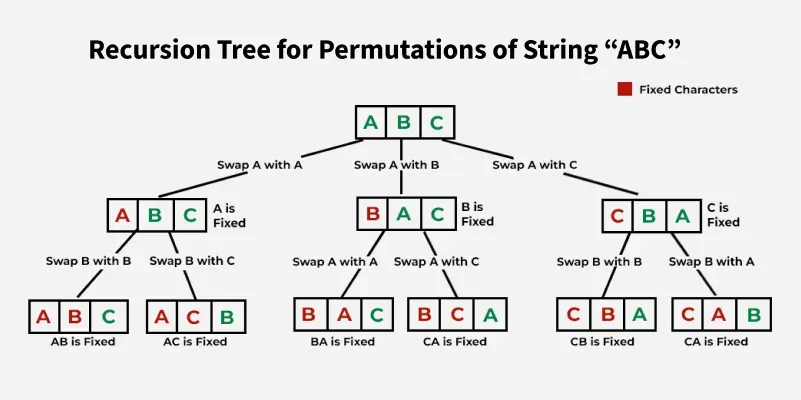
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ `
// C++ Program to generate all unique // permutations of a string #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
// Recursive function to generate // all permutations of string s void recurPermute(int index, string &s, vector &ans) {
// Base Case
if (index == s.size()) {
ans.push_back(s);
return;
}
// Swap the current index with all
// possible indices and recur
for (int i = index; i < s.size(); i++) {
swap(s[index], s[i]);
recurPermute(index + 1, s, ans);
swap(s[index], s[i]);
}}
// Function to find all unique permutations vector findPermutation(string &s) {
// Stores the final answer
vector<string> ans;
recurPermute(0, s, ans);
// sort the resultant vector
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());
return ans;}
int main() { string s = "ABC"; vector res = findPermutation(s); for(auto x: res) { cout << x << " "; } return 0; }
Java
// Java Program to generate all unique // permutations of a string import java.util.*;
class GfG {
// Recursive function to generate
// all permutations of string s
static void recurPermute(int index, StringBuilder s,
List<String> ans) {
// Base Case
if (index == s.length()) {
ans.add(s.toString());
return;
}
// Swap the current index with all
// possible indices and recur
for (int i = index; i < s.length(); i++) {
swap(s, index, i);
recurPermute(index + 1, s, ans);
swap(s, index, i);
}
}
// Swap characters at positions i and j
static void swap(StringBuilder s, int i, int j) {
char temp = s.charAt(i);
s.setCharAt(i, s.charAt(j));
s.setCharAt(j, temp);
}
// Function to find all unique permutations
static List<String> findPermutation(String s) {
// Stores the final answer
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(s);
recurPermute(0, str, ans);
// sort the resultant list
Collections.sort(ans);
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "ABC";
List<String> res = findPermutation(s);
for (String x : res) {
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}}
Python
Python Program to generate all unique
permutations of a string
Recursive function to generate
all permutations of string s
def recurPermute(index, s, ans):
# Base Case
if index == len(s):
ans.append("".join(s))
return
# Swap the current index with all
# possible indices and recur
for i in range(index, len(s)):
s[index], s[i] = s[i], s[index]
recurPermute(index + 1, s, ans)
s[index], s[i] = s[i], s[index]Function to find all unique permutations
def findPermutation(s):
# Stores the final answer
ans = []
recurPermute(0, list(s), ans)
# sort the resultant list
ans.sort()
return ansif name == "main": s = "ABC" res = findPermutation(s) for x in res: print(x, end=" ")
C#
// C# Program to generate all unique // permutations of a string using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG {
// Recursive function to generate
// all permutations of string s
static void recurPermute(int index, char[] s,
List<string> ans) {
// Base Case
if (index == s.Length) {
ans.Add(new string(s));
return;
}
// Swap the current index with all
// possible indices and recur
for (int i = index; i < s.Length; i++) {
Swap(s, index, i);
recurPermute(index + 1, s, ans);
Swap(s, index, i);
}
}
// Swap characters at positions i and j
static void Swap(char[] s, int i, int j) {
char temp = s[i];
s[i] = s[j];
s[j] = temp;
}
// Function to find all unique permutations
static List<string> findPermutation(string s) {
// Stores the final answer
List<string> ans = new List<string>();
recurPermute(0, s.ToCharArray(), ans);
// sort the resultant list
ans.Sort();
return ans;
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
string s = "ABC";
List<string> res = findPermutation(s);
foreach (string x in res) {
Console.Write(x + " ");
}
}}
JavaScript
// JavaScript Program to generate all unique // permutations of a string
// Recursive function to generate // all permutations of string s function recurPermute(index, s, ans) {
// Base Case
if (index === s.length) {
ans.add(s.join(""));
return;
}
// Swap the current index with all
// possible indices and recur
for (let i = index; i < s.length; i++) {
[s[index], s[i]] = [s[i], s[index]];
recurPermute(index + 1, s, ans);
[s[index], s[i]] = [s[i], s[index]];
}}
// Function to find all unique permutations function findPermutation(s) {
// sort input string
s = s.split("").sort();
// Stores all unique permutations
let res = new Set();
recurPermute(0, s, res);
// Convert Set to Array for the final answer
return Array.from(res).sort();}
const s = "ABC"; const res = findPermutation(s); console.log(res.join(" "));
`
Output
ABC ACB BAC BCA CAB CBA
**Time Complexity: O(n * n!)
**Auxiliary Space: O(n!)
**Related articles:
