An acidic link (original) (raw)
- News & Views
- Published: 26 June 2013
Cancer
Nature volume 499, pages 37–38 (2013)Cite this article
- 14k Accesses
- 6 Citations
- 14 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Subjects
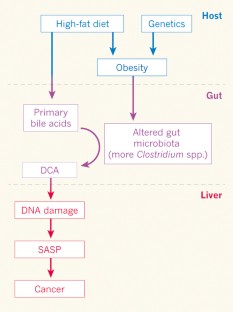
Obese people are at higher risk of multiple types of cancer, but why? One explanation could be that obesity enhances the production of pro-inflammatory, and carcinogenic, bile acids by gut microorganisms. See Letter p.97
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1: How obesity increases cancer risk.
Notes
- *This article and the paper under discussion4 were published online on 26 June 2013.
References
- Park, E. J. et al. Cell 140, 197–208 (2010).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Greenblum, S., Turnbaugh, P. J. & Borenstein, E. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 594–599 (2012).
Article CAS ADS Google Scholar - Fei, N. & Zhao, L. ISME J. 7, 880–884 (2013).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Yoshimoto, S. et al. Nature 499, 97–101 (2013).
Article CAS ADS Google Scholar - Coppe, J. P. et al. PLoS Biol. 6, 2853–2868 (2008).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Turnbaugh, P. J., Backhed, F., Fulton, L. & Gordon, J. I. Cell Host Microbe 3, 213–223 (2008).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Nagengast, N. M. et al. Eur. J. Cancer 31, 1067–1070 (1995).
Article Google Scholar - Devkota, S. et al. Nature 487, 104–108 (2012).
Article CAS ADS Google Scholar - Martens, E. C. et al. PLoS Biol. 9, e1001221 (2011).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Sayin, S. I. et al. Cell Metab. 17, 225–235 (2013).
Article CAS MathSciNet Google Scholar - Ahmad, N. N., Pfalzer, A. & Kaplan, L. M. Int. J. Obes. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.38 (2013).
- Swann, J. R. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108 (Suppl. 1), 4523–4530 (2011).
Article CAS ADS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Suzanne Devkota is at the Joslin Diabetes Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02215, USA.,
Suzanne Devkota - Peter. J. Turnbaugh is at the FAS Center for Systems Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138, USA.,
Peter. J. Turnbaugh
Authors
- Suzanne Devkota
- Peter. J. Turnbaugh
Corresponding author
Correspondence toPeter. J. Turnbaugh.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devkota, S., Turnbaugh, P. An acidic link.Nature 499, 37–38 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12404
- Published: 26 June 2013
- Issue date: 04 July 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12404