Cancer immunology and immunotherapy (original) (raw)
Editorial
Cancer immunology research is diverse, uses cutting-edge technologies and continues to excite with its constantly evolving contribution to new therapeutic options, and not just for patients with cancer.
Review
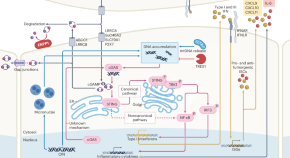
The balance of STING signaling orchestrates immunity in cancer
In this Review, the authors summarize the literature around immune cancer cell STING signaling and how it is finely balanced between pro-tumorigenic and anti-tumorigenic functions.
- Klara Rasmussen Bollerup Lanng
- Emil Leth Lauridsen
- Martin Roelsgaard Jakobsen
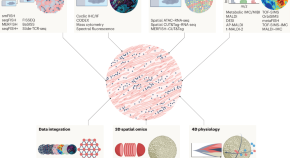
Decoding the tumor microenvironment with spatial technologies
We are in the midst of an explosion of multiomics and spatial data along with constant innovation of the tools used to study these data. In this Review article, as part of our Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy series, the authors discuss these innovations and their application to study the tumor microenvironment.
- Logan A. Walsh
- Daniela F. Quail
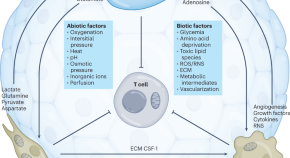
The immunometabolic ecosystem in cancer
Bantug and Hess discuss the metabolic interplay between tumor-resident cells and how the effect of metabolism-targeted anticancer strategies on non-transformed or immune cells in the tumor needs to be considered.
- Glenn R. Bantug
- Christoph Hess
From the archive
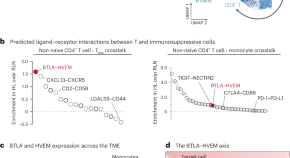
The BTLA–HVEM axis restricts CAR T cell efficacy in cancer
Here the authors show that BTLA on effector T cells interacts with HVEM on other immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment. The authors also present evidence that overcoming this checkpoint can ehance CAR T functionality.
- Puneeth Guruprasad
- Alberto Carturan
- Marco Ruella
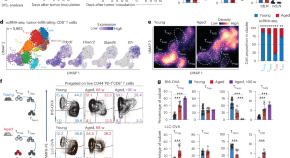
The aged tumor microenvironment limits T cell control of cancer
Cancer and aging are associated with each other, but underlying mechanisms contributing to this correlation are unclear. Here the authors identify a dysfunctional T cell state that is distinct from typical T cell exhaustion and only occurs in the tumor microenvironment during later life.
- Alex C. Y. Chen
- Sneha Jaiswal
- Debattama R. Sen
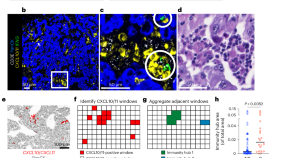
Human lung cancer harbors spatially organized stem-immunity hubs associated with response to immunotherapy
The spatial organization of cells in solid tumors is considered to be important for immune response and response to therapy. Here the authors use multiomics including spatial transcriptomics of human lung tumors prior to patients being treated and show among other things an association of stem-immunity hubs rich in stem-like CD8+ T cells with positive response to anti-PD-1 therapy.
- Jonathan H. Chen
- Linda T. Nieman
- Nir Hacohen
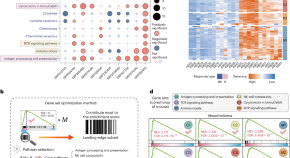
A method for predicting drugs that can boost the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade
Here the authors present a method they call CM-Drug for the identification of combination drugs that can boost the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. They validate this method with melanoma and lung cancer models in mice and explore in further depth one hit from their screen, the thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) analog taltirelin.
- Yun Xia
- Xin Li
- An-Yuan Guo
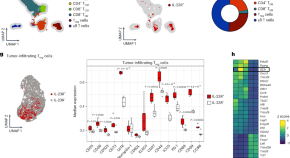
IL-23 stabilizes an effector Treg cell program in the tumor microenvironment
IL-23 promotes tumor growth in preclinical cancer models and correlates with adverse clinical outcomes. Here, Becher and colleagues find that IL-23 produced by tumor-associated macrophages stabilizes Treg cell identity, promoting immunosuppression and tumor growth.
- Tobias Wertheimer
- Pascale Zwicky
- Burkhard Becher
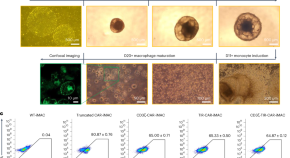
A second-generation M1-polarized CAR macrophage with antitumor efficacy
Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived macrophages (iMACs) are being used to make chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) macrophages for immunotherapy. Here the authors design a second-generation macrophage-specific CAR by integrating CD3ζ and toll/IL-1R (TIR) domains resulting in an M1-polarized CAR-iMAC with increased antitumor functions.
- Anhua Lei
- Hua Yu
- Jin Zhang
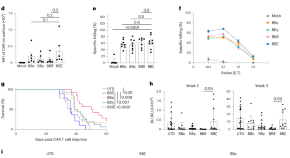
Harnessing CD3 diversity to optimize CAR T cells
Minguet and colleagues systematically examine how individual CD3 chains of the TCR–CD3 complex can improve chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell performance.
- Rubí M.-H. Velasco Cárdenas
- Simon M. Brandl
- Susana Minguet
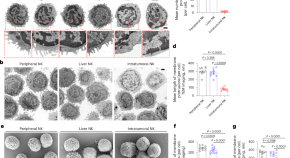
Tumors evade immune cytotoxicity by altering the surface topology of NK cells
NK cells require an immunological synapse to kill cancer cells and these synapses have been shown to have membranous protrusions. Here the authors use cutting-edge imaging and other techniques to show that tumor serine metabolism results in a reduction in NK cell sphingomyelin content and a lack of these membranous protrusions, which could contribute to a failure to kill cancer cells.
- Xiaohu Zheng
- Zhuanghao Hou
- Haiming Wei

Exhausted intratumoral Vδ2− γδ T cells in human kidney cancer retain effector function
γδ T cells contribute to cancer immunity by killing tumor cells, but their function in the context of immune checkpoint inhibition is less clear. Here the authors show that a Vδ2− subset of γδ T cells in human kidney tumors phenotypically resembles exhausted T cells yet retains this cytolytic function and can be used to predict response to immune checkpoint inhibition.
- Chiara Rancan
- Marcel Arias-Badia
- Lawrence Fong

CD40 signal rewires fatty acid and glutamine metabolism for stimulating macrophage anti-tumorigenic functions
Unlike metabolic reprogramming that is characteristic of macrophage inflammatory polarization responses to lipopolysaccharide and TLR4 stimulation, the metabolism underlying inflammatory responses to CD40 signaling is not well characterized. Here the authors show CD40 signaling drives fatty acid oxidation and glutamine metabolism resulting in regulation of the NAD+/NADH ratio, which in turn promotes antitumor and pro-inflammatory macrophage functions.
- Pu-Ste Liu
- Yi-Ting Chen
- Ping-Chih Ho
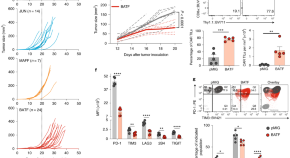
BATF and IRF4 cooperate to counter exhaustion in tumor-infiltrating CAR T cells
Chronic antigen stimulation leads to CD8+ T cell exhaustion, which is mediated by persistent activation of the transcription factor NFAT in the absence of AP-1. Seo, González-Avalos and colleagues show that overexpressed BATF cooperates with IRF4 to counteract NFAT-induced exhaustion and promote better tumor control by CAR T cells in mouse models.
- Hyungseok Seo
- Edahí González-Avalos
- Patrick G. Hogan
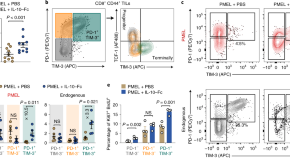
Metabolic reprogramming of terminally exhausted CD8+ T cells by IL-10 enhances anti-tumor immunity
Tang and colleagues show that a half-life-extended IL-10–Fc fusion protein acts directly on terminally exhausted PD1+TIM-3+CD8+ T cells to enhance their proliferation and effector function by reprogramming the cellular metabolism to oxidative phosphorylation in a mitochondrial pyruvate carrier–dependent manner. Treatment of tumor-bearing mice with IL-10–Fc and adoptive T cell therapy led to eradication of their established solid tumors and durable cures.
- Yugang Guo
- Yu-Qing Xie
- Li Tang