Synthesis of Heterobifunctional Protein Fusions Using Copper-Free Click Chemistry and the Aldehyde Tag (original) (raw)
Figure 3.
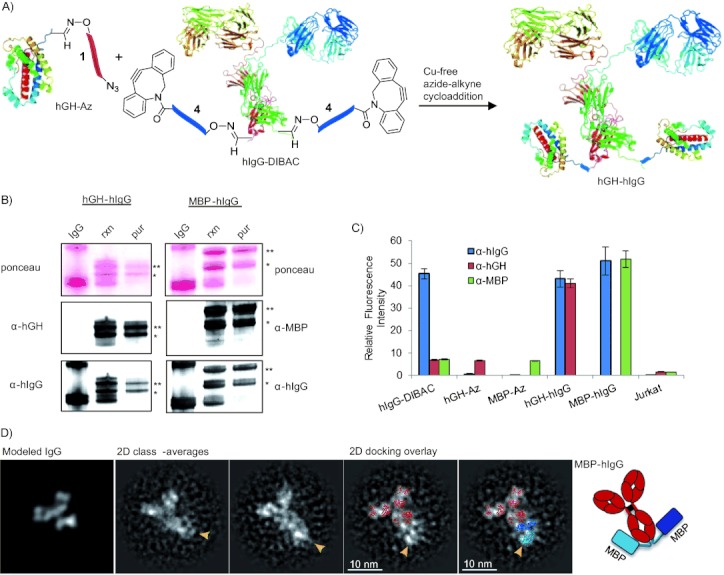
Protein–protein conjugation of hIgG with hGH and MBP. A) Aldehyde-tagged protein functionalized with azide 1 (hGH-Az) reacts specifically with protein functionalized with 4 (hIgG-DIBAC). As hIgG is a homodimer, two molecules of hGH-Az can react with hIgG-DIBAC to form a trimer. B) Western blot analysis of hIgG-hGH and hIgG-MBP chemical conjugations, nonreduced to highlight mono- and diconjugation. rxn: after reaction at 4 °C for 16 h. pur: after purification. Top blots: ponceau stain. Middle blots: blot probed with α-hGH or α-MBP and subsequently by α-mIgG HRP. Bottom blots: same blot probed with α-hIgG 647. * Denotes single conjugate; ** denotes diconjugate. C) Flow cytometry analysis of SKOV3 cells treated with aldehyde-tagged α-HER2-hIgG. Chemically conjugated hGH-hIgG and MBP-hIgG labeled the cell surface by α-HER2 binding, whereas azide-modified hGH-Az or MBP-Az alone did not. Blue=α-hlgG; red=α-hGH; green=α-MBP.D) Negative stain TEM image of C-terminal-tagged MBP-hIgG conjugates. A gallery of 2D class-averages of negatively stained MBP-hIgG shows a flexible additional density at the tip of one of the hIgG density lobes (arrows) that is consistent with a C-terminal attachment. The left panel displays a simulated density map of unconjugated IgG; the averages on the right are overlaid with a 2D docking of IgG1 alone (red) or with additional MBP crystal structures (light and dark blue; Protein Data Bank (PDB) 1IGY, 1JW4).