A multicentre, randomised, double blind, placebo controlled phase II study of subcutaneous interferon beta-1a in the treatment of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (original) (raw)
Abstract
Objective: To assess the efficacy of interferon beta (IFNß) in combination with methotrexate in treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: 209 patients with active rheumatoid arthritis, who had been on methotrexate for at least six months and at a stable dose for four weeks before study entry, were randomised in double blind fashion to receive placebo (0.05 ml or 0.5 ml), IFNß 2.2 µg (0.05 ml), or IFNß 44 µg (0.5 ml), given subcutaneously three times weekly for 24 weeks. The primary efficacy measure was a change in radiological scores at week 24. The secondary endpoint was the proportion of patients who met the ACR 20% improvement criteria at the end of the study. Synovial biopsy specimens were obtained before and after treatment from a subset of patients. Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the presence of inflammatory cells and the results were measured by digital image analysis. Collagen crosslinks were measured in urine at different times throughout the study.
Results: Analysis of radiological scores and clinical variable showed no changes in any of the groups, and there were no differences between the groups. On microscopic analysis of synovial tissue there was no significant change in the scores for infiltration by inflammatory cells after IFNß treatment. Urinary levels of collagen crosslinks were unchanged between the treatment groups.
Conclusions: At the doses tested, treatment with IFNß three times weekly in combination with methotrexate did not have a clinical or radiological effect in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (88.3 KB).
Figure 1.
Patient disposition.
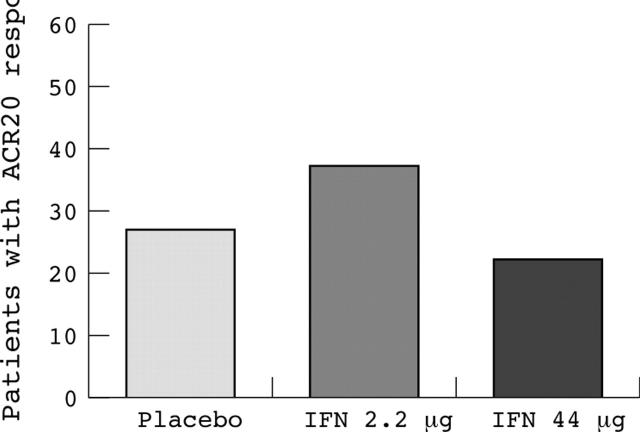
Figure 2.
American College of Rheumatology 20% (ACR20) response in the treatment groups (placebo groups combined).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boers M., Verhoeven A. C., Markusse H. M., van de Laar M. A., Westhovens R., van Denderen J. C., van Zeben D., Dijkmans B. A., Peeters A. J., Jacobs P. Randomised comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate and sulphasalazine with sulphasalazine alone in early rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1997 Aug 2;350(9074):309–318. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)01300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Alvaro-Gracia J. M., Cobby M., Doherty M., Domljan Z., Emery P., Nuki G., Pavelka K., Rau R., Rozman B. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Dec;41(12):2196–2204. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199812)41:12<2196::AID-ART15>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coclet-Ninin J., Dayer J. M., Burger D. Interferon-beta not only inhibits interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha but stimulates interleukin-1 receptor antagonist production in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1997 Dec;8(4):345–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery P. Therapeutic approaches for early rheumatoid arthritis. How early? How aggressive? Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Nov;34 (Suppl 2):87–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann J., Mueller A., Voigt A., Carl H. D., Gursche A., Zacher J., Stein G., Hein G. Hydroxypyridinium collagen crosslinks in serum, urine, synovial fluid and synovial tissue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003 Feb;42(2):314–320. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan M. C., Haringman J. J., Ahern M. J., Breedveld F. C., Smith M. D., Tak P. P. Quantification of the cell infiltrate in synovial tissue by digital image analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Jan;39(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan M. C., Reece R. J., Barg E. C., Smeets T. J., Farnell J., Rosenburg R., Veale D. J., Breedveld F. C., Emery P., Tak P. P. Modulation of inflammation and metalloproteinase expression in synovial tissue by leflunomide and methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Findings in a prospective, randomized, double-blind, parallel-design clinical trial in thirty-nine patients at two centers. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Aug;43(8):1820–1830. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200008)43:8<1820::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li D. K., Paty D. W. Magnetic resonance imaging results of the PRISMS trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of interferon-beta1a in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Prevention of Relapses and Disability by Interferon-beta1a Subcutaneously in Multiple Sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1999 Aug;46(2):197–206. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(199908)46:2<197::aid-ana9>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R., St Clair E. W., Breedveld F., Furst D., Kalden J., Weisman M., Smolen J., Emery P., Harriman G., Feldmann M. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet. 1999 Dec 4;354(9194):1932–1939. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)05246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland L. W., Schiff M. H., Baumgartner S. W., Tindall E. A., Fleischmann R. M., Bulpitt K. J., Weaver A. L., Keystone E. C., Furst D. E., Mease P. J. Etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1999 Mar 16;130(6):478–486. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-130-6-199903160-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G., Mezin F., Juge-Aubry C. E., Plater-Zyberk C., Gabay C., Guerne P-A. Interferon beta stimulates interleukin 1 receptor antagonist production in human articular chondrocytes and synovial fibroblasts. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Jan;63(1):43–49. doi: 10.1136/ard.2002.005546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets T. J., Dayer J. M., Kraan M. C., Versendaal J., Chicheportiche R., Breedveld F. C., Tak P. P. The effects of interferon-beta treatment of synovial inflammation and expression of metalloproteinases in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Feb;43(2):270–274. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200002)43:2<270::AID-ANR5>3.0.CO;2-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets T. J., Kraan M. C., Versendaal J., Breedveld F. C., Tak P. P. Analysis of serial synovial biopsies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: description of a control group without clinical improvement after treatment with interleukin 10 or placebo. J Rheumatol. 1999 Oct;26(10):2089–2093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. S., Kalden J. R., Scott D. L., Rozman B., Kvien T. K., Larsen A., Loew-Friedrich I., Oed C., Rosenburg R. Efficacy and safety of leflunomide compared with placebo and sulphasalazine in active rheumatoid arthritis: a double-blind, randomised, multicentre trial. European Leflunomide Study Group. Lancet. 1999 Jan 23;353(9149):259–266. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(98)09403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Hart B. A., Kraan M. C., Jonker M., Smeets T. J., Breedveld F. C. The effects of interferon beta treatment on arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999 Apr;38(4):362–369. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.4.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Taylor P. C., Breedveld F. C., Smeets T. J., Daha M. R., Kluin P. M., Meinders A. E., Maini R. N. Decrease in cellularity and expression of adhesion molecules by anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jul;39(7):1077–1081. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., van der Lubbe P. A., Cauli A., Daha M. R., Smeets T. J., Kluin P. M., Meinders A. E., Yanni G., Panayi G. S., Breedveld F. C. Reduction of synovial inflammation after anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Oct;38(10):1457–1465. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi Hiroshi, Kim Sunhwa, Matsuo Koichi, Suzuki Hiroshi, Suzuki Tomohiko, Sato Kojiro, Yokochi Taeko, Oda Hiromi, Nakamura Kozo, Ida Nobutaka. RANKL maintains bone homeostasis through c-Fos-dependent induction of interferon-beta. Nature. 2002 Apr 18;416(6882):744–749. doi: 10.1038/416744a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triantaphyllopoulos K. A., Williams R. O., Tailor H., Chernajovsky Y. Amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis and suppression of interferon-gamma, interleukin-12, and tumor necrosis factor alpha production by interferon-beta gene therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jan;42(1):90–99. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199901)42:1<90::AID-ANR12>3.0.CO;2-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vencovský J., Machácek S., Sedová L., Kafková J., Gatterová J., Pesáková V., Růzicková S. Autoantibodies can be prognostic markers of an erosive disease in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 May;62(5):427–430. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.5.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinblatt M. E., Kaplan H., Germain B. F., Block S., Solomon S. D., Merriman R. C., Wolfe F., Wall B., Anderson L., Gall E. Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. A five-year prospective multicenter study. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Oct;37(10):1492–1498. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Holten Judith, Plater-Zyberk Christine, Tak Paul P. Interferon-beta for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Res. 2002 Sep 18;4(6):346–352. doi: 10.1186/ar598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Holten Judith, Reedquist Kris, Sattonet-Roche Pascale, Smeets Tom J. M., Plater-Zyberk Christine, Vervoordeldonk Margriet J., Tak Paul P. Treatment with recombinant interferon-beta reduces inflammation and slows cartilage destruction in the collagen-induced arthritis model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004 Mar 23;6(3):R239–R249. doi: 10.1186/ar1165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heide A., Jacobs J. W., Bijlsma J. W., Heurkens A. H., van Booma-Frankfort C., van der Veen M. J., Haanen H. C., Hofman D. M., van Albada-Kuipers G. A., ter Borg E. J. The effectiveness of early treatment with "second-line" antirheumatic drugs. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1996 Apr 15;124(8):699–707. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-124-8-199604150-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. How to read radiographs according to the Sharp/van der Heijde method. J Rheumatol. 2000 Jan;27(1):261–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]