Associations between increases in plasma n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids following supplementation and decreases in anger and anxiety in substance abusers - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2008 Feb 15;32(2):568-75.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.10.020. Epub 2007 Nov 1.
Affiliations
- PMID: 18060675
- PMCID: PMC2275606
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.10.020
Randomized Controlled Trial
Associations between increases in plasma n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids following supplementation and decreases in anger and anxiety in substance abusers
Laure Buydens-Branchey et al. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008.
Abstract
Objective: Mounting evidence indicates that low levels of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) play a role in the pathophysiology of a large number of psychiatric disorders. In light of the suboptimal n-3 PUFAs intake due to poor dietary habits among substance abusers and the strong associations between aggression, anxiety and substance use disorders we examined if insurance of adequate intakes of n-3 PUFAs with supplementation would decrease their anger and anxiety scores.
Method: Substance abusers (n=22) were assigned to either 3 g of n-3 PUFAs, mainly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) or soybean oil in identically looking capsules. The trial was double-blind, randomized and lasted 3 months. Anger and anxiety scales were administered at baseline and once a month thereafter. Blood samples were collected at baseline and at the end of the trial.
Results: Patients' dietary intakes of n-3 PUFAs fell below recommended levels. Assignment to n-3 PUFA treatment was accompanied by significant decreases in anger and anxiety scores compared to placebo assignment. These changes were associated with increases in plasma levels of both EPA and DHA but an increase in EPA was more robustly correlated with low end-of-trial anxiety scores and an increase in DHA was more robustly correlated with low end-of-trial anger scores.
Conclusion: These pilot data indicate that ensuring adequate n-3 PUFA intake via supplementation benefits substance abusers by reducing their anger and anxiety levels. The strong correlations between an increase in plasma EPA and lower anxiety scores and between an increase in plasma DHA and lower anger scores suggests a need for the further exploration of the differential responses to these two n-3 PUFAs in different psychiatric conditions.
Figures
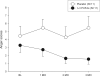
Figure 1
Anger scores of substance abusers during a 3-month administration of n-3 PUFAs or placebo. Values are means±SEM. A comparison of the scores of the two patient groups by a repeated measures ANCOVA, with baseline values as covariates, revealed a significant difference (p=.040). The effect size was large (f=.506).
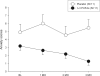
Figure 2
Anxiety scores of substance abusers during a 3-month administration of n-3 PUFAs or placebo. Values are means±SEM. A comparison of the scores of the two patient groups by a repeated measures ANCOVA, with baseline values as covariates, revealed a significant difference (p=.023). The effect size was large (f=.567).
Similar articles
- n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease anxiety feelings in a population of substance abusers.
Buydens-Branchey L, Branchey M. Buydens-Branchey L, et al. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2006 Dec;26(6):661-5. doi: 10.1097/01.jcp.0000246214.49271.f1. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17110827 Clinical Trial. - Long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease feelings of anger in substance abusers.
Buydens-Branchey L, Branchey M. Buydens-Branchey L, et al. Psychiatry Res. 2008 Jan 15;157(1-3):95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2007.01.004. Epub 2007 Sep 27. Psychiatry Res. 2008. PMID: 17900705 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Similar eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid plasma levels achieved with fish oil or krill oil in a randomized double-blind four-week bioavailability study.
Yurko-Mauro K, Kralovec J, Bailey-Hall E, Smeberg V, Stark JG, Salem N Jr. Yurko-Mauro K, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2015 Sep 2;14:99. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0109-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2015. PMID: 26328782 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - A meta-analytic review of polyunsaturated fatty acid compositions in dementia.
Lin PY, Chiu CC, Huang SY, Su KP. Lin PY, et al. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012 Sep;73(9):1245-54. doi: 10.4088/JCP.11r07546. Epub 2012 Aug 7. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22938939 Review.
Cited by
- Human Milk Omega-3 Fatty Acid Composition is Associated with Infant Temperament.
Hahn-Holbrook J, Fish A, Glynn LM. Hahn-Holbrook J, et al. Nutrients. 2019 Dec 4;11(12):2964. doi: 10.3390/nu11122964. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31817237 Free PMC article. - Experiences with healthy eating among individuals with opioid dependence: insights from a dietary assessment.
Al-Shibli MK, Fadnes LT, Henriksen HB, Arjmand EJ, Thomassen LM, Lid TG, Carlsen SL. Al-Shibli MK, et al. BMC Nutr. 2025 Jun 5;11(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s40795-025-01106-1. BMC Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40474270 Free PMC article. - Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) status in major depressive disorder with comorbid anxiety disorders.
Liu JJ, Galfalvy HC, Cooper TB, Oquendo MA, Grunebaum MF, Mann JJ, Sublette ME. Liu JJ, et al. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013 Jul;74(7):732-8. doi: 10.4088/JCP.12m07970. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23945451 Free PMC article. - Maternal fish consumption during pregnancy and smoking behavioural patterns.
Gow RV, Heron J, Hibbeln JR, Davis JM, SanGiovanni JP. Gow RV, et al. Br J Nutr. 2018 Jun;119(11):1303-1311. doi: 10.1017/S0007114517003592. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Br J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29587894 Free PMC article. - Omega-3 Supplementation for Psychotic Mania and Comorbid Anxiety in Children.
Vesco AT, Lehmann J, Gracious BL, Arnold LE, Young AS, Fristad MA. Vesco AT, et al. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2015 Sep;25(7):526-34. doi: 10.1089/cap.2013.0141. Epub 2015 Aug 19. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26288263 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Alessandri JM, Guesnet P, Vancassel S, Astorg P, Denis I, Langelier B, et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acids in the central nervous system: evolution of concepts and nutritional implications throughout life. Reprod Nutr Dev. 2004;44:509–38. - PubMed
- Buydens-Branchey L, Branchey M. N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease anxiety feelings in a population of substance abusers. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2006;26:661–5. - PubMed
- Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. Lawrence Earlbaum; Hillsdale, NJ: 1988.
- First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM IV Axis I Disorders (SCID-I) American Psychiatric Press; Washington, DC: 1997.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials