B cell autonomous TLR signaling and autoimmunity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
B cell autonomous TLR signaling and autoimmunity
Almut Meyer-Bahlburg et al. Autoimmun Rev. 2008 Feb.
Abstract
B cells play a central role in the pathogenesis of multiple autoimmune diseases and the recognition of the importance of B cells in these disorders has grown dramatically in association with the remarkable success of B cell depletion as a treatment for autoimmunity. The precise mechanisms that promote alterations in B cell tolerance remain incompletely defined. There is increasing evidence, however, that TLRs play a major role in these events. Stimulation of B cells via the TLR pathway not only leads to an increase in antibody production but also promotes additional changes including cytokine production and up-regulation of activation markers increasing the effectiveness of B cells as APCs. Understanding the role of TLRs in systemic autoimmunity will not only provide insight into the disease pathogenesis but may also lead to the development of novel therapies. This article gives an overview of TLR signaling in B cells and the possible involvement of such signals in autoimmune diseases.
Figures
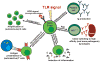
Figure
Combined stimulation through the TLR and an autoreactive BCR leads to activation of B cells in multiple ways. Autoreactive B cells can then proliferate, or up-regulate co-stimulatory molecules turning them into more efficient APCs. They also secrete cytokines and can differentiate into plasma cells that produce large amounts of immunoglobulins (Ig). In addition, expression of activation induced cytidine deaminase (AID) is directly induced by TLR signals. This results in class switching to higher affinity immunoglobulins, and -if autoreactivity is retained-, increasingly pathogenic antibodies are generated.
Similar articles
- B cell toll-like receptors with respect to the pathogenesis of Sjögren's syndrome.
Berglová I, Krejsek J, Kolácková M, Slezák R. Berglová I, et al. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2011;54(2):51-7. doi: 10.14712/18059694.2016.18. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2011. PMID: 21842717 Review. - Pattern recognition by Toll-like receptors.
Bauer S, Müller T, Hamm S. Bauer S, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;653:15-34. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-0901-5_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19799109 Review. - The role of toll-like receptors in B-cell development and immunopathogenesis of common variable immunodeficiency.
Sharifi L, Mirshafiey A, Rezaei N, Azizi G, Magaji Hamid K, Amirzargar AA, Asgardoon MH, Aghamohammadi A. Sharifi L, et al. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016;12(2):195-207. doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2016.1114885. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26654573 Review. - Modulation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells response in inflammation and autoimmunity.
Ah Kioon MD, Laurent P, Chaudhary V, Du Y, Crow MK, Barrat FJ. Ah Kioon MD, et al. Immunol Rev. 2024 May;323(1):241-256. doi: 10.1111/imr.13331. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38553621 Review. - Roles of B Cell-Intrinsic TLR Signals in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
Ma K, Li J, Fang Y, Lu L. Ma K, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jun 9;16(6):13084-105. doi: 10.3390/ijms160613084. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26068236 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- B cell TLRs and induction of immunoglobulin class-switch DNA recombination.
Pone EJ, Xu Z, White CA, Zan H, Casali P. Pone EJ, et al. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jun 1;17(7):2594-615. doi: 10.2741/4073. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22652800 Free PMC article. Review. - CD22 regulates adaptive and innate immune responses of B cells.
Kawasaki N, Rademacher C, Paulson JC. Kawasaki N, et al. J Innate Immun. 2011;3(4):411-9. doi: 10.1159/000322375. Epub 2010 Dec 17. J Innate Immun. 2011. PMID: 21178327 Free PMC article. - Toll-like receptors and B-cell receptors synergize to induce immunoglobulin class-switch DNA recombination: relevance to microbial antibody responses.
Pone EJ, Zan H, Zhang J, Al-Qahtani A, Xu Z, Casali P. Pone EJ, et al. Crit Rev Immunol. 2010;30(1):1-29. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v30.i1.10. Crit Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20370617 Free PMC article. Review. - CD27(-) B-cells produce class switched and somatically hyper-mutated antibodies during chronic HIV-1 infection.
Cagigi A, Du L, Dang LV, Grutzmeier S, Atlas A, Chiodi F, Pan-Hammarström Q, Nilsson A. Cagigi A, et al. PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005427. Epub 2009 May 1. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19412542 Free PMC article. - Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) of Shigella flexneri 2a induces TLR2-mediated activation of B cells: involvement of protein tyrosine kinase, ERK and NF-κB.
Bhowmick R, Pore D, Chakrabarti MK. Bhowmick R, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Oct 6;9(10):e109107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109107. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25286253 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
- Sfikakis PP, Boletis JN, Lionaki S, Vigklis V, Fragiadaki KG, Iniotaki A, et al. Remission of proliferative lupus nephritis following B cell depletion therapy is preceded by down-regulation of the T cell costimulatory molecule CD40 ligand: an open-label trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(2):501–13. - PubMed
- Wardemann H, Yurasov S, Schaefer A, Young JW, Meffre E, Nussenzweig MC. Predominant autoantibody production by early human B cell precursors. Science. 2003;301(5638):1374–7. - PubMed
- Uematsu S, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. J Mol Med. 2006;84(9):712–25. - PubMed
- Bernasconi NL, Onai N, Lanzavecchia A. A role for Toll-like receptors in acquired immunity: up-regulation of TLR9 by BCR triggering in naive B cells and constitutive expression in memory B cells. Blood. 2003;101(11):4500–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous