Potentials and capabilities of the Extracellular Vesicle (EV) Array - PubMed (original) (raw)
Potentials and capabilities of the Extracellular Vesicle (EV) Array
Malene Møller Jørgensen et al. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015.
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) and exosomes are difficult to enrich or purify from biofluids, hence quantification and phenotyping of these are tedious and inaccurate. The multiplexed, highly sensitive and high-throughput platform of the EV Array presented by Jørgensen et al., (J Extracell Vesicles, 2013; 2: 10) has been refined regarding the capabilities of the method for characterization and molecular profiling of EV surface markers. Here, we present an extended microarray platform to detect and phenotype plasma-derived EVs (optimized for exosomes) for up to 60 antigens without any enrichment or purification prior to analysis.
Keywords: EV Array; exosomes; phenotyping; protein microarray.
Figures
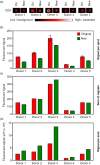
Fig. 1
Comparison of the applied microarray printing technologies; the original (ori.) non-contact printing and the new contact printing technologies. (a) Spots printed with anti-CD9 was used to analyse plasma from 5 donors for the contents of vesicles carrying CD9. The bar shows the color-coded intensities. (b) Mean and standard deviation of the fluorescent signals of the individual anti-CD9 spots shown in (a). Duplicates and triplicates were used for the original array (red bars) and new array (green bars), respectively. (c) Sum of the fluorescent signal for all replicates. (d) Fluorescent signal per area showing a higher signal per area of the improved array.
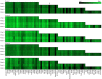
Fig. 2
Summary of the phenotyping of the exosomal population (positive for CD9, CD63 and/or CD81) in plasma from 5 selected, healthy donors. The exosomes were profiled using an EV Array printed with either 21 (Print 1), 33 (Print 2), 50 (Print 3) or 60 (Print 4) different capturing antibodies. The relative fluorescence intensity was log2 transformed prior to the visualization presented as a heat map. Black indicates no signal and green corresponds to maximum signal as indicated by the color-coded bar.
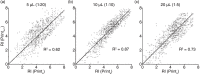
Fig. 3
Scatter plot of the log2 transformed intensities of the 60 capture antibodies for 5 healthy donors. Intensities for each capturing antibody in each printing (Printx, x = Print 1 to 3) was plotted against the similar intensity for the printings with additional antibodies on the array (Printx + 1). The coefficient of determination (R2) was calculated for the linear regression (black line) with the intercept of (0,0). (a) Analysis using 5 µL plasma, (b) analysis using 10 µL plasma and (c) analysis using 20 µL plasma.
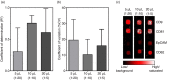
Fig. 4
(a) Comparison (5, 10 and 20 µL plasma) of the calculated coefficient of determination (R2) for the linear regression for each individual antibody (mean + SD). All calculated slopes and R2 values for each antibody and dilution are given in Supplementary Table I. (b) Evaluation of the coefficient of variation (%CV) calculated across the different prints (1–4) for all antibodies and all donors (mean + SD) in relation to the amount of plasma used (5, 10 or 20 µL). (c) Example of representative spots obtained by the extended EV Array in relation to the amount of plasma analysed (5, 10 or 20 µL). Black indicates low signal (background) and white indicates a highly saturated signal as given by the color-coded bar.
Similar articles
- Multiplexed Phenotyping of Small Extracellular Vesicles Using Protein Microarray (EV Array).
Bæk R, Jørgensen MM. Bæk R, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1545:117-127. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6728-5_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27943210 - Extracellular Vesicle (EV) Array: microarray capturing of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for multiplexed phenotyping.
Jørgensen M, Bæk R, Pedersen S, Søndergaard EK, Kristensen SR, Varming K. Jørgensen M, et al. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013 Jun 18;2. doi: 10.3402/jev.v2i0.20920. eCollection 2013. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013. PMID: 24009888 Free PMC article. - Extracellular Vesicle (EV) Dot Blotting for Multiplexed EV Protein Detection in Complex Biofluids.
Momenbeitollahi N, Aggarwal R, Strohle G, Bouriayee A, Li H. Momenbeitollahi N, et al. Anal Chem. 2022 May 24;94(20):7368-7374. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c00846. Epub 2022 May 9. Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35533397 - Chromatography and its hyphenation to mass spectrometry for extracellular vesicle analysis.
Pocsfalvi G, Stanly C, Fiume I, Vékey K. Pocsfalvi G, et al. J Chromatogr A. 2016 Mar 25;1439:26-41. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2016.01.017. Epub 2016 Jan 11. J Chromatogr A. 2016. PMID: 26830636 Review. - High-throughput capture and in situ protein analysis of extracellular vesicles by chemical probe-based array.
Feng X, Shen A, Zhang W, Jia S, Iliuk A, Wang Y, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Tao WA, Hu L. Feng X, et al. Nat Protoc. 2024 Oct 22. doi: 10.1038/s41596-024-01082-z. Online ahead of print. Nat Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39438698 Review.
Cited by
- Immunocapture-based ELISA to characterize and quantify exosomes in both cell culture supernatants and body fluids.
Logozzi M, Di Raimo R, Mizzoni D, Fais S. Logozzi M, et al. Methods Enzymol. 2020;645:155-180. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2020.06.011. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Methods Enzymol. 2020. PMID: 33565970 Free PMC article. Review. - Approaches to incorporate extracellular vesicles into exposure science, toxicology, and public health research.
Carberry CK, Keshava D, Payton A, Smith GJ, Rager JE. Carberry CK, et al. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2022 Sep;32(5):647-659. doi: 10.1038/s41370-022-00417-w. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 35217808 Free PMC article. Review. - Postprandial Increase in Blood Plasma Levels of Tissue Factor-Bearing (and Other) Microvesicles Measured by Flow Cytometry: Fact or Artifact?
Mørk M, Nielsen MH, Bæk R, Jørgensen MM, Pedersen S, Kristensen SR. Mørk M, et al. TH Open. 2018 Apr 16;2(2):e147-e157. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1642021. eCollection 2018 Apr. TH Open. 2018. PMID: 31249938 Free PMC article. - Progress in exosome associated tumor markers and their detection methods.
Shen M, Di K, He H, Xia Y, Xie H, Huang R, Liu C, Yang M, Zheng S, He N, Li Z. Shen M, et al. Mol Biomed. 2020 Aug 14;1(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s43556-020-00002-3. Mol Biomed. 2020. PMID: 35006428 Free PMC article. Review. - Multiplexed Profiling of Extracellular Vesicles for Biomarker Development.
Jiang C, Fu Y, Liu G, Shu B, Davis J, Tofaris GK. Jiang C, et al. Nanomicro Lett. 2021 Dec 2;14(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s40820-021-00753-w. Nanomicro Lett. 2021. PMID: 34855021 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Revenfeld ALS, Bæk R, Nielsen MH, Stensballe A, Varming K, Jørgensen M. Diagnostic and prognostic potential of extracellular vesicles in peripheral blood. Clin Ther. 2014;36:830–46. - PubMed
- Théry C, Boussac M, Véron P, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Raposo G, Garin J, et al. Proteomic analysis of dendritic cell-derived exosomes: a secreted subcellular compartment distinct from apoptotic vesicles. J Immunol. 2001;166:7309–18. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous