Gene Model Annotations for Drosophila melanogaster: The Rule-Benders - PubMed (original) (raw)
Gene Model Annotations for Drosophila melanogaster: The Rule-Benders
Madeline A Crosby et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2015.
Abstract
In the context of the FlyBase annotated gene models in Drosophila melanogaster, we describe the many exceptional cases we have curated from the literature or identified in the course of FlyBase analysis. These range from atypical but common examples such as dicistronic and polycistronic transcripts, noncanonical splices, trans-spliced transcripts, noncanonical translation starts, and stop-codon readthroughs, to single exceptional cases such as ribosomal frameshifting and HAC1-type intron processing. In FlyBase, exceptional genes and transcripts are flagged with Sequence Ontology terms and/or standardized comments. Because some of the rule-benders create problems for handlers of high-throughput data, we discuss plans for flagging these cases in bulk data downloads.
Keywords: bicistronic; multiphasic exon; non-AUG translation start; shared promoter; stop-codon suppression.
Copyright © 2015 Crosby et al.
Figures
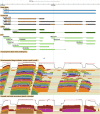
Figure 1
A dicistronic transcript isoform for
primo-1 and primo-2 is produced from a stage- and tissue-specific promoter. A GBrowse view showing (top to bottom): the gene extents and the gene models; cDNAs and ESTs; transcription start site(s); unstranded RNA-Seq coverage data corresponding to a developmental series (early embryos, top, to adults, bottom); and stranded RNA-Seq coverage data (plus strand top, minus strand bottom) corresponding to testis (red), male accessory gland (magenta), ovary from virgin females (orange), and ovaries from mated females (tan). More information on data presented in GBrowse may be found at http://flybase.org/wiki/FlyBase:GBrowse\_Tracks#General.
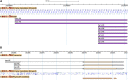
Figure 2
Noncanonical splices supported by RNA-Seq junction data. (A) Of three alternative splice acceptors for intron 6 of the
bifid (bi) gene, two are noncanonical TGs, including the splice acceptor used at the highest frequency (first highlighted junction). A GBrowse view showing (top to bottom): nucleotide sequence; region of the gene model showing one intron/exon boundary; EST data; RNA-Seq junction data; and unstranded RNA-Seq coverage data corresponding to a developmental series (early embryos, top, to adults, bottom). More information on data presented in GBrowse may be found at http://flybase.org/wiki/FlyBase:GBrowse\_Tracks#General. (B) Report for an RNA-Seq junction that corresponds to a noncanonical splice but is aligned to incorrect noncanonical sites, one of several cases that were slightly misaligned.
Figure 3
Noncanonical terminal extensions of the CDS. (A) CUG start codon in
Fmr1 results in a 48-aa N-terminal extension; a GBrowse view showing amino acid sequence and amino ends of annotated polypeptides. Use of this alternative start codon has been confirmed by Western blot, mutagenesis of reported constructs, and rescue constructs (Beerman and Jongens 2011). (B) For the dan gene model, a stop-codon readthrough annotated for dan-RB is supported by PhyloCSF analysis (conservation of protein signatures). A GBrowse view showing (top to bottom): the gene model; stop codons on the plus strand in each of the three open reading frames; and regions of protein conservation among the Drosophila species (tan extents at the bottom). More information on data presented in GBrowse may be found at http://flybase.org/wiki/FlyBase:GBrowse\_Tracks#General.
Similar articles
- Gene Model Annotations for Drosophila melanogaster: Impact of High-Throughput Data.
Matthews BB, Dos Santos G, Crosby MA, Emmert DB, St Pierre SE, Gramates LS, Zhou P, Schroeder AJ, Falls K, Strelets V, Russo SM, Gelbart WM; FlyBase Consortium. Matthews BB, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Jun 24;5(8):1721-36. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.018929. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26109357 Free PMC article. - FlyBase: introduction of the Drosophila melanogaster Release 6 reference genome assembly and large-scale migration of genome annotations.
dos Santos G, Schroeder AJ, Goodman JL, Strelets VB, Crosby MA, Thurmond J, Emmert DB, Gelbart WM; FlyBase Consortium. dos Santos G, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(Database issue):D690-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1099. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25398896 Free PMC article. - Towards comprehensive annotation of Drosophila melanogaster enzymes in FlyBase.
Garapati PV, Zhang J, Rey AJ, Marygold SJ. Garapati PV, et al. Database (Oxford). 2019 Jan 1;2019:bay144. doi: 10.1093/database/bay144. Database (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 30689844 Free PMC article. - Annotation of the Drosophila melanogaster euchromatic genome: a systematic review.
Misra S, Crosby MA, Mungall CJ, Matthews BB, Campbell KS, Hradecky P, Huang Y, Kaminker JS, Millburn GH, Prochnik SE, Smith CD, Tupy JL, Whitfied EJ, Bayraktaroglu L, Berman BP, Bettencourt BR, Celniker SE, de Grey AD, Drysdale RA, Harris NL, Richter J, Russo S, Schroeder AJ, Shu SQ, Stapleton M, Yamada C, Ashburner M, Gelbart WM, Rubin GM, Lewis SE. Misra S, et al. Genome Biol. 2002;3(12):RESEARCH0083. doi: 10.1186/gb-2002-3-12-research0083. Epub 2002 Dec 31. Genome Biol. 2002. PMID: 12537572 Free PMC article. Review. - The Drosophila melanogaster genome sequencing and annotation projects: a status report.
Drysdale R. Drysdale R. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003 Jul;2(2):128-34. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/2.2.128. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003. PMID: 15239934 Review.
Cited by
- Gene Model Annotations for Drosophila melanogaster: Impact of High-Throughput Data.
Matthews BB, Dos Santos G, Crosby MA, Emmert DB, St Pierre SE, Gramates LS, Zhou P, Schroeder AJ, Falls K, Strelets V, Russo SM, Gelbart WM; FlyBase Consortium. Matthews BB, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Jun 24;5(8):1721-36. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.018929. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26109357 Free PMC article. - Population biology of accessory gland-expressed de novo genes in Drosophila melanogaster.
Cridland JM, Majane AC, Zhao L, Begun DJ. Cridland JM, et al. Genetics. 2022 Jan 4;220(1):iyab207. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab207. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 34791207 Free PMC article. - UGGT1 retains proinsulin in the endoplasmic reticulum in an arginine dependent manner.
Cho J, Hiramoto M, Masaike Y, Sakamoto S, Imai Y, Imai Y, Handa H, Imai T. Cho J, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jun 30;527(3):668-675. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.04.158. Epub 2020 May 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32423812 Free PMC article. - Deconstructing internal ribosome entry site elements: an update of structural motifs and functional divergences.
Lozano G, Francisco-Velilla R, Martinez-Salas E. Lozano G, et al. Open Biol. 2018 Nov 28;8(11):180155. doi: 10.1098/rsob.180155. Open Biol. 2018. PMID: 30487301 Free PMC article. Review. - Widespread polycistronic gene expression in green algae.
Gallaher SD, Craig RJ, Ganesan I, Purvine SO, McCorkle SR, Grimwood J, Strenkert D, Davidi L, Roth MS, Jeffers TL, Lipton MS, Niyogi KK, Schmutz J, Theg SM, Blaby-Haas CE, Merchant SS. Gallaher SD, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Feb 16;118(7):e2017714118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2017714118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33579822 Free PMC article.
References
- Andjelkovic M., Jones P. F., Grossniklaus U., Cron P., Schier A. F., et al. , 1995. Developmental regulation of expression and activity of multiple forms of the Drosophila RAC protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 4066–4075. - PubMed
- Bainton R. J., Tsai L. T. Y., Schwabe T., DeSalvo M., Gaul U., et al. , 2005. moody encodes two GPCRs that regulate cocaine behaviors and blood-brain barrier permeability in Drosophila. Cell 123: 145–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P41 HG000739/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG000739/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- G1000968/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U41 HG00739/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases