Saffron: A Natural Potent Antioxidant as a Promising Anti-Obesity Drug - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Saffron: A Natural Potent Antioxidant as a Promising Anti-Obesity Drug
Maryam Mashmoul et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2013.
Abstract
Obesity is associated with various diseases, particularly diabetes, hypertension, osteoarthritis and heart disease. Research on possibilities of herbal extracts and isolated compounds from natural products for treating obesity has an upward trend. Saffron (Crocus Sativus L. Iridaceae) is a source of plant polyphenols/carotenoids, used as important spice and food colorant in different parts of the world. It has also been used in traditional medicine for treatment of different types of illnesses since ancient times. Many of these medicinal properties of saffron can be attributed to a number of its compounds such as crocetin, crocins and other substances having strong antioxidant and radical scavenger properties against a variety of radical oxygen species and pro-inflammatory cytokines. The aim of this article is to assess the potential role of saffron and its constituents in the regulation of metabolic functions, which can beneficially alter obesity pathophysiology.
Keywords: antioxidant; crocin; obesity; overweight; saffron; weight loss.
Figures
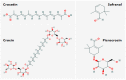
Figure 1
Chemical composition of the most active constituents of saffron.
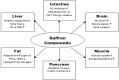
Figure 2
Schematic of possible anti-obesity effect of saffron compounds.
Similar articles
- Anti-inflammatory properties of drugs from saffron crocus.
Poma A, Fontecchio G, Carlucci G, Chichiriccò G. Poma A, et al. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2012;11(1):37-51. doi: 10.2174/187152312803476282. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22934747 Review. - A review of the chemistry and uses of crocins and crocetin, the carotenoid natural dyes in saffron, with particular emphasis on applications as colorants including their use as biological stains.
Bathaie SZ, Farajzade A, Hoshyar R. Bathaie SZ, et al. Biotech Histochem. 2014 Aug;89(6):401-11. doi: 10.3109/10520295.2014.890741. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Biotech Histochem. 2014. PMID: 24665936 Review. - Evaluation of antioxidant activities of bioactive compounds and various extracts obtained from saffron (Crocus sativus L.): a review.
Rahaiee S, Moini S, Hashemi M, Shojaosadati SA. Rahaiee S, et al. J Food Sci Technol. 2015 Apr;52(4):1881-8. doi: 10.1007/s13197-013-1238-x. Epub 2014 Mar 11. J Food Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 25829569 Free PMC article. Review. - Petals of Crocus sativus L. as a potential source of the antioxidants crocin and kaempferol.
Zeka K, Ruparelia KC, Continenza MA, Stagos D, Vegliò F, Arroo RRJ. Zeka K, et al. Fitoterapia. 2015 Dec;107:128-134. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2015.05.014. Epub 2015 May 23. Fitoterapia. 2015. PMID: 26012879 - Saffron: a promising natural medicine in the treatment of metabolic syndrome.
Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H. Razavi BM, et al. J Sci Food Agric. 2017 Apr;97(6):1679-1685. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8134. Epub 2017 Jan 12. J Sci Food Agric. 2017. PMID: 27861946 Review.
Cited by
- Enhancement of the Antiobesity and Antioxidant Effect of Purple Sweet Potato Extracts and Enhancement of the Effects by Fermentation.
Lee SG, Chae J, Kim DS, Lee JB, Kwon GS, Kwon TK, Nam JO. Lee SG, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 31;10(6):888. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060888. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073118 Free PMC article. - Saffron and crocin improved appetite, dietary intakes and body composition in patients with coronary artery disease.
Abedimanesh N, Bathaie SZ, Abedimanesh S, Motlagh B, Separham A, Ostadrahimi A. Abedimanesh N, et al. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2017;9(4):200-208. doi: 10.15171/jcvtr.2017.35. Epub 2017 Dec 30. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2017. PMID: 29391933 Free PMC article. - The effects of Crocus sativus (saffron) and its constituents on nervous system: A review.
Khazdair MR, Boskabady MH, Hosseini M, Rezaee R, M Tsatsakis A. Khazdair MR, et al. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2015 Sep-Oct;5(5):376-91. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2015. PMID: 26468457 Free PMC article. Review. - Nidus vespae Built by an Invasive Alien Hornet, Vespa velutina nigrithorax, Inhibits Adipose Tissue Expansion in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice.
Lee SG, Kim DS, Chae J, Lee E, Hahn D, Kim IK, Kim CJ, Choi MB, Nam JO. Lee SG, et al. Biology (Basel). 2022 Jul 6;11(7):1013. doi: 10.3390/biology11071013. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36101393 Free PMC article. - Saffron, Its Active Components, and Their Association with DNA and Histone Modification: A Narrative Review of Current Knowledge.
Rashid M, Brim H, Ashktorab H. Rashid M, et al. Nutrients. 2022 Aug 12;14(16):3317. doi: 10.3390/nu14163317. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36014823 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- World Health Organization Obesity and Overweight—Factsheet No. 311. Sep, 2006. [(accessed on 18 January 2011)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/index.html.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources