Anserine and glucosamine supplementation attenuates the levels of inflammatory markers in rats with rheumatoid arthritis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Anserine and glucosamine supplementation attenuates the levels of inflammatory markers in rats with rheumatoid arthritis
Jiang Minghao Zhao et al. AMB Express. 2020.
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder that affects the joint synovium. Anserine is a functional dipeptide containing methylhistidine and β-alanine, and is present in the brain and skeletal muscle of birds and mammals. Glucosamine is an amino sugar used in the synthesis of glycosylated proteins and lipids. We evaluated the effects of anserine and glucosamine on RA. Rats were assigned into the control group, RA group, anserine group (1 mg/kg), glucosamine group (200 mg/kg), or anserine plus glucosamine group (anserine, 1 mg/kg + glucosamine, 200 mg/kg). Treatment was continued for 45 consecutive days and was administered orally. The serum levels of catalase, glutathione peroxidase (Gpx), superoxide dismutase (SOD), reduced glutathione (GSH), lipid peroxidation, uric acid, nitric oxide, ceruloplasmin, zinc, copper, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6 were assayed. The mRNA and protein levels of nuclear factor (NF)-κB and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in synovial tissue were also determined. Anserine plus glucosamine significantly increased the catalase, SOD, Gpx, GSH, and zinc levels compared to the control, anserine, and glucosamine groups. Also, anserine plus glucosamine significantly reduced the PGE2, MMP-3, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels compared to the control, anserine, and glucosamine groups. Furthermore, anserine plus glucosamine significantly reduced the mRNA and protein levels of NF-κB and iNOS compared to the control, anserine, and glucosamine groups. Therefore, supplementation of anserine plus glucosamine shows therapeutic potential for RA.
Keywords: Anserine; Antioxidant; Glucosamine; Rats; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Fig. 1
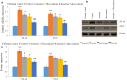
Anserine plus glucosamine supplementation reduced the mRNA and protein levels of NF-κB and iNOS in synovial tissue. a mRNA levels of NF-κB and iNOS. b Western blots of NF-κB and iNOS. c Densitometric analysis of the data in b
Fig. 2
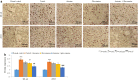
Anserine plus glucosamine supplementation reduced the protein levels of NF-κB and iNOS in synovial tissue. a Immunohistochemical analysis of NF-κB and iNOS. b Analysis of the protein levels in a. Scale bar is 100 µm
Similar articles
- Synergistic effect of glucosamine and vitamin E against experimental rheumatoid arthritis in neonatal rats.
Dai W, Qi C, Wang S. Dai W, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Sep;105:835-840. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.136. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30021375 - Methionine attenuates the intensity of rheumatoid arthritis by downregulating NF-κB and iNOS expression in neonatal rats.
Wang S, Tian S, Li M, Li Z. Wang S, et al. 3 Biotech. 2018 Jul;8(7):303. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1311-2. Epub 2018 Jun 30. 3 Biotech. 2018. PMID: 30002993 Free PMC article. - Mechanistic evaluation of anti-arthritic activity of β-methylphenylalanine in experimental rats.
Ren SX, Zhang B, Lin Y, Ma DS, Li H. Ren SX, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 May;113:108730. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108730. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30861411 - Fangchinoline supplementation attenuates inflammatory markers in experimental rheumatoid arthritis-induced rats.
Shan L, Tong L, Hang L, Fan H. Shan L, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Mar;111:142-150. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.043. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30579253
Cited by
- Anti-arthritic effect of chicken embryo tissue hydrolyzate against adjuvant arthritis in rats (X-ray microtomographic and histopathological analysis).
Rzhepakovsky I, Anusha Siddiqui S, Avanesyan S, Benlidayi M, Dhingra K, Dolgalev A, Enukashvily N, Fritsch T, Heinz V, Kochergin S, Nagdalian A, Sizonenko M, Timchenko L, Vukovic M, Piskov S, Grimm WD. Rzhepakovsky I, et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Aug 18;9(10):5648-5669. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2529. eCollection 2021 Oct. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34646534 Free PMC article. - Multi-Omics Analysis of the Microbiome and Metabolome Reveals the Relationship Between the Gut Microbiota and Wooden Breast Myopathy in Broilers.
Kang K, Zhou N, Peng W, Peng F, Ma M, Li L, Fu F, Xiang S, Zhang H, He X, Song Z. Kang K, et al. Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jun 23;9:922516. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.922516. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35812872 Free PMC article. - Identification of potential ferroptosis key genes and immune infiltration in rheumatoid arthritis by integrated bioinformatics analysis.
Fan Y, Li Y, Fu X, Peng J, Chen Y, Chen T, Zhang D. Fan Y, et al. Heliyon. 2023 Oct 18;9(11):e21167. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21167. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37920499 Free PMC article. - Identification of ferroptosis related markers by integrated bioinformatics analysis and In vitro model experiments in rheumatoid arthritis.
Xia J, Zhang L, Gu T, Liu Q, Wang Q. Xia J, et al. BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Jan 30;16(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01445-7. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36717858 Free PMC article. - Thermo-Responsive Hyaluronan-Based Hydrogels Combined with Allogeneic Cytotherapeutics for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis.
Porcello A, Gonzalez-Fernandez P, Jeannerat A, Peneveyre C, Abdel-Sayed P, Scaletta C, Raffoul W, Hirt-Burri N, Applegate LA, Allémann E, Laurent A, Jordan O. Porcello A, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 18;15(5):1528. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051528. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242774 Free PMC article.
References
- Ally MM, Hodkinson B, Meyer PW, Musenge E, Tikly M, Anderson R. Serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 in comparison with acute phase proteins as a marker of disease activity and radiographic damage in early rheumatoid arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:183653. doi: 10.1155/2013/183653. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Balic MN, Rapp S, Stanzer H, Lin J, Strutz J, Szkandera MG, Daidone H, Samonigg RJ, Cote N. Dandachi, Novel immunofluorescence protocol for multimarker assessment of putative disseminating breast cancer stem cells. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2011;19:33–40. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0b013e3181ebf4e8. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous