Restoring microRNA-499-5p Protects Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury Mice Via Targeting Sox6 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Restoring microRNA-499-5p Protects Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury Mice Via Targeting Sox6
Wenjie Zhang et al. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2021.
Retraction in
- Retraction Note to: Restoring microRNA-499-5p Protects Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury Mice Via Targeting Sox6.
Zhang W, Li J, Yao H, Li T. Zhang W, et al. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2022 Sep 6;17(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s11671-022-03725-0. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2022. PMID: 36066631 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRs) are known to participate in sepsis; hence, we aim to discuss the protective effect of miR-499-5p targeting sex-determining region Y-related high-mobility-group box 6 (Sox6) on sepsis-induced lung injury in mice.
Methods: The sepsis-induced lung injury model was established by cecal ligation and puncture. The wet/dry weight (W/D) ratio, miR-499-5p, Sox6, Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 expression in lung tissues of mice were tested. Lung injury score, collagen fibers and the degree of pulmonary fibrosis in lung tissues were determined. Further, the cell apoptosis in lung tissues was measured. The inflammatory factors contents and oxidative stress indices in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lung tissues were detected via loss- and gain-of-function assays. The targeting relation between miR-499-5p and Sox6 was verified.
Results: W/D ratio and Sox6 were increased while miR-499-5p was decreased in lung tissues of sepsis-induced lung injury mice. Restored miR-499-5p or depleted Sox6 alleviated lung tissues pathology, reduced lung injury score, collagen fibers, the degree of pulmonary fibrosis, TUNEL positive cells, Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 protein expression and inflammatory factors contents in BALF and lung tissues as well as oxidative stress response in lung tissues of sepsis-induced lung injury mice. miR-499-5p targeted Sox6.
Conclusion: High expression of miR-499-5p can attenuate cell apoptosis in lung tissues and inhibit inflammation of sepsis-induced lung injury mice via depleting Sox6, and it is a potential candidate marker and therapeutic target for sepsis-induced lung injury.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Inflammatory factors; MicroRNA-499-5p; Oxidative stress; Sepsis-induced lung injury; Sox6.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
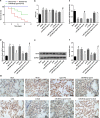
Fig. 1
W/D ratio and Sox6 are increased while miR-499-5p is decreased in lung tissues of sepsis-induced lung injury mice. a Survival curve of mice made by Kaplan–Meier. b W/D ratio of lung tissue in each group. c Expression of miR-499-5p in lung tissues of mice. d Expression of Sox6 mRNA in lung tissues of mice. e Protein band of Sox6 by western blot analysis. f Protein expression of Sox6 in lung tissues of mice. g Sox6 immunohistochemistry of lung tissues of mice. (a) P < 0.05 versus the sham group. (b) P < 0.05 versus the agomir NC group. (c) P < 0.05 versus the si-NC group. (d) P < 0.05 versus the miR-499-5p agomir + oe-NC group. Measurement data were depicted as mean ± standard deviation, and data were assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test
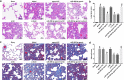
Fig. 2
Restored miR-499-5p or depleted Sox6 alleviates lung tissues pathology, reduces lung injury score, collagen fibers and the degree of pulmonary fibrosis in sepsis-induced lung injury mice. a Results of HE staining in lung tissues of mice. b The lung tissue injury score of mice in each group. c Masson staining of lung tissue in mice. d The pulmonary fibrosis scores of mice in each group. (a) P < 0.05 versus the sham group. (b) P < 0.05 versus the agomir NC group. (c) P < 0.05 versus the si-NC group. (d) P < 0.05 versus the miR-499-5p agomir + oe-NC group. Measurement data were depicted as mean ± standard deviation, and data were assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test
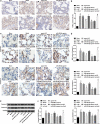
Fig. 3
Restored miR-499-5p or depleted Sox6 reduces TUNEL positive cells, Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 protein expression in lung tissues of sepsis-induced lung injury mice. a TUNEL positive cells in lung tissues of mice. b Number of TUNEL positive cells in lung tissues of mice. c Immunohistochemistry of Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 in lung tissue of mice; d Mean OD value of Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 in lung tissue of mice. e Protein bands of Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 in lung tissues of mice. f Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 protein expression in lung tissues of mice in each group. (a) P < 0.05 versus the sham group. (b) P < 0.05 versus the agomir NC group. (c) P < 0.05 versus the si-NC group. (d) P < 0.05 versus the miR-499-5p agomir + oe-NC group. Measurement data were depicted as mean ± standard deviation, and data were assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test
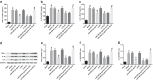
Fig. 4
Restored miR-499-5p or depleted Sox6 reduces TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 contents in BALF and lung tissues of sepsis-induced lung injury mice. a TNF-α content in BALF of mice in each group. b IL-1β content in BALF of mice in each group. c IL-6 content in BALF of mice in each group. d protein bands of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in lung tissues of mice in each group. e protein expression of TNF-α in lung tissues of mice in each group. f protein expression of IL-1β in lung tissues of mice in each group. G protein expression of IL-6 in lung tissues of mice in each group. (a) P < 0.05 versus the sham group. (b) P < 0.05 versus the agomir NC group. (c) P < 0.05 versus the si-NC group. (d) P < 0.05 versus the miR-499-5p agomir + oe-NC group. Measurement data were depicted as mean ± standard deviation, and data were assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test
Fig. 5
Restored miR-499-5p or depleted Sox6 raises SOD, CAT and GSH-Px activities as well as reduces MDA and MPO contents in lung tissues of sepsis-induced lung injury mice. a SOD activity in lung tissues of mice. b MDA content in lung tissue of mice. c GSH-Px activity in lung tissues of mice. d CAT activity in lung tissues of each group of mice. e MPO content in lung tissues of mice. (a) P < 0.05 versus the sham group. (b) P < 0.05 versus the agomir NC group. (c) P < 0.05 versus the si-NC group. (d) P < 0.05 versus the miR-499-5p agomir + oe-NC group. Measurement data were depicted as mean ± standard deviation, and data were assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test
Fig. 6
miR-499-5p directly targets to Sox6. a The target relationship between miR-499-5p and Sox6 predicated by biological website. b The verification results of dual luciferase reporter gene assay. *P < 0.05 versus the mimic NC group. Measurement data were depicted as mean ± standard deviation, and comparisons between two groups were conducted by t test
Similar articles
- MicroRNA-139-5p improves sepsis-induced lung injury by targeting Rho-kinase1.
Zhao X, Wang M, Sun Z, Zhuang S, Zhang W, Yang Z, Han X, Nie S. Zhao X, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2021 Oct;22(4):1059. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10493. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34434273 Free PMC article. - Circular RNA circ_0000712 regulates high glucose-induced apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis in (DN) by targeting the miR-879-5p/SOX6 axis.
Zhao L, Chen H, Zeng Y, Yang K, Zhang R, Li Z, Yang T, Ruan H. Zhao L, et al. Endocr J. 2021 Oct 28;68(10):1155-1164. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ20-0739. Epub 2021 May 11. Endocr J. 2021. PMID: 33980772 - Overexpression of miR-129-5p Mitigates Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Targeting High Mobility Group Box 1.
Yang P, Xiong W, Chen X, Liu J, Ye Z. Yang P, et al. J Surg Res. 2020 Dec;256:23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2020.05.101. Epub 2020 Jul 15. J Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32682121 - MicroRNA-129-5p alleviates nerve injury and inflammatory response of Alzheimer's disease via downregulating SOX6.
Zeng Z, Liu Y, Zheng W, Liu L, Yin H, Zhang S, Bai H, Hua L, Wang S, Wang Z, Li X, Xiao J, Yuan Q, Wang Y. Zeng Z, et al. Cell Cycle. 2019 Nov;18(22):3095-3110. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1669388. Epub 2019 Sep 29. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 31564203 Free PMC article. Retracted. - MiR-539-5p alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by targeting ROCK1.
Meng L, Cao H, Wan C, Jiang L. Meng L, et al. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2019;57(4):168-178. doi: 10.5603/FHC.a2019.0019. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2019. PMID: 31825519
Cited by
- Predictive value and regulatory mechanism of serum miR-499a-5p on myocardial dysfunction in sepsis.
Yang C, Wen K. Yang C, et al. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021 Oct 15;16(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s13019-021-01679-5. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021. PMID: 34654440 Free PMC article. - Mechanisms of Qingyi Decoction in Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Acute Lung Injury via Gut Microbiota: Targeting the Short-Chain Fatty Acids-Mediated AMPK/NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway.
Wang Z, Liu J, Li F, Ma S, Zhao L, Ge P, Wen H, Zhang Y, Liu X, Luo Y, Yao J, Zhang G, Chen H. Wang Z, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0366422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03664-22. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37338348 Free PMC article. - miR-155: A Potential Biomarker for Predicting Mortality in COVID-19 Patients.
Kassif-Lerner R, Zloto K, Rubin N, Asraf K, Doolman R, Paret G, Nevo-Caspi Y. Kassif-Lerner R, et al. J Pers Med. 2022 Feb 21;12(2):324. doi: 10.3390/jpm12020324. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35207812 Free PMC article. - Expression of MicroRNAs in Sepsis-Related Organ Dysfunction: A Systematic Review.
Maiese A, Scatena A, Costantino A, Chiti E, Occhipinti C, La Russa R, Di Paolo M, Turillazzi E, Frati P, Fineschi V. Maiese A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 19;23(16):9354. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169354. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012630 Free PMC article. Review. - HIV-1 gp120 protein promotes HAND through the calcineurin pathway activation.
Shrestha J, Santerre M, Allen CN, Arjona SP, Hooper R, Mukerjee R, Kaul M, Shcherbik N, Soboloff J, Sawaya BE. Shrestha J, et al. Mitochondrion. 2023 May;70:31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2023.03.003. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Mitochondrion. 2023. PMID: 36925028 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials