West English River Provincial Park Management Statement (original) (raw)
Interim Management Statement
© 2004, Queen’s Printer for Ontario
Additional copies of this publication can be obtained from the following offices:
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources
Kenora District
808 Robertson St.
P.O. Box 5080
Kenora, ON
P9N 3X9
Telephone: 807-468-2501
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources
Red Lake District
P.O. Box 5003
Howey St.
Red Lake, ON
P0V 2M0
Ontario Parks Northwest Zone Office
Suite 221D
435 James Street South
Thunder Bay, ON
P7E 6S8
807-475-1321
Approval statement
This Interim Management Statement will provide interim direction for the management of West English River Provincial Park until a comprehensive park management plan is prepared.
This statement will provide the basis for the subsequent preparation of the West English River Provincial Park Management Plan.
I am pleased to approve this Interim Management Statement for West English River Provincial Park.
Signed by:
Tim P. Sullivan
Zone Manager, Ontario Parks
Northwest Zone
Date: February, 2004
Prelude
The purpose of this Interim Management Statement is to identify:
- park values, which are to be protected
- resource management prescriptions necessary to protect these values in their current state; and
- restrictions, according to existing park policy, on use of natural resources within the park
This Interim Management Statement is not intended to replace a Park Management Plan. Rather it is intended to guide the use of natural resources and related activities within the park until such a time as a Park Management Plan is prepared.
Park management planning for West English River Provincial Park will be scheduled as issues and development needs arise and as staff and resources become available. Park management planning is a comprehensive public process intended to provide a 20-year horizon for management activities and to set the context for routine park operations.
The guidelines that have been developed are based upon information contained in the Ontario Provincial Parks Planning and Management Policies (1992) and Ontario’s Living Legacy Land Use Strategy (1999).
Background information
| Name: | West English River Provincial Park |
|---|---|
| Classification: | Waterway |
| MNR District: | Kenora, Red Lake |
| MNR Region: | Northwest |
| Total Area (ha): | 22,924 |
| Ecoregion / Ecodistrict: | 4S-2 |
| Date In Regulation: | May, 2003 |
Refer to the maps at the end of the document.
Life science representation
| Site Type / Landscape Unit | Species / Communities |
|---|---|
| Landform/Vegetation Representation Analysis A representation analysis (Lipsett-Moore et al., in prep.; Harris and Foster 2003) in 2003 of the Landform/Vegetation (L/V) Classes within the ecodistricts applicable to West English River Provincial Park reveals important contributions to representation benchmarks for Ecodistrict 4S-2. Ecodistrict 4S-2 The park contributes to approximately 24% (19/78) of the Ecodistrict’s L/V Classes. The following L/V types within West English River Provincial Park make an important contribution (i.e., at least 20%) to achieving L/V representation benchmarks within Ecodistrict 4S-2: Bedrock-Mixed Forest – mainly Deciduous Glaciolacustrine Deposits – Dense Deciduous Forest Glaciolacustrine Deposits – Mixed Forest – mainly Deciduous Glaciolacustrine Deposits – Mixed Forest – mainly Coniferous Glaciolacustrine Deposits – Sparse Coniferous Forest Glaciolacustrine Deposits – Sparse Deciduous Forest Glaciolacustrine Deposits – Bedrock Outcrop | Forests of West English River Provincial Park are predominantly mixed wood with balsam fir, black and white spruce and trembling aspen. Ecosites 16,19, & 28 make up approximately 74% of the park with Ecosite 19 (Hardwood – Fir-Spruce Mixedwood on fresh sandy – coarse loamy soils) making up almost half (45%) of the park’s forests (Harris & Foster 2003). (See Racey et al. (1996) for a detailed description of ecosite types) Significant Species Provincially significant plant species include: Siberian Yarrow, Torrey’s Sedge, Wild Licorice, American Parsley Fern, Blue-lips, Clinton’s Club Rush, Inland Rush,June Grass, Little Prickly Pear Cactus, Prairie Onion, Prairie Spikemoss, Ross' Sedge, New England Violet, Long-stemmed Waterwort, Oregon Woodsia, Prairie buttercup, Prairie Gray Sedge, and Vasey’s Rush. Several regionally significant plant species are also found in the park. Provincially rare fauna include: Bald Eagle, American White Pelican, Lake Sturgeon, Elusive Clubtail, Williamson’s Emerald, and Woodland Caribou Significant Communities Red and White Pine Communities (including old growth) The park is near the northern limit of the range of both of these species. Provincially significant Prairie and Savannah Communities |
Earth science representation
| Geological Theme | Feature(s) |
|---|---|
| Bedrock: English River Subprovince (migmatites with garnet and cordierite) and Winnipeg River Subprovince (grantic rocks of magmatic origin) | Surficial: Weakly broken topography with excellent exposures of glaciolacustrine clays along the riverbanks, beaches, sand bars and spits |
Cultural resource representation
| Cultural Resource Representation | Theme Segment |
|---|---|
| Fur Trade and Fur Trading Communities | Lake Superior - Rainy River Area |
Recreational opportunities
| Day Use | Car Camping | Wilderness / Backcountry |
|---|---|---|
| Angling and hunting | N/A | Angling and hunting Remote outposts and lodges Camping Canoeing |
Inventories
| Level / Type | Reconnaissance? – Completion Date | Detailed? – Completion Date | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Earth science | Yes – 2002 | No | Yes |
| Life science | Yes– 2002 | Yes- 2003 | No |
| Cultural | No | No | Yes |
| Recreational | No | Yes - 2002 | Yes |
| Other | N/A | N/A | N/A |
I Introduction
West English River Provincial Park (P2345) was established as part of Ontario’s Living Legacy, a land use strategy developed to guide the planning and management of Crown lands in central and portions of northern Ontario. Under this initiative, 378 new protected areas were identified. West English River Provincial Park is part of this significant expansion of Ontario’s protected areas system.
West English River Provincial Park (22,924 hectares) is designated a Waterway class park in recognition of its representative natural features and high quality recreational water route. West English River Provincial Park runs approximately 65 kms along the English River form Barnston Lake to Tide Lake and abuts Tide Lake and Maynard Lake Provincial Parks. The park contains old growth red and white pine at the northern extent of their range, wilderness environments, tourism and recreational attributes. It is also a historical travel corridor.
II Aboriginal interests
West English River Provincial Park lies within the boundaries of the Treaty 3 Area. The closest First Nation communities to the park are Grassy Narrows (approximately 15 kms south) and Wabauskang (approximately 40 kms east). There are no formal land claims regarding West English River Provincial Park, at this time. Current First Nation activities within the park include trapping, fishing, hunting, and gathering. Three traplines intersecting the park are registered to Aboriginal people.
Guideline:
Any management guidelines will reflect the Ontario government’s approach to aboriginal rights:
- All decisions related to the identification, planning or disposition of provincial parklands, or other lands set aside to protect significant natural or cultural heritage values, will be the subject of public consultation. Aboriginal peoples who identify traditional ties to those lands will be integral to the consultation and decision making processes. In some cases, there may be a need for separate consultation or negotiation processes to address Aboriginal interest in parklands. If required, some issues regarding how a park is used may also be the subjects of negotiation with Aboriginal people.
- The Government of Ontario will consider all the available options when seeking to determine the land component, if any, during negotiations involving land claim settlements with First Nat Options for uses that involve lands that are not to be considered for provincial park purposes will be preferred.
- As described in the Province’s Interim Enforcement Policy (1991), aboriginal people hunting or fishing in provincial parks will be subject to all relevant treaties and laws. However, an agreement reached between the Province and a First Nation may modify the application of those treaties and laws (Ontario Provincial Parks: Planning and Management Policies, 1992).
III Land tenure/acquisition/disposition
West English River Provincial Park is composed entirely of Crown land within Ministry of Natural Resources Districts of Kenora and Red Lake. The park includes a section of the English River system from Barnston Lake to Tide Lake, including Wegg Lake, Goose Lake, Wilcox Lake, Unexpected Lake, Oak Lake, Maynard Lake and Tide Lake. The park boundary has generally been set at 200m from water’s edge.
Tide Lake Provincial Nature Reserve and Maynard Lake Provincial Nature Reserve abut West English River Provincial Park. Management direction for both these nature reserves is contained in Interim Management Statements, which are available at the Ontario Parks Office in Thunder Bay, the MNR District Office in Kenora and the main Ontario Parks office in Peterborough.
Eight small parcels of private land exist within the park area. These parcels include private cottages and tourist lodges. One land use permit (LUP) associated with commercial fishing exists on Oak Lake. Four LUPs associated with outpost camps have been issued for Goose, Oak, Maynard and Unexpected Lake. There are no mining claims within the park.
Guideline:
- No land disposition for the private use of individuals or corporations will be considered within the park
- Dispositions for commercial uses associated with activities permitted in this Interim Management Statement (IMS) will be considered
- The two provincial nature reserves that abut the park will remain in their current designation, but may be examined though future park management planning for inclusion within West English River Provincial Park
IV Natural resource stewardship
West English River Provincial Park (22,924 hectares) is situated within Ecoregion 4S and Ecodistrict 4S-2. A number of landform-vegetation (LV) types found in the park contribute to representation benchmarks (Lipsett-Moore et al., in prep.) for Ecodistrict 4S-2. These LV types include conifer, mixed and deciduous forests on glaciolacustrine deposits, and to a lesser extent on bedrock. The park also includes representative stands of red and white pine, including old growth, as well as provincially significant prairie communities and species.
Lands and waters
The park is located within the English River and Winnipeg River subprovinces of the Archean-age Superior Province. A number of significant earth science values have been identified in the park. The migmatites found in the park are of provincial significance, as they provide good examples of metatexitic and diatexitic metasedimentary rocks.
The boundary between these subprovinces, which runs in a west southwest – east northeast direction, is located north from the north shore of Oak Lake. North of this boundary, in the English River subprovince, the rocks are mostly migmatites derived from the partial to complete melting of sedimentary rocks. The metamorphic minerals found in these migmatites include garnet and cordierite and granitic rocks of the sodic type intrude the migmatites. In the Winnipeg River subprovince, the rocks are predominately granitic of magmatic origin that belong to four different suites. The largest being a group of foliated porphyritic granodiorite to quartz monzonite that underlies much of Tide and Maynard lakes and the central and western portions of Oak Lake.
Glaciolacustrine clays account for approximately half of the park and are predominant along the shorelines. Till ground moraine, often in a veneer over bedrock, occupies most of the rest of the park, particularly on higher ground adjacent to the lower half of the river system.
West English River Provincial Park is 66% water. The park stretches approximately 65 kms and includes parts of the English River, Barnston, Wegg, Goose, Wilcox, Oak, Maynard and Tide Lakes. The lakes are mesotrophic and are relatively turbid compared to other lakes in the area (Harris and Foster 2003). Elevation drops 11 m throughout the length of the park. Upper and lower Oak Falls account for over half of the overall elevation change with a combined 6 m drop. The park is situated between two dams; Manitou Dam (20 km upstream from Barnston Lake) and Caribou Falls Dam (100 km downstream from Tide Lake). Water regulation from the Manitou Dam results in an unnatural flow regime. Water levels peak in October whereas in an unregulated section of the river peak flows are in May. Harris and Foster (2003, p. 13) suggest that "the unnatural flow regime has probably had impacts on wild rice productivity, loon nesting success, shoreline erosion, fish spawning, and shoreline vegetation".
Guideline:
- Aggregate extraction is not permitted
- Peat extraction is not permitted
- Commercial hydro development is not permitted
- Water control structures are permitted in certain zones in waterway class parks to perpetuate natural and cultural values or to enhance recreational opportunities. The need for any water control structures will be determined in the park management plan
- Mineral exploration and mining are not permitted within West English River Provincial Park
Vegetation management
Forests within West English River Provincial Park are fairly uniform with a relatively small range of primary ecosites and over-story species although, the nutrient-rich soils have given rise to a greater diversity of under-story plants. Ecosites (ES) 16 (Hardwood-Fir-Spruce Mixedwood:Sandy Soil);19 (Hardwood-Fir-Spruce Mixedwood on fresh, sandy-coarse loamy soil); and 28 (Hardwood-Fir-Spruce Mixedwood: Fresh, Silty Soil) make up 74% of the forest within the park, with ES19 accounting for almost half (45%) of the park’s forests (See Racey et al. (1996) for a more detailed description of Ecosite types). The park also contains good examples of red and white pine communities including old growth, prairie and open bur oak communities as well as alluvial thicket swamps.
Flora in West English River Provincial Park is typical of the southern boreal forest with influences from the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Forest and the prairies. Harris and Foster (2003) documented 307 vascular plant species with a total of 18 provincially rare species. Many of these rare species are associated with the small pockets of prairie and bur oak communities that are found at numerous locations in the park.
Natural disturbances play important roles in influencing the ecology of West English River Provincial Park and the boreal forest of Ecoregion 4S. They include wildfire, insect outbreaks and windthrow. Fire frequency and the proportion of area burned since the 1920's in West English River Provincial Park is lower than that for Ecoregion 4S (Harris and Foster 2003). Much of the park has been affected by severe spruce-budworm infestations from 1988 through 1995.
A great deal of West English River Provincial Park’s forests have been harvested. White and red pine was harvested during the early part of the 20th century. Since then there have been regular forest cutting activities in the park and surrounding area. Large cut over areas dating back to the 1990's can be seen from the waters of the park on Maynard, Wilcox, and Goose Lakes (Harris and Foster 2003). The park is currently contained entirely within the Whiskey Jack Forest which is licensed to Abitibi-Consolidated.
Guideline:
- Commercial forest operations are not permitted
- Fuelwood cutting is not permitted
- Insect/disease suppression of non-native infestations is permitted
- Aboriginal rights to harvest wild rice are not affected
- In the absence of a fire management plan for the park, the fire management objectives of the surrounding fire management zone will apply. All human caused fires will be suppressed
- The need for a Vegetation Management plan, which will include prescriptions for fire management, will be determined in the park management plan
- Ontario Parks will act as a plan advisor and reviewer during the forest management planning process, according to the northwest zone’s protocol for Ontario Parks' participation in forest management planning. This process ensures that park values and park-related values are recognized and that protection and mitigation measures are worked out through the development of the forest management plan when these values are potentially affected by adjacent forestry operations
Wildlife management
The fauna of West English River Provincial Park is typical of the southern boreal forest. Banfield (1974) indicates that the park is situated within the geographical range of 42 mammal species. Harris and Foster (2003) recorded 16 species of mammal, 76 birds, 5 amphibians, 2 reptiles, and 18 odonates during the 2001 and 2002 field seasons. Large mammal observations included white-tailed deer, moose, black bear and timber wolf. Bald eagle nests have been reported at 35 locations within the park. Osprey are also known to nest within the park. A great blue heron colony and a trumpeter swan nesting site have been observed adjacent to the park, in the vicinity of Tide Lake.
Eight active Bear Management Areas (BMAs) and seven registered trap lines intersect the park boundaries. BMAs include: RL-05-92, RL-03-43, RL-05-91, KE-05-73, KE-05-144, KE-05-143, DR-05-01, KE-06-28. Traplines include: RL-32, RL-36, RL-37, DR-61, KE-046, KE-041, and KE-040. There are five trap cabins located in the park.
Guideline:
Hunting (general)
Commercial bear hunting
Trapping
- Non-invasive wildlife monitoring may be permitted. The need for a Wildlife Management Plan will be resolved in the park management plan
- Sport hunting is permitted, subject to the relevant Ontario Hunting Regulations. Consideration of safety and conservation with respect to hunting will be made during park management planning with public involvement
- Aboriginal and Treaty rights to hunt are not affected
- When a management plan is approved, any hunting that is occurring in a nature reserve zone will be addressed through the management planning process consistent with the Ontario Living Legacy Land Use Strategy and Ontario Provincial Park Policies
- Commercial bear hunting will be allowed to continue in areas of the park where it has traditionally occurred
- In situations where licenses have not been issued and inventories have been completed that identify candidate or probable nature reserve zones, licensing should not be issued for these areas
- Existing commercial bear hunting operations are permitted to continue but the introduction of new operations will not be allowed
- The issuance of licenses or permits for commercial trapping will be allowed where the activity has been licensed or permitted since January 1, 1992 unless:
- The government has taken action to discontinue the activity
- Proceeding would create/aggravate resource sustainability issues (e.g., wildlife management reasons, impacts on values in nature reserve zones) or
- Licensing or permitting should be deferred due to Aboriginal issues
- Status Indians exercising treaty rights are permitted to continue trapping, subject to applicable legislation and regulation
- No new commercial fur harvesting operations will be permitted, including new cabins and trails. The relocation of existing trails will be subject to ecological principles and park management planning
- Snowmobile trails used for access to trap lines are permitted
Fisheries management
West English River Provincial Park is part of the Winnipeg River Watershed. Lake surveys were conducted for Goose Lake, Maynard Lake, Oak Lake and Tide Lake in the late 1960s. The results of these surveys indicate the main fish species in the park are walleye, sauger, yellow perch, smallmouth bass, rock bass, northern pike, muskellunge, ciscoes and mooneye. Tide Lake appears to have the richest fish community with 16 species. Harris and Foster (2003) suggest that this may be due to its position below the barrier of Maynard Falls. Walleye, northern pike, bass and muskellunge are the most popular sport fish (Harris and Foster 2003).
A commercial fishing operation exists on Oak Lake. The main species harvested are lake whitefish, walleye and northern pike.
Eight registered baitfish blocks intersect the park.
Guideline:
Sport fishing
Bait fish harvesting
Commercial fishing
- Non-invasive fisheries monitoring may be permitted. The need for a Fisheries Management Plan will be resolved in the park management plan
- Fish stocking of non-native species not permitted
- Sport fishing is permitted subject to the relevant Ontario Sport Fishing Regulations
- Unless this park is determined to be a high intensity waterway during park management planning, live baitfish should not be used or possessed in this provincial park. Until such time as a regulation is established under the Ontario Fishing Regulations, Ontario Parks will discourage the use or possession of live baitfish in this provincial park
- Aboriginal and Treaty rights to fish are not affected
- The issuance of licenses for baitfish harvesting will be allowed where the activity has been licensed or permitted since January 1, 1992 unless:
- The government has taken action to discontinue the activity
- Proceeding would create/aggravate resource sustainability issues (e.g., wildlife management reasons, impacts on values in nature reserve zones) or
- Licensing or permitting should be deferred due to Aboriginal issues
- Existing bait harvesting is permitted to continue indefinitely, subject to possible conditions identified in subsequent Provincial Park and/or Fisheries Management Plans. Active licenses may be transferred where it is an established permitted use
- The issuance of licenses for commercial fishing will be allowed where the activity has been licensed or permitted since January 1, 1992 unless:
- The government has taken action to discontinue the activity
- Proceeding would create/aggravate resource sustainability issues (e.g., wildlife management reasons, impacts on values in nature reserve zones) or
- Licensing or permitting should be deferred due to Aboriginal issues
V Cultural resources
To date, the cultural resources of West English River Provincial Park have not been rigorously investigated. There are a number of archaeological sites within the park. Only one has been registered by the Ontario Ministry of Citizenship and Culture.
Guideline:
- Further inventory is required to assess the cultural resources of the park. Approved archeological fieldwork will be encouraged
- The locations of any archeological sites will not be public information. Necessary measures (access/development restrictions) to protect the integrity of any archeological sites will be implemented
- The need for a Cultural Resources Plan/Strategy for cultural features/sensitive areas will be determined through consultation with local First Nations communities and through park management planning
VI Existing/proposed development
Existing development within West English River Provincial Park is associated with forestry, trapping, commercial fishing, and remote tourism activities.
Guideline:
- Development of access zones and car/backcountry campsites will be addressed via park management planning
- Continuing custodial management for roads contained within the park and capital development of new/additional roads and trails will be determined through park management planning
- New commercial tourism facilities may be considered through the park management planning process
VII Recreation activities
West English River Provincial Park provides good opportunities for remote tourism, backcountry canoeing, wildlife viewing, as well as sport angling and hunting. Sport fishing and hunting are the primary recreational activities taking place within West English River Provincial Park (Reaburn and Thomson (2002), Harris and Foster 2003). The tourist lodges and outposts in the park provide facilities and services mostly to anglers and hunters.
Two canoe routes exist within the park. They include the Ball Lake Loop and the Upper Wabigoon– English River Route. The condition of these routes is unknown as they are not maintained by OMNR or Ontario Parks. The level of canoeing currently taking place within the park is minimal (Harris and Foster 2003; Reaburn and Thomson 2002).
There are several boat caches located in the park authorized for commercial tourism, resource harvesting and private recreation purposes.
Guideline:
- Park management planning will determine policies for recreation management, including camping and canoeing
- Existing motorized use is permitted to continue indefinitely, subject to possible conditions identified in the Park Provincial Park Management Plan. Motorized land vehicles, aircraft and watercraft (private and commercial) may be restricted in certain park zones. Motor size restrictions may be imposed, subject to park management planning
- Self-guided nature appreciation and wildlife observation is permitted
- Sport fishing and hunting are addressed in Section IV – Natural Resources Stewardship
- New boat caches will not be permitted
- Private recreation boat caches will be phased out by December 31, 2009
VIII Access
Road access into West English River Provincial Park is limited. Barnston Lake is the only lake within the park that is easily accessible by road (via Highway 804). The park is easily accessed by water from below Manitou Falls west of Ear Falls and from Ball Lake in the south.
Guideline:
- Access into the park from traditionally used roads will be permitted to continue pending park management planning. No new access to the park will be created from roads adjacent to the park until resolved via park management planning
- Decisions on new roads, parking facilities and long-term management of roads abutting / crossing parklands will be clarified via park management planning when access zones are delineated. New roads abutting the park are determined during forest management planning, reflecting the need to harmonize the Whiskey Jack Forest Management Plan with the direction given in this IMS and future park management plans
- Existing and future road crossings of waterway class parks for forest operations occurring outside park boundaries are permitted subject to provisions of the Environmental Assessment Act. The number of road crossing will be minimized and they will be managed to reduce their impact on natural, recreational and aesthetic values
- Access by Aboriginal people exercising their Aboriginal or Treaty rights is not affected
X Client services
There are currently no client services available for West English River Provincial Park. Canoe route information is available from local tourist outfitters.
Guideline:
- Client services will be limited to a map/brochure until an approved park management plan is completed. Development of an operations plan and a natural heritage education strategy will be considered when developing the park management plan
XI Research and inventories
A detailed life science and recreation resource inventory were carried out in 2002.
Guideline:
- Detailed earth science and cultural values inventories will be undertaken when funding permits
- Additional research / inventories to document park values will be permitted if not in conflict with park values and consistent with the Ontario Parks Research and Information Strategy
- MNR, Ontario Parks or partnered groups and individuals may undertake research projects. The Park Superintendent/Zone Manager must approve all research applications
XII Marketing
Marketing of West English River Provincial Park has to date been limited to Ontario’s Living Legacy (OLL) initiatives.
Guideline:
- When resources are available, Ontario Parks may promote West English River Provincial Park with the methods consistent with other provincial parks
XIII Sources/references
Banfield, A.W.F. 1974. Mammals of Canada. University of Toronto Press, Toronto.
Harris, A.G., and Foster, R.F. 2003. Life Science Inventory – West English River Provincial Park. Northern Bioscience Ecological Consulting Unpublished Report.
Lipsett-Moore, G., Bookey, N., Kingston, S. and J. Shuter. In Prep. Representation, Focal Species and Systematic Conservation Planning for the Northern Boreal Initiative. Ontario Parks, Northwest Zone.
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources (OMNR). 1999. Ontario’s Living Legacy Land Use Strategy.
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources (OMNR). 1992 Update. Ontario Provincial Parks: Planning and Management Policies.
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources (OMNR). 2002. NRVIS – Kenora and Red Lake Districts.
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources (OMNR). 1983. Kenora District Land Use Guidelines (DLUG).
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources (OMNR) 1983. Red Lake District Land Use Guidelines (DLUG).
Racey, G.D., Harris, A.G., Jeglum, J.K., Foster, R.F. and G.M. Wickware. 1996. Terrestrial and Wetland Ecosites of Northwestern Ontario. Queen’s Printer for Ontario, Thunder Bay.
Reaburn, C., and S. Thomson. 2002. Recreation Inventory Report: West English River Provincial Park (P2345). Ontario Parks, Unpublished internal report.
Permitted Uses Table for West English River Provincial Park
Commercial activities
| Activity | Permitted? | Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| Aggregate extraction | No | |
| Bait fishing (commercial) – existing | Yes | The issuance of licenses for baitfish harvesting will be allowed where the activity has been licensed or permitted since January 1, 1992 unless: The government has taken action to discontinue the activity Proceeding would create/aggravate resource sustainability issues (e.g., wildlife management reasons, impacts on values in nature reserve zones) or Licensing or permitting should be deferred due to Aboriginal issues |
| Bait fishing (commercial) – new | No | |
| Commercial fishing – existing | Yes | The issuance of licenses for commercial fishing will be allowed where the activity has been licensed or permitted since January 1, 1992 unless: The government has taken action to discontinue the activity Proceeding would create/aggravate resource sustainability issues (e.g., wildlife management reasons, impacts on values in nature reserve zones) or; Licensing or permitting should be deferred due to Aboriginal issues |
| Commercial fishing – new | No | |
| Commercial fur harvest – existing | Yes | Existing trap line operations can continue indefinitely. New operations, including trap line cabins and trails will not be permitted. The relocation of existing trails and cabins will be subject to ecological principles and management planning. Snowmobile trails used for access to the trap lines are permitted. The issuance of licenses or permits for commercial trapping will be allowed where the activity has been licensed or permitted since January 1, 1992 unless: The government has taken action to discontinue the activity Proceeding would create/aggravate resource sustainability issues (e.g., wildlife management reasons, impacts on values in nature reserve zones) or Licensing or permitting should be deferred due to Aboriginal issues Commercial bear hunting will be allowed to continue in areas of the park where it has traditionally occurred. When a management plan is approved, any hunting that is occurring in a nature reserve zone will be addressed through the management planning process consistent with OLL-LUS and Park Policies. In situations where licenses have not been issued and inventories have been completed that identify candidate or probable nature reserve zones, licensing should not be issued for these areas. Existing commercial bear hunting operations are permitted to continue but the introduction of new operations will not be allowed. |
| Commercial fur harvest – new | No | |
| Commercial hydro development | No | |
| Commercial timber harvest | No | |
| Commercial Tourism (e.g. outfitting services, outpost camps, resorts/lodges) – existing | Yes | Existing authorized facilities/operations are permitted to continue, subject to management prescriptions determined through planning. Existing tourism facilities may be eligible for enhanced tenure as decided through planning. |
| Commercial Tourism (e.g. outfitting services, outpost camps, resorts/lodges) – new | Maybe | New facilities/operations may be considered through planning. |
| Energy transmission & communications corridors (new) | Maybe | Utility line crossings may be necessary to maintain essential public services. The number of new crossings will be minimized where possible and they will be managed to reduce their impact on recreational and aesthetic values. |
| Mineral exploration and development | No | |
| Wild rice harvesting – existing | Yes | |
| Wild rice harvesting – new | No |
Land and resource management activities
| Activity | Permitted? | Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| Crown land disposition – private use | No | No land disposition for the private use of individuals is permitted, except for minor dispositions in support of existing uses (e.g., reconstruction of a septic system). All existing tenure issued by the Crown for private use, except private recreation camps will be phased out no later than January 1, 2010. |
| Crown land disposition – commercial use | Maybe | Land disposition for commercial use may occur, under the authority of a land use permit or lease, subject to approval through planning. Existing tourism facilities may be eligible for enhanced tenure. |
| Fire suppression | Maybe | In the absence of a fire management plan for the park, the fire management objectives of the surrounding fire management zone will apply. All human caused fires will be suppressed. |
| Fish habitat management | Maybe | May be considered through planning. |
| Fish stocking – native species | Maybe | May be considered through planning. |
| Fish stocking – non-native species | No | May be considered through planning. |
| Insect/disease suppression | Maybe | May be considered through planning. |
| Inventory/monitoring | Yes | |
| Personal use permits for wood harvesting | Maybe | Long-term management direction will be determined through planning. Existing authorized permits may continue on an interim basis for properties that do not have road access. |
| Prescribed burning | Maybe | May be considered through planning. |
| Roads (non-park use) - existing | Maybe | Access into the park from traditionally used roads will be permitted to continue pending park management planning. |
| Roads (non-park use) - new | Maybe | New roads abutting the park are determined during forest management planning. No new access to the park will be created from adjacent roads until resolved via park management planning. Future road crossings for forestry operations outside park boundaries may be permitted, subject to provisions of the Environmental Assessment Act including park management planning and forest management planning. The number of crossings will be minimized where possible and they will be managed to reduce their impact on recreational and aesthetic values. |
| Vegetation management | Maybe | May be considered through planning. |
| Water control structure –existing | Maybe | No structures exist in West English River Provincial Park. |
| Water control structure – new | Maybe | New structures may be considered through planning. |
| Wildlife population management | Maybe | May be considered through planning. |
Science, education & heritage appreciation
| Activity | Permitted? | Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| Demonstration areas | Maybe | May be considered through planning. |
| Historical appreciation – self-guided | Maybe | Support facilities to be identified through planning. |
| Nature appreciation – self-guided | Maybe | Support facilities to be identified through planning. |
| Photography and painting | Maybe | Support facilities to be identified through planning. |
| Research | Yes | Subject to authorization. |
| Wildlife viewing | Maybe | Support facilities to be identified through planning. |
Recreation activities and facilities
| Activity | Permitted? | Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| Aircraft landing (water) | Maybe | Under the authority of a valid aircraft landing authorization, as per O. Reg 952/01, s. 24(2) under the Provincial Parks Act. |
| ATV use – on trails | Yes | Existing ATV use on authorized trails can continue, subject to management prescriptions determined through park management planning. |
| ATV use – off trails | No | |
| Camping | Maybe | Long-term management direction for camping facilities will be determined through planning. Existing use may continue in the interim, unless park values are threatened. |
| Horseback riding (trail) | Maybe | Long-term management direction will be determined through planning. Existing use may continue in the interim, unless park values are threatened. |
| Hunting | Yes | Subject to regulation under the Fish and Wildlife Conservation Act. Consult the Ontario Hunting Regulation Summary for specific local details. Hunting may be restricted in certain zones as determined through park management planning. |
| Mountain bike use | Maybe | Long-term management direction will be determined through planning. Existing use may continue on authorized trails, as designated by the park superintendent, in the interim, unless park values are threatened. No authorized trails exist. |
| Motor boat use – private | Maybe | Long-term management direction for private and commercial motor boat use will be determined through management planning. Existing use may continue in the interim, unless park values are threatened. Consult regulations under the Provincial Parks Act for specific local details. |
| Motor boat use – commercial | Maybe | Long-term management direction for commercial motor boat use will be determined through management planning. Existing use may continue in the interim, unless park values are threatened. Consult regulations under the Provincial Parks Act for specific local details. |
| Non-motorized recreation travel (canoeing, kayaking, hiking, cross- country skiing, snowshoeing) | Maybe | Long-term management direction will be determined through planning. Existing uses may continue in the interim, unless park values are threatened. |
| Private recreation camps ("hunt camps") – existing | Yes | Existing authorized camps permitted to continue, eligible for enhanced tenure but not purchase of land. |
| Private recreation camps ("hunt camps") – new | No | |
| Rock climbing | Maybe | Long-term management direction will be determined through planning. Rock climbing is permitted only in areas designated for that purpose by the park superintendent as per O. Reg 952/01, s. 5.1 under the Provincial Parks Act. No area are currently designated. |
| Sailing and sailboarding | Maybe | Long-term management direction will be determined through planning. Existing uses may continue in the interim, unless park values are threatened. |
| Scuba and skin diving | Maybe | Long-term management direction will be determined through planning. Existing uses may continue in the interim, unless park values are threatened. |
| Snowmobiling – on trails | Maybe | Existing snowmobile use on authorized trails can continue, subject to management prescriptions determined through planning. |
| Snowmobiling – off trails | No | |
| Sport fishing | Yes | Consult the Ontario Recreational Fishing Regulations Summary for specific local details. Using live bait is discouraged. |
| Trail development | Maybe | Certain trails may be considered through planning. |
Maps
Map 1: Regional context West English River Provincial Park P2345
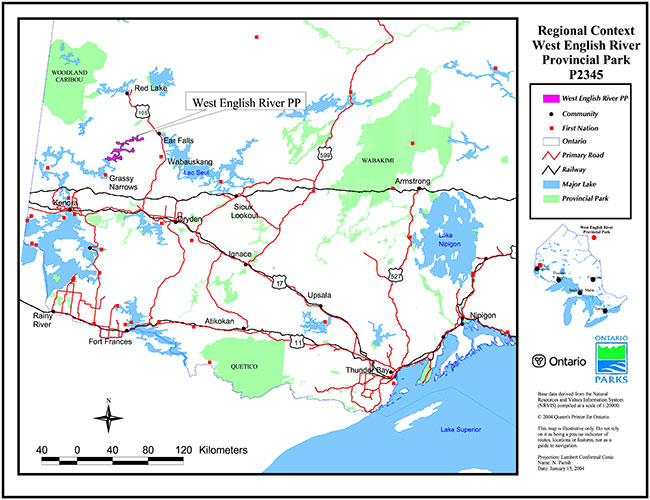
Enlarge Map 1: Regional context West English River Provincial Park P2345
Map 2: Site map West English River Provincial Park P2345
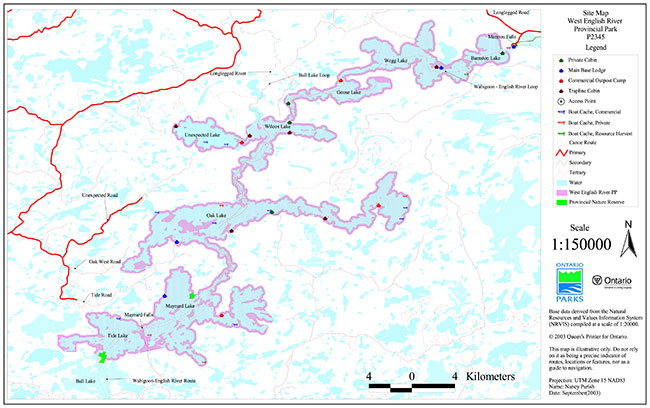
Enlarge Map 2: Site map West English River Provincial Park P2345