Divergent Mortality Patterns Associated With Dementia in the United States: 1999–2020 (original) (raw)
Presently, dementia ranks as the seventh leading cause of death and stands as a significant contributor to disability and dependency in the older population worldwide. According to 1 report, approximately 50 million individuals are living with dementia globally, and projections indicate a surge to 152 million by the year 2050.1 As of 2020, over 7 million Americans aged ≥65 years were estimated to have dementia, and the lifetime risk of developing dementia is estimated to be 34.7%.2 Among the various causes, Alzheimer disease (AD) prevails as the most common, accounting for 60%–70% of cases.3 AD affects 6.2 million elderly Americans, ranking as the sixth leading cause of death in the United States and the fifth among those aged ≥65 years. With the aging population, AD cases are expected to rise significantly, with every US state projected to witness at least a 6.7% increase between 2020 and 2025.4 This projection foretells a future marked by increased mortality and morbidity, even as medical advancements occur.
Major neurocognitive disorder in the DSM-5, previously labeled as dementia, is a progressive and irreversible condition marked by a deterioration in cognitive functions.5 Dementia, a diverse syndrome stemming from a range of neurological and medical conditions, is characterized by its heterogeneous nature.6 Major contributors to this condition include neurodegeneration, vascular injury, and nutritional/ metabolic disorders.6 One study2 indicated a potential trade-off, where the progress in combatting chronic diseases among future elderly adults in the United States comes with a heightened risk of developing dementia.
The findings imply that with longer life expectancies, individuals are more likely to encounter challenges related to cognitive decline.2 This heightened probability of facing cognitive issues poses difficulties for both the affected individuals and the support systems designed to assist them, including families and government programs catering to individuals with disabilities.
The dementia study by Livingston et al1 sheds light on risk factors spanning different life phases. Early life elements such as education contribute, while midlife risks involve hypertension, obesity, hearing loss, traumatic brain injury, and alcohol misuse.1 In later life, smoking, depression, physical inactivity, social isolation, diabetes, and air pollution are identified as potential contributors to an increased risk of dementia. Nevertheless, the study1 recognizes that certain late-life factors, such as depression, may exert a bidirectional impact and could also be part of the dementia prodrome.
In a separate study,7 it might be inferred that, beyond the specific dementia type, key factors strongly linked to mortality due to dementia during follow-up encompass being male, being white, and identifying as non-Hispanic (NH). The consistent observation that male sex, and to a lesser extent gender, is associated with higher mortality or reduced survival aligns with findings from various dementia studies, although disparities exist in the literature.8 Additionally, the indication that individuals of NH white race/ethnicity may encounter a heightened risk of mortality compared to their African American and Hispanic/Latino counterparts, a trend frequently observed in studies, also displays some variability.7–9
We acknowledge that there is a notable dearth of information regarding comparative mortality patterns from dementia among various demographic and regional groups in the United States. Consequently, the objective of this study was to analyze contemporary trends of dementia and dementia-related mortality categorized by demographic and regional attributes. Such analysis not only quantifies the current and impending dementia burden but also guides policymakers by assessing the adequacy of existing policies and emphasizing the need to address the vulnerabilities within specific populations across the United States.
METHODS
Study Sample
We utilized the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research (WONDER)10 to retrieve data concerning dementia-related deaths in the United States. Since the data had been deidentified and made publicly accessible, institutional review board approval was not required. Dementia was selected as a contributing or underlying cause of death on countrywide death certificates using International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD 10-CM) codes F01 (vascular dementia), F03 (unspecified dementia), and G30 (AD) from the multiple cause-of death public use record death certificates. We obtained population data with 10-year age categories from age 35 years to ≥85 years.
Variables
Dementia-related mortality data spanning from 1999 to 2020 were segmented by age, gender, ethnicity, and race. The categories for ethnicity included Hispanic, NH black/African American, NH white, NH American Indian or Alaska Native, and NH Asian or Pacific Islander. Furthermore, we categorized population data by place of death, region, and US state. To calculate the crude mortality rate, we divided the number of dementia-related deaths by the corresponding US population for each year.
Statistical Analysis
As previously indicated,11 age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMR) were determined by standardizing dementia-related deaths to the 2000 US population as a reference. The analysis employed the Joinpoint regression tool version 5.0.2 developed by the National Cancer Institute to assess AAMR patterns through the annual percent change (APC) method.
In this investigation, log-linear regression models were applied to detect and analyze significant fluctuations in AAMR across different time intervals. To estimate the average annual mortality rates for identified line segments connecting join locations, the Monte Carlo permutation test was used, and the results were presented as adjusted prevalence ratios along with their corresponding 95% CIs.
To assess APCs, we determined whether there was a statistically significant departure from zero in the slope characterizing the mortality variation. This was accomplished through a 2-tailed t test, with a significance level set at P < .05. The analysis was conducted in July 2023.
RESULTS
During the period spanning from 1999 to 2020, a cumulative number of 6,601,680 fatalities associated with dementia were recorded among individuals aged 35 years to ≥85 years (as indicated in Supplementary eTable 1 of the Supplementary Material). Of these, 2,226,222 (33.7%) were men and 4,375,458 (66.3%) were women. In terms of racial distribution, 5,645,455 (85.5%) were NH white, 530,413 (8%) were NH black, 286,677 (4.34%) were Hispanic or Latino, 107,873 (1.6%) were NH Asian or Pacific Islander, and 19,423 (0.3%) were NH American Indian or Alaska Native (see Supplementary eTables 2–4 of the Supplementary Material). Among the 6,584,630 deaths with available location information, 16.3% (1,071,727 deaths) occurred within medical facilities. Additionally, 55.3% (3,646,943 deaths) occurred in nursing homes or long term care facilities, 4.1% (271,355 deaths) occurred in hospice, and 18.0% (1,185,570 deaths) took place at home (as shown in Supplementary eTable 5 of the Supplementary Material).
The AAMR observed throughout the study period was 17.49. Notably, the AAMR was found to be higher among women in comparison to men, with rates of 18.19 and 16.05, respectively. Additionally, the AAMR was found to be higher among NH black adults when compared to Hispanic or Latino and NH white adults, with rates of 18.23, 12.7, and 18.09, respectively.
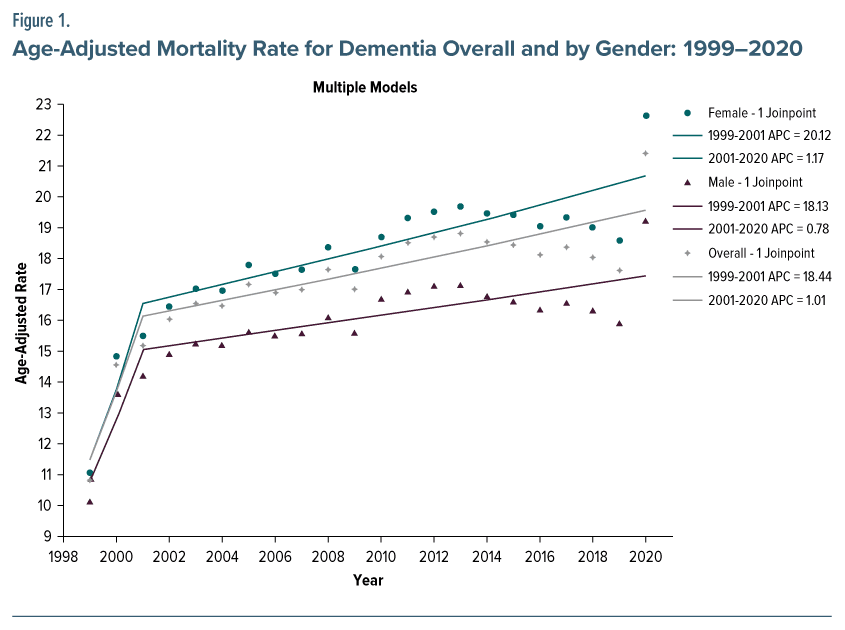
In general, the AAMR for dementia within our group exhibited an upward trend, increasing from 10.86 in 1999 to 21.42 in 2020, as depicted in Figure 1. The annual AAMR exhibited an upward trend from 1999 to 2001, with an average APC of 18.4% (95% CI, 4.7–31.0). Subsequently, the AAMR remained relatively stable from 2001 to 2020, with an APC of 1.0% (95% CI, 0.4–1.4) (Figure 1).
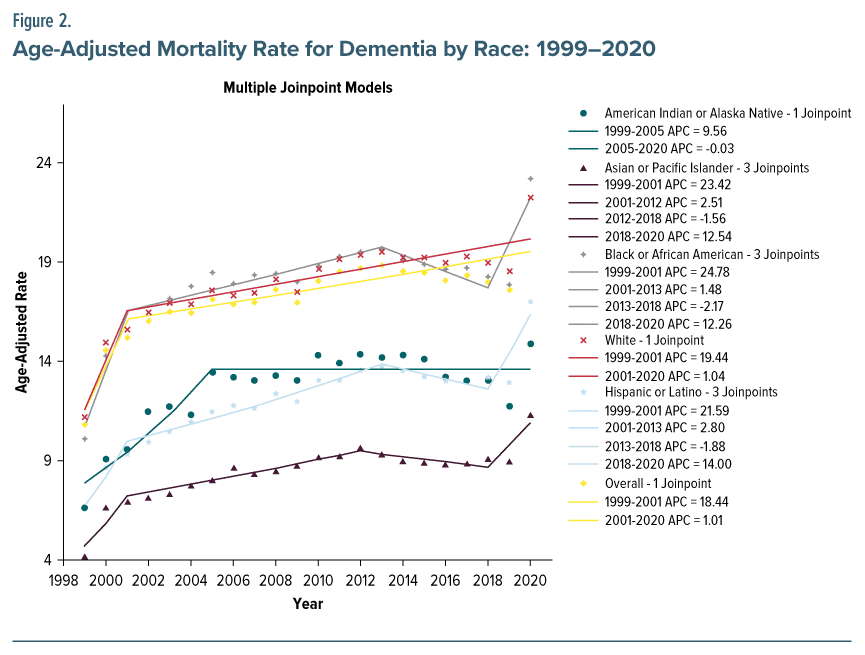
Dementia mortality increased in men and women. The AAMR in men exhibited a notable increase from 10.16 in 1999 to 19.26 in 2020. Similarly, the AAMR in women increased from 11.08 in 1999 to 22.64 in 2020, as depicted in Figure 1. The AAMR demonstrated an increase across all racial and ethnic groupings. The AAMR for adults identifying as NH black or African American exhibited an upward trend, increasing from 10.12 in 1999 to 23.24 in 2020. Similarly, the AAMR for adults identifying as Hispanic or Latino experienced an increase from 6.51 in 1999 to 17.06 in 2020. Furthermore, the AAMR for individuals identifying as NH Asian or Pacific Islander also had an upward trajectory, increasing from 4.23 in 1999 to 11.34 in 2020. The AAMR for NH American Indians or Alaska Natives and for NH whites showed an increase from 6.62 to 14.92 and from 11.23 to 22.29, correspondingly, throughout the identical time frame (Figure 2).
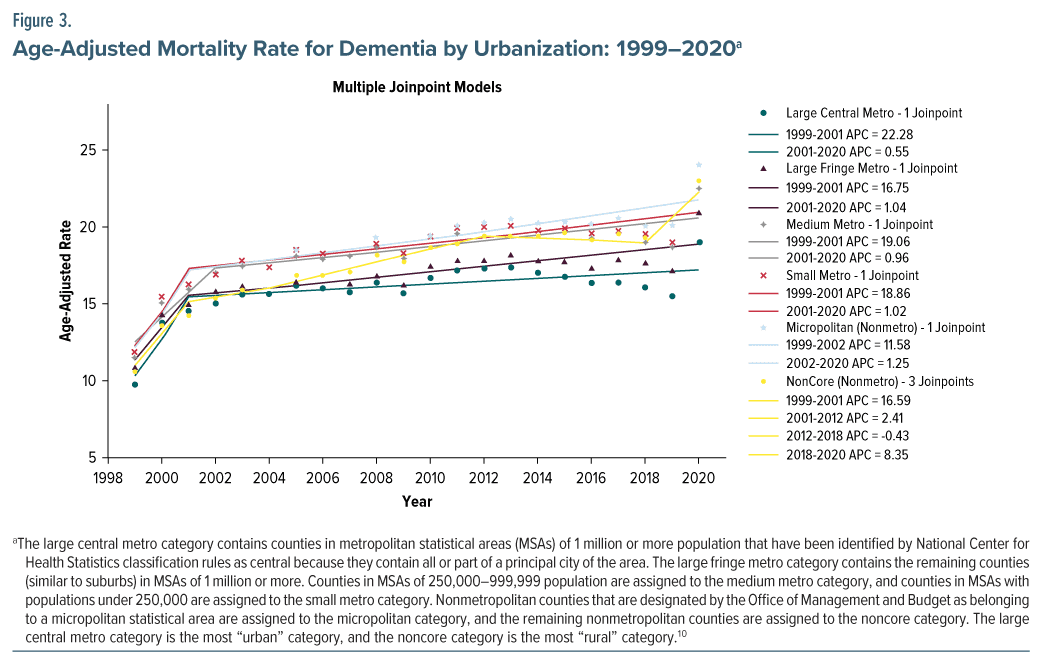
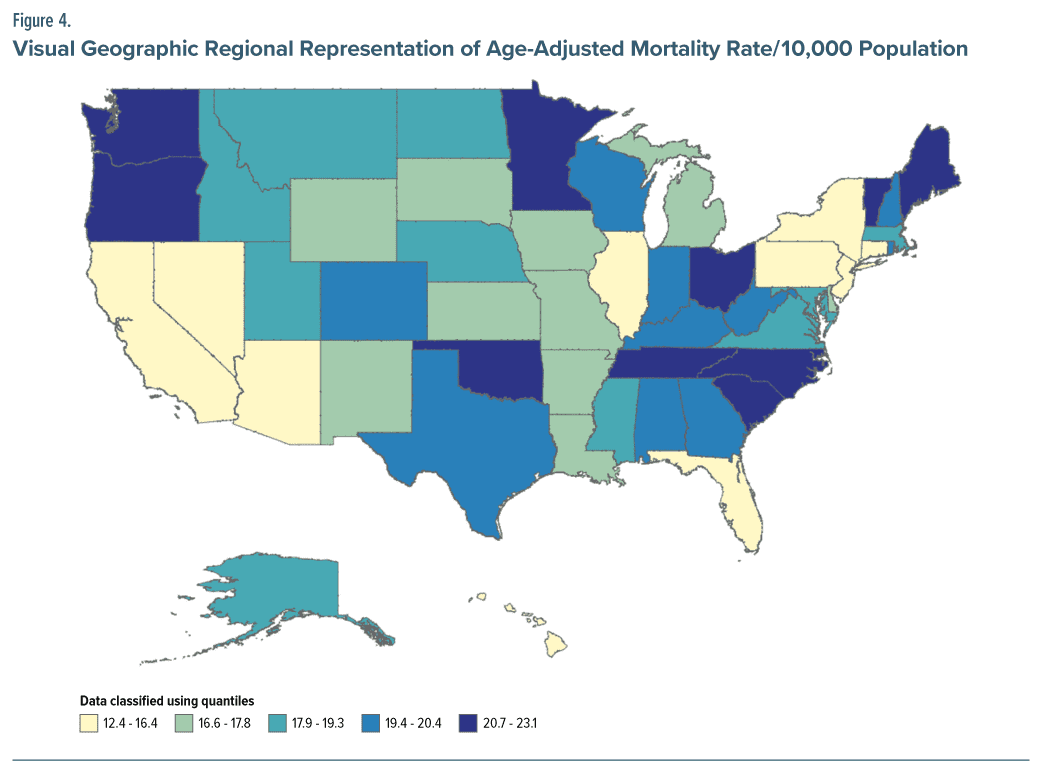
The AAMR in nonmetropolitan areas had the most pronounced increase, from 11.69 in 1999 to 24.06 in 2020. The research period had a comparable increase in mortality rates in both major and medium/small urban areas, as depicted in Figure 3 and Supplementary eTable 6 in the Supplementary Material. There were notable variations in the prevalence of mortality related to dementia across different regions. States such as Tennessee, South Carolina, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Vermont, and Oregon, which fell within the upper 90th percentile of dementia-related mortality, exhibited a considerably higher burden of mortality compared to states in the bottom 10th percentile. This information is visually represented in Figure 4 and can be further explored in Supplementary eTable 7 of the Supplementary Material.
DISCUSSION
This study analyzed a 22-year trend in mortality from 1999 to 2020 from the CDC WONDER database, particularly for those death certificates that mention mortality due to vascular dementia, AD, and unspecified dementia. Across all races, genders, ethnicities, and geographic distributions, the trend is unfortunately upward.
The present study found emerging racial and ethnic differences in dementia-related mortality in the United States with black adults having the highest AAMR (a 13% increase from 1999) followed by NH whites, Hispanics, American Indians, and Asian adults. This increasing trend in black adult mortality due to dementia corroborates the findings of previous studies.12–15 Genetic variants such as ABCA7 and APOE ε4 have been attributed to a high risk of dementia in black American adults.16 Nonetheless, numerous additional factors also play a role in this, including health disparities, socioeconomic status, limited health literacy, reduced access to quality education, family income, financial instability, chronic health conditions, stress, and experiences of racial discrimination.15,17 Research indicates that African American, Hispanic American, and Asian American adults encounter obstacles when trying to access health care services, including specialists and support services for dementia. Furthermore, these groups are less likely to receive an early and precise dementia diagnosis compared to NH white adults, potentially leading to missed opportunities for timely intervention and support.18,19
Our results also depict significant geographic variations in dementia-related mortality, with nonmetropolitan states having the highest increase in the AAMR over time. Our findings are in line with a recent similar study depicting difference in dementia-related mortality.20 The study’s findings reveal a concerning urban-rural divergence in AD and related dementias (ADRD) mortality in the United States, with nonmetropolitan areas experiencing a rapid increase in ADRD mortality rates. This emerging trend is contributing significantly to the urban-rural life expectancy gap, particularly among women, surpassing the impact of other leading causes of death.20 These similar findings can be attributed to rapidly aging rural areas of the United States. These regions are facing adverse mortality trends and increasing disadvantages in terms of socioeconomic resources and health care infrastructure, which can be challenging to address.
The higher prevalence of dementia among women can be primarily attributed to their longer lifespan, as age stands out as the most significant risk factor for AD (the most prevalent form of dementia).21 However, it’s worth noting that, regardless of age, women exhibit a higher risk of developing dementia compared to men.22 These findings align with data from the Framingham Study,23 and we can infer that there is a striking disparity in the remaining lifetime risk of AD and dementing illnesses between men and women. Specifically, for a 65-year-old woman, the lifetime risk of developing AD is approximately twice as high as that of a man of the same age.23 These findings highlight the importance of delving deeper into the genetic and environmental factors that may elevate women’s susceptibility to dementia.
Enhancing public health awareness regarding dementia risk factors, promoting screening and early detection, ensuring equitable health care access, and implementing effective health policy interventions hold the promise of substantially mitigating regional and racial disparities in dementia mortality across the United States. Tailored interventions can be crafted to cater to the specific needs and challenges of specific populations and geographic areas. Ongoing research into regional and racial variations in dementia mortality can offer insights into emerging trends and the assessment of intervention efficacy. Collaborative efforts involving public health authorities, health care providers, community organizations, and policymakers can foster holistic and integrated approaches to dementia care and mortality reduction in the United States.
This study has several limitations to consider. First, the use of ICD-CM codes and reliance on death certificates may have led to instances where dementia was misclassified as a cause of death. Second, an increase in dementia diagnoses in electronic health records might have contributed to higher reporting on death certificates, potentially affecting the accuracy of trends in dementia-related mortality as a predictive measure of actual dementia mortality trends. Additionally, the database lacks information on disease characteristics that could offer a more comprehensive characterization of the dementia phenotype, including neurological and neuropsychological examinations, electroencephalograms, computed tomography scans, magnetic resonance imaging, and genetic testing.
CONCLUSION
The study spanning 1999–2020 revealed concerning trends in dementia-related mortality in the United States. Overall, there was a substantial increase in mortality rates, affecting both men and women across various ethnicities. Nonmetropolitan areas saw the steepest rise in dementia-related deaths. There is a critical need for targeted health care policy initiatives aimed at mitigating the increasing dementia burden. These measures should prioritize prevention, early detection, and the reduction of disparities in dementia care.
Article Information
Published Online: August 13, 2024. https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.24m03724
© 2024 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
Submitted: February 17, 2024; accepted May 2, 2024.
To Cite: Ali M, Talha M, Naseer B, et al. Divergent mortality patterns associated with dementia in the united states: 1999–2020. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2024;26(4):24m03724.
Author Affiliations: Department of Psychiatry, King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Pakistan (Ali); Combined Military Hospitals Medical College, Lahore, Pakistan (Talha); King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Pakistan (Naseer); School of Global Public Health, New York University, New York City, New York (Jaka); Department of Psychiatry, Bronx Care Health System, Bronx, New York (Gunturu); Department of Psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, New York (Gunturu).
Corresponding Author: Mohsan Ali, MBBS, Department of Psychiatry, King Edward Medical University, Neela Gumbad Chowk, Lahore 54000, Pakistan ([email protected]).
Relevant Financial Relationships: None.
Funding/Support: None.
Supplementary Material: Available at Psychiatrist.com.
Clinical Points
- There was a significant increase in dementia-related mortality rates from 1999 to 2020, which emphasizes the growing public health concern surrounding dementia and the need for improved management strategies.
- Disparities in dementia mortality across racial and ethnic groups, with non-Hispanic black adults experiencing a higher age-adjusted mortality rate compared to other groups, suggest a need for targeted interventions to address these disparities and ensure equitable access to care.
- A higher increase in dementia mortality rates in nonmetropolitan areas compared to urban areas suggests a potential need for increased health care resources and support systems for individuals with dementia residing in rural locations.