An Essential Guide to the Python is operator (original) (raw)
Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn about the Python is operator and the differences between the is operator and equality (==) operators.
Introduction to the Python is operator #
Python is operator compares two variables and returns True if they reference the same object. If the two variables reference different objects, the is operator returns False.
In other words, the is operator compares the identity of two variables and returns True if they reference the same object.
Let’s take a look at the following example:
a = 100 b = a result = a is b print(result)Code language: PHP (php)
Output:
TrueCode language: PHP (php)
How it works:
- First, define the
avariable that references anintobject with the value of100. - Second, define another variable
bthat references the same object referenced by theavariable. - Third, use the
isoperator to check ifaandbreference the same object and display the result.
Since both a and b reference the same object, the result is True.
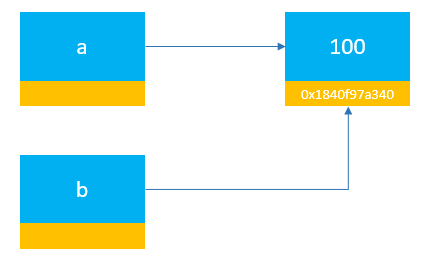
The following example defines two variables a and b and initialize them to 100:
`a = 100 b = 100
result = a is b print(result)`Code language: PHP (php)
Output:
TrueCode language: PHP (php)
In this example, there’s no link between a and b. However, when you assign 100 to b, Python Memory Manager reuses the existing object. Therefore, both a and b references the same object:

Note that the result of this example may be different, depending on how the Python Memory Manager is implemented. And you should not count on it.
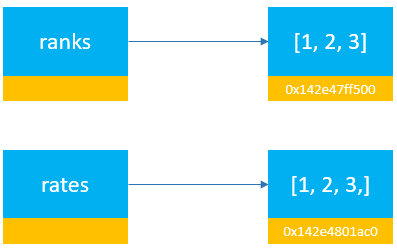
The following example defines two lists with the same elements and uses the is operator to check if they reference the same list object:
`ranks = [1, 2, 3] rates = [1, 2, 3]
result = ranks is rates print(result)`Code language: PHP (php)
Output:
FalseCode language: PHP (php)
In this example, lists are mutable objects. Python Memory Manager doesn’t reuse the existing list but creates a new one in the memory. Therefore, the ranks and rates variables reference different lists:
The equality operator (==) compares two variables for equality and returns True if they are equal. Otherwise, it returns False.
The following example uses both is operator and == operator:
`a = 100 b = a
is_identical = a is b is_equal = a == b
print(is_identical) print(is_equal)`Code language: PHP (php)
Output:
True TrueCode language: PHP (php)
Since a and b references the same object, they’re both identical and equal.
In the following example, both lists have the same elements, so they’re equal.
However, since they reference different list objects in the memory, they’re not identical:
`ranks = [1, 2, 3] rates = [1, 2, 3]
is_identical = ranks is rates is_equal = ranks == rates
print(is_identical) print(is_equal) `Code language: PHP (php)
Output:
False TrueCode language: PHP (php)
Python is not operator #
To negate the is operator, you use the not operator. The is not operator returns False if two variables reference the same object. Otherwise, it returns True.
The following example uses the is not operator to check if the two variables don’t reference the same list object:
`ranks = [1, 2, 3] rates = [1, 2, 3]
result = ranks is not rates print(result) # True`Code language: PHP (php)
Output:
TrueCode language: PHP (php)
Summary #
- Use the
isoperator to check if two variables reference the same object. - Use the
isoperator to check two variables for identity and==to check for two variables for equality. - Use the
notoperator to negate the result of theisoperator.
Was this tutorial helpful ?