Tkinter Open File Dialog (original) (raw)
Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to show an open file dialog in Tkinter applications.
Introduction to the Tkinter Open File Dialog functions #
When developing a Tkinter application that deals with the file system, you need to provide a dialog that allows file selections.
To do that, you can use the tkinter.filedialog module. The following steps show how to display an open file dialog:
First, import the tkinter.filedialog module:
from tkinter import filedialog as fdCode language: Python (python)
Second, call the fd.askopenfilename() function to show a dialog that allows a single file selection:
filename = fd.askopenfilename()Code language: Python (python)
The askopenfilename() function returns the file name that you selected.
The askopenfilename() also supports other useful options including the initial directory displayed by the dialog or filtering files by their extensions.
The following program displays a button:
If you click the button, it’ll open a file dialog:
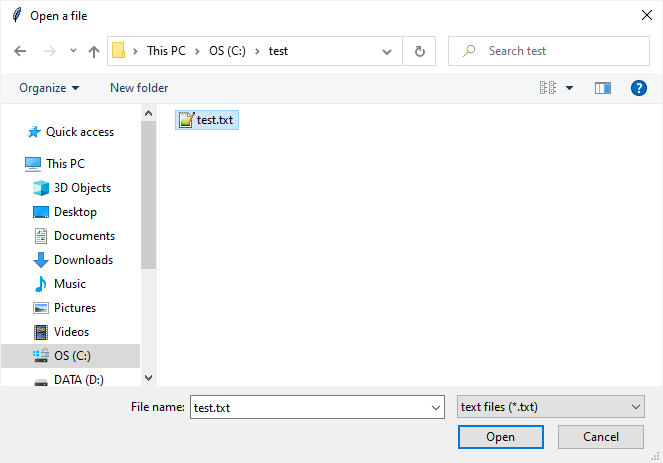
After you select a file, the program will show the full path of the selected file:
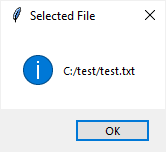
The program:
`import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter import filedialog as fd from tkinter.messagebox import showinfo
create the root window
root = tk.Tk() root.title('Tkinter Open File Dialog') root.resizable(False, False) root.geometry('300x150')
def select_file(): filetypes = ( ('text files', '.txt'), ('All files', '.*') )
filename = fd.askopenfilename(
title='Open a file',
initialdir='/',
filetypes=filetypes)
showinfo(
title='Selected File',
message=filename
)open button
open_button = ttk.Button( root, text='Open a File', command=select_file )
open_button.pack(expand=True)
run the application
root.mainloop() `Code language: Python (python)
Selecting multiple files #
The askopenfilenames() function displays a file dialog for multiple file selections. It returns the selected file names as a tuple. For example:
`import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter import filedialog as fd from tkinter.messagebox import showinfo
create the root window
root = tk.Tk() root.title('Tkinter File Dialog') root.resizable(False, False) root.geometry('300x150')
def select_files(): filetypes = ( ('text files', '.txt'), ('All files', '.*') )
filenames = fd.askopenfilenames(
title='Open files',
initialdir='/',
filetypes=filetypes)
showinfo(
title='Selected Files',
message=filenames
)open button
open_button = ttk.Button( root, text='Open Files', command=select_files )
open_button.pack(expand=True)
root.mainloop()`Code language: Python (python)
Opening files directly #
After getting the selected file names, you can open them using the open() method.
To make it more convenient, the tkinter.filedialog module also provides some functions that allow you to select one or more files and return the file objects directly.
The askopenfile() function displays a file dialog and returns a file object of the selected file:
f = fd.askopenfile()Code language: Python (python)
And the askopenfiles() function shows a file dialog and returns file objects of the selected files:
f = fd.askopenfiles()Code language: Python (python)
The following program illustrates how to use the askopenfile() function:

It’ll allow you to open a text file and display the file content on a Text widget:
`import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter import filedialog as fd
Root window
root = tk.Tk() root.title('Display a Text File') root.resizable(False, False) root.geometry('550x250')
Text editor
text = tk.Text(root, height=12) text.grid(column=0, row=0, sticky='nsew')
def open_text_file(): # file type filetypes = ( ('text files', '.txt'), ('All files', '.*') ) # show the open file dialog f = fd.askopenfile(filetypes=filetypes) # read the text file and show its content on the Text text.insert('1.0', f.readlines())
open file button
open_button = ttk.Button( root, text='Open a File', command=open_text_file )
open_button.grid(column=0, row=1, sticky='w', padx=10, pady=10)
root.mainloop()`Code language: Python (python)
Summary #
- Use the
askopenfilename()function to display an open file dialog that allows users to select one file. - Use the
askopenfilenames()function to display an open file dialog that allows users to select multiple files. - Use the
askopenfile()oraskopenfiles()function to display an open file dialog that allows users to select one or multiple files and receive a file or multiple file objects.
Was this tutorial helpful ?