An Essential Guide to the Ttk Elements By Practical Examples (original) (raw)
Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn about the ttk elements and how they are assembled into styles of widgets.
Introduction to ttk elements #
So far, you have learned that a theme is a collection of styles that defines the appearance of all ttk widgets.
A style is a description of the appearance of a widget class. A style is composed of one or more elements.
For example, a Label consists of border, padding and label elements. And these elements are nested within each other like the following picture:

In general, most of the built-in ttk styles use the concept of a layout to organize the different element layers that build up a widget.
To get the layout of a widget class, you use the layout() method of the Style object like this:
style.layout(widget_class)Code language: Python (python)
If a widget class doesn’t have a layout, the layout() method will raise a tk.TclError exception.
The layout() method returns a list of tuples (element_name, description), where:
element_nameis the name of the element.descriptionis a dictionary that describes the element.
The following example uses the layout() method to get the layout of the TLabel widget class:
`import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk
class App(tk.Tk): def init(self): super().init()
style = ttk.Style(self)
layout = style.layout('TLabel')
print(layout)if name == "main": app = App() app.mainloop()`Code language: Python (python)
The following output shows the style’s layout of the TLabel:
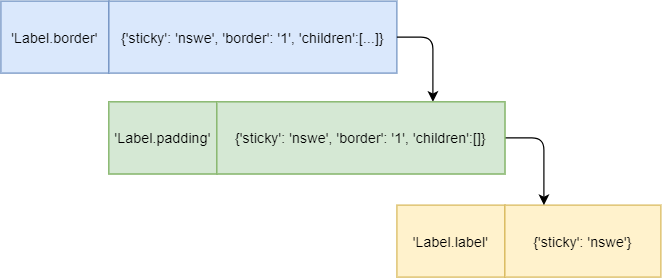
[('Label.border', {'sticky': 'nswe', 'border': '1', 'children': [('Label.padding', {'sticky': 'nswe', 'border': '1', 'children': [('Label.label', {'sticky': 'nswe'})] })] } )]Code language: Python (python)
The TLabel has three elements nested within each other:
- The
Label.borderis the outermost element that has thesticky,border, andchildrenkeys. - The
Label.paddingis nested inside theLabel.border. It also has thesticky,border, andchildrenkeys. - The
Label.labelis the innermost element that has only onestickykey.
For example, when an element has a sticky key with the value of nswe, it would be stretched to adhere to the north, south, west, and east of the parent element.
Note that the style’s layout of a widget’s class depends on the current theme. If you change the theme, the layout may be different.
Element options #
Each element has a list of options that specify the appearance of the element. To get the list of option names, you use the element_options() method of Style object:
style.element_options(styleName)Code language: Python (python)
The following program shows the element options of the Label.border, Label.padding, and Label.label elements:
`import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk
class App(tk.Tk): def init(self): super().init()
style = ttk.Style(self)
# layout
layout = style.layout('TLabel')
print(layout)
# element options
print(style.element_options('Label.border'))
print(style.element_options('Label.padding'))
print(style.element_options('Label.label'))if name == "main": app = App() app.mainloop()`Code language: Python (python)
Output:
('relief',) ('padding', 'relief', 'shiftrelief') ('compound', 'space', 'text', 'font', 'foreground', 'underline', 'width', 'anchor', 'justify', 'wraplength', 'embossed', 'image', 'stipple', 'background')Code language: Python (python)
In this output:
- The
Label.borderelement has one option:'relief'. - The
Label.paddingelement has three options:'padding','relief', and'shiftrelief'. - The
Label.labelelement has many options including'font','foreground','with', etc.
Attributes of element options #
To get a list of attributes associated with an element option, you use the lookup() method of the Style object:
style.lookup(layout_name, option_name)Code language: Python (python)
The following example shows the attributes of the font, foreground, and background options in the TLabel.label element:
`import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk
class App(tk.Tk): def init(self): super().init()
style = ttk.Style(self)
# attributes of the font, foreground, and background
# of the Label.label element
print(style.lookup('Label.label', 'font'))
print(style.lookup('Label.label', 'foreground'))
print(style.lookup('Label.label', 'background'))if name == "main": app = App() app.mainloop()`Code language: Python (python)
Output:
TkDefaultFont SystemWindowText SystemButtonFaceCode language: Python (python)
As you can see clearly from the output, the font is TkDefaultFont, the foreground is SystemWindowText, and the background is SystemButtonFace.
Put it all together #
The following shows how to change the appearance of a Label widget:
`import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk
class App(tk.Tk): def init(self): super().init()
self.geometry('500x100')
message = 'This is an error message!'
label = ttk.Label(self, text=message, style='Error.TLabel')
label.pack(expand=True)
style = ttk.Style(self)
style.configure('Error.TLabel', foreground='white')
style.configure('Error.TLabel', background='red')
style.configure('Error.TLabel', font=('Helvetica', 12))
style.configure('Error.TLabel', padding=(10, 10))if name == "main": app = App() app.mainloop()`Code language: Python (python)
Summary #
- A ttk widget is made up of elements. The
layoutdetermines how elements assembled the widget. - Use the
Style.layout()method to retrieve the layout of a widget class. - Use the
Style.element_options()method to get the element options of an element. - Use the
Style.lookup()method to get the attributes of an element option.
Was this tutorial helpful ?