Mental Health and Sleep (original) (raw)
Table of Contents
- How Is Mental Health Related to Sleep?
- Sleep and Specific Mental Health Problems
- Ways To Improve Both Sleep and Mental Health
Key Takeaways
- Mental health impacts thoughts, feelings, and actions and influences our ability to handle stress, relate to others, and make choices.
- Quality sleep is crucial for good mental health, but sleep issues can worsen mental health conditions, and mental health problems can lead to poor sleep.
- Adhering to sleep hygiene practices can improve sleep quality and mental well-being.
Most people know firsthand that sleep affects their mental state. After all, there’s a reason it’s said that someone in a bad mood “woke up on the wrong side of the bed.”
As it turns out, there’s quite a bit of truth behind this colloquial saying. Sleep is closely connected to mental and emotional health and has demonstrated links to depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and other conditions.
Research is ongoing to better understand the bidirectional relationship between mental health and sleep. Both are complex issues affected by a multitude of factors, but, given their close association, there is strong reason to believe that improving sleep can have a beneficial impact on mental health and can be a component of treating many psychiatric disorders.
Brain activity fluctuates during sleep, increasing and decreasing during different sleep stages that make up the sleep cycle. Each stage plays a role in brain health, allowing activity in different parts of the brain to ramp up or down and enabling better thinking, learning, and memory. Research has also uncovered that brain activity during sleep has profound effects on emotional and mental health.
Sufficient sleep, especially rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, facilitates the brain’s processing of emotional information. During sleep, the brain works to evaluate and remember thoughts and memories, and it appears that a lack of sleep is especially harmful to the consolidation of positive emotional content. This can influence mood and emotional reactivity and is tied to mental health disorders and their severity, including the risk of suicidal ideas or behaviors .
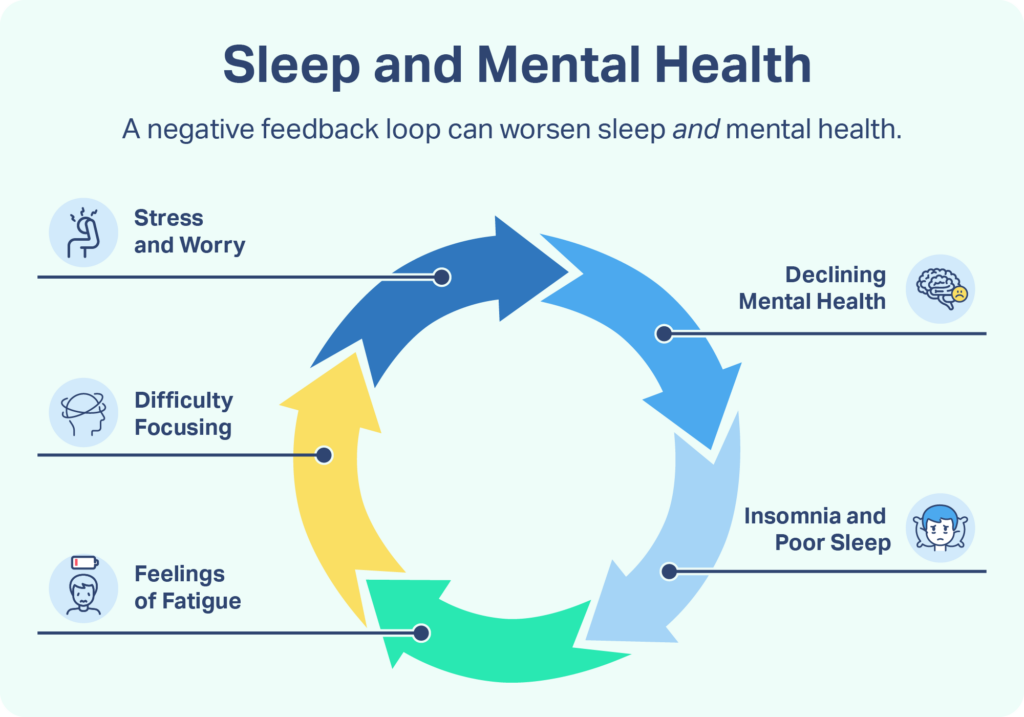
As a result, the traditional view, which held that sleep problems were a symptom of mental health disorders, is increasingly being called into question. Instead, it is becoming clear that there is a bidirectional relationship between sleep and mental health in which sleeping problems may be both a cause and consequence of mental health problems. Further research is needed to identify the diverse connections between sleep and mental health as well as how their multifaceted relationship can be influenced by numerous factors in any specific person’s case.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is another aspect of sleep that has been linked to mental health. OSA is a disorder that involves pauses in breathing during sleep and a reduction in the body’s oxygen levels, creating fragmented and disturbed sleep. OSA occurs more frequently in people with psychiatric conditions and may detract from their physical health and heighten their risk of serious mental distress.

Sleep and Specific Mental Health Problems
The way that sleep and mental health are intertwined becomes even more apparent by reviewing what is known about how sleep is tied to a number of specific mental health conditions and neurodevelopmental disorders.
Depression
It is estimated that over 300 million people worldwide have depression, a type of mood disorder marked by feelings of sadness or hopelessness. Around 75% of depressed people show symptoms of insomnia , and many people with depression also suffer from excessive daytime sleepiness and hypersomnia, which is sleeping too much.
Historically, sleeping problems were seen as a consequence of depression, but growing evidence suggests that poor sleep may induce or exacerbate depression. The difficulty in identifying clear cause and effect reflects what is believed to be a bidirectional relationship in which sleep problems and depressive symptoms are mutually reinforcing.
While this can create a negative feedback loop — poor sleep worsens depression that then further interrupts sleep — it also opens a potential avenue for new types of treatment for depression. For example, for at least some people, a focus on improving sleep may have a corollary benefit of reducing the symptoms of depression .
Seasonal Affective Disorder
Seasonal affective disorder is a subtype of depression that most often affects people during times of the year with reduced daylight hours. For example, people in northern climates may experience seasonal affective disorder during the fall and winter.
This condition is closely tied to the disruption of a person’s internal biological clock, or circadian rhythm, that helps control multiple bodily processes, including sleep. Not surprisingly, then, people with seasonal affective disorder tend to sleep too much or too little or experience changes to their sleep cycles.
Anxiety Disorders
Every year, anxiety disorders in America affect an estimated 20% of adults and 25% of teenagers . These disorders create excess fear or worry that can affect everyday life and create risks for health problems including heart disease and diabetes. Types of anxiety disorders include general anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, panic disorder, specific phobias, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Anxiety disorders have a strong association with sleeping problems. Worry and fear contribute to a state of hyperarousal in which the mind is racing, and hyperarousal is considered to be a central contributor to insomnia. Sleep problems may become an added source of worry, creating anticipatory anxiety at bedtime that makes it harder to fall asleep.
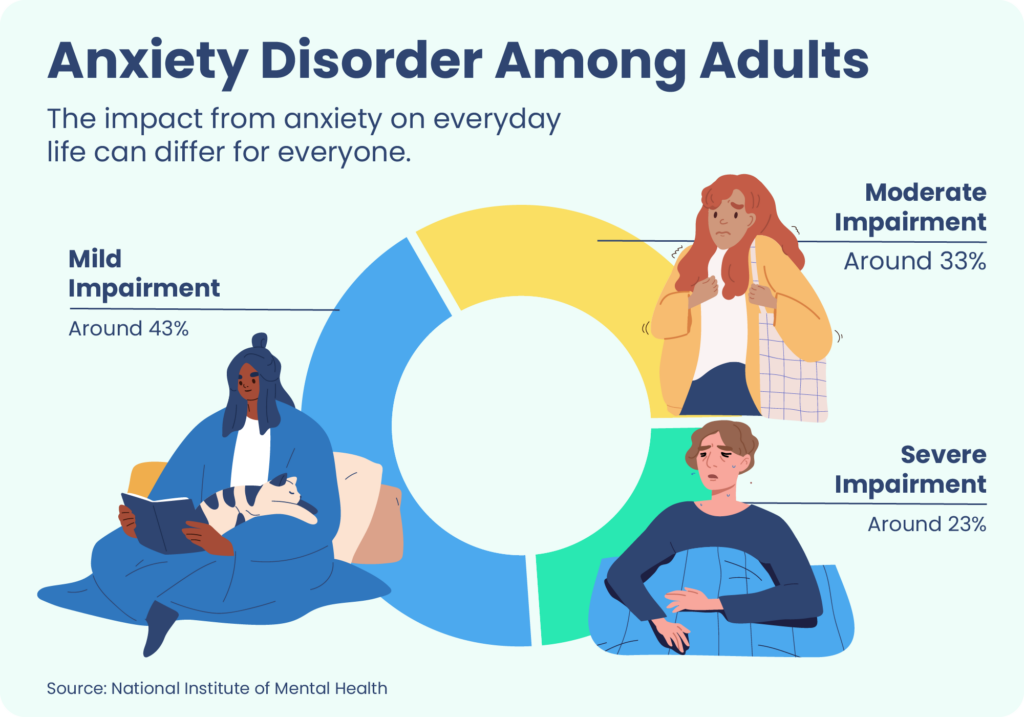
Research has found an especially strong connection between PTSD and sleep. People with PTSD frequently replay negative events in their mind, suffer from nightmares, and experience a state of being on alert, all of which can interfere with sleep. PTSD affects many veterans, and at least 90% of U.S. veterans with combat-related PTSD from recent wars have insomnia symptoms .
Sleeping problems aren’t just a result of anxiety. Research indicates that poor sleep can activate anxiety in people who are high-risk for it , and chronic insomnia may be a predisposing trait among people who go on to develop anxiety disorders.
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder involves episodes of extreme moods that can be both high (mania) and low (depression). A person’s feelings and symptoms are quite different depending on the type of episode; however, both manic and depressive periods can cause major impairment in everyday life.
In people with bipolar disorder, sleep patterns change considerably depending on their emotional state. During manic periods, they usually feel less need to sleep, but during depressed periods, they may sleep excessively.
There is also evidence that sleeping problems induce or worsen manic and depressive periods and that, because of the bidirectional relationship between bipolar disorder and sleep, treatment for insomnia can reduce the impact of bipolar disorder.
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental health disorder characterized by a difficulty in differentiating between what is and is not real. People with schizophrenia are more likely to experience insomnia and circadian rhythm disorders . Sleeping problems may be exacerbated by medications that are used to treat schizophrenia. Poor sleep and symptoms of schizophrenia may be mutually reinforcing, so there are potential benefits to stabilizing and normalizing sleep patterns.
ADHD
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that involves reduced attention span and increased impulsiveness. ADHD is usually diagnosed in children , but it may last into adulthood and is sometimes only formally diagnosed when someone is already an adult.
Sleeping problems are common in people with ADHD. They may have difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings, and excessive daytime sleepiness. Rates of other sleeping problems, such as restless leg syndrome (RLS) also appear to be higher in people with ADHD . Sleep difficulties associated with ADHD have been studied primarily in children but have been found to affect adults as well.
There is evidence of a bidirectional relationship between sleep and ADHD. In addition to being a consequence of ADHD, sleep problems may aggravate symptoms like reduced attention span or behavior problems.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a term that encompasses several neurodevelopmental conditions affecting communication and social interaction. These conditions are usually diagnosed early in childhood and may persist in adulthood.
Children and adolescents with ASD have a higher prevalence of sleep problems including insomnia and sleep-disordered breathing. These issues tend to be more persistent than sleeping problems in children without ASD, and they can contribute to a worsening of symptoms and quality of life for people with the condition . Addressing insomnia and other sleep disturbances is an important component of care as it may decrease excessive daytime sleepiness as well as other health and behavior problems in people with ASD.
Ways To Improve Both Sleep and Mental Health
This multifaceted relationship between sleep and mental health makes for complex connections between sleep and psychiatric disorders, but it also means that treatment for both issues can go hand-in-hand. Steps to improve sleep may even form part of a preventive mental health strategy.
Every individual’s situation is different, so the optimal treatment for mental health and sleep problems depends on the person. Because these conditions can have a major impact on quality of life, it’s important to receive proper care, which entails working with a trained health professional.
A medical doctor or psychiatrist can review the potential benefits and risks of different types of treatments and provide tailored care – even in situations with multiple co-occurring physical or mental health issues.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) describes a type of counseling known as talk therapy. It works by examining patterns of thinking and working to reformulate negative thoughts in new ways. For many patients, help from a trained counselor to reframe their thinking can meaningfully improve both their sleep and mental state.
Different types of CBT have been developed for specific problems such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. In addition, CBT for insomnia (CBT-I) has a proven track record in reducing sleeping problems. A large clinical trial also showed that CBT-I could reduce symptoms of many mental health conditions , improving emotional well-being and decreasing psychotic episodes.
Improve Sleep Habits
A common cause of sleeping problems is poor sleep hygiene. Stepping up sleep hygiene by cultivating habits and a bedroom setting that are conducive to sleep can go a long way in reducing sleep disruptions.
Examples of steps towards healthier sleep habits include:
- Having a set bedtime and maintaining a steady sleep schedule
- Finding ways to wind-down, such as with relaxation techniques, as part of a standard routine before bedtime
- Avoiding alcohol, tobacco, and caffeine in the evening
- Dimming lights and putting away electronic devices for an hour or more before bed
- Getting regular exercise and natural light exposure during the daytime
- Maximizing comfort and support from your mattress, pillows, and bedding
- Blocking out excess light and sound that could disrupt sleep
Finding the best routines and bedroom arrangement may take some trial and error to determine what’s best for you, but that process can pay dividends in helping you fall asleep quickly and stay asleep through the night.

Still have questions? Ask our community!
Join our Sleep Care Community — a trusted hub of sleep health professionals, product specialists, and people just like you. Whether you need expert sleep advice for your insomnia or you’re searching for the perfect mattress, we’ve got you covered. Get personalized guidance from the experts who know sleep best.

Written By
Eric Suni, Staff Writer
Eric Suni has over a decade of experience as a science writer and was previously an information specialist for the National Cancer Institute.

Medically Reviewed by
Alex Dimitriu, Psychiatrist MD
Dr. Dimitriu is the founder of Menlo Park Psychiatry and Sleep Medicine. He is board-certified in psychiatry as well as sleep medicine.
Learn more about our Editorial Team
References
15 Sources
- Bernert, R. A., Kim, J. S., Iwata, N. G., & Perlis, M. L. (2015). Sleep disturbances as an evidence-based suicide risk factor. Current psychiatry reports, 17(3), 554.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25698339/ - Knechtle, B., Economou, N. T., Nikolaidis, P. T., Velentza, L., Kallianos, A., Steiropoulos, P., Koutsompolis, D., Rosemann, T., & Trakada, G. (2019). Clinical Characteristics of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Psychiatric Disease. Journal of clinical medicine, 8(4), 534.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31003451/ - Friedrich, M. J. (2017, April). Depression Is the Leading Cause of Disability Around the World. JAMA, 317(15), 1517.
http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jama.2017.3826 - Nutt, D., Wilson, S., & Paterson, L. (2008). Sleep disorders as core symptoms of depression. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience, 10(3), 329–336.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18979946/ - Bishop, T. M., Simons, K. V., King, D. A., & Pigeon, W. R. (2016). Sleep and Suicide in Older Adults: An Opportunity for Intervention. Clinical therapeutics, 38(11), 2332–2339.
https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S014929181630738X - National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2016, March). NIH News in Health: Understanding Anxiety Disorders.
https://newsinhealth.nih.gov/2016/03/understanding-anxiety-disorders - Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA). (n.d.). Facts & Statistics.
https://adaa.org/about-adaa/press-room/facts-statistics - Gehrman, P. (2020, March 26). Sleep Problems in Veterans with PTSD.
https://www.ptsd.va.gov/professional/treat/cooccurring/sleep_problems_vets.asp - Goldstein, A. N., Greer, S. M., Saletin, J. M., Harvey, A. G., Nitschke, J. B., & Walker, M. P. (2013). Tired and apprehensive: anxiety amplifies the impact of sleep loss on aversive brain anticipation. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 33(26), 10607–10615.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23804084/ - Harvey, A. G., Kaplan, K. A., & Soehner, A. M. (2015). Interventions for Sleep Disturbance in Bipolar Disorder. Sleep medicine clinics, 10(1), 101–105.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25750600/ - Khurshid K. A. (2018). Comorbid Insomnia and Psychiatric Disorders: An Update. Innovations in clinical neuroscience, 15(3-4), 28–32.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5906087/ - National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). (2016). Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): The Basics.
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd-the-basics/index.shtml - Spruyt, K., & Gozal, D. (2011). Sleep disturbances in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Expert review of neurotherapeutics, 11(4), 565–577.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21469929/ - Williams Buckley, A., Hirtz, D., Oskoui, M., Armstrong, M. J., Batra, A., Bridgemohan, C., Coury, D., Dawson, G., Donley, D., Findling, R. L., Gaughan, T., Gloss, D., Gronseth, G., Kessler, R., Merillat, S., Michelson, D., Owens, J., Pringsheim, T., Sikich, L., Stahmer, A., … Ashwal, S. (2020). Practice guideline: Treatment for insomnia and disrupted sleep behavior in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology, 94(9), 392–404.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32051244/ - Freeman, D., Sheaves, B., Goodwin, G. M., Yu, L. M., Nickless, A., Harrison, P. J., Emsley, R., Luik, A. I., Foster, R. G., Wadekar, V., Hinds, C., Gumley, A., Jones, R., Lightman, S., Jones, S., Bentall, R., Kinderman, P., Rowse, G., Brugha, T., Blagrove, M., … Espie, C. A. (2017). The effects of improving sleep on mental health (OASIS): a randomised controlled trial with mediation analysis. The lancet. Psychiatry, 4(10), 749–758.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28888927/