What is AWS Migration Hub? (original) (raw)
AWS Migration Hub is a service from Amazon Web Services that enables AWS users to simplify migration to the AWS public cloud. Its purpose is to simplify discovery, assessment, planning and execution to streamline organizations' end-to-end migrations and modernization journeys.
AWS Migration Hub supports and integrates with native migration tools, such as AWS Server Migration Service and AWS Database Migration Service, as well as several partner tools to provide accurate data migrations.
Purpose of AWS Migration Hub
With AWS Migration Hub, business users can plan migrations, track the migration status of each application, get full visibility into the entire application portfolio, and collect and view data from on-premises resources including servers. AWS Migration Hub facilitates discovery of applications, migration execution, grouping servers into applications and accelerating application refactoring. The service also enables users to manage existing applications and microservices as one application.
AWS Migration Hub provides guidance, tools, automation recommendations and prescriptive plans to accelerate cloud migration. It also provides proven journey templates and facilitates cross-team collaboration and tracking, enabling businesses to define the migration and modernization strategy that is most likely to help accelerate the process of rehosting, replatforming or refactoring applications. The AWS Migration Hub console enables users to track the migration progress of their applications into AWS.
Important features of AWS Migration Hub
AWS Migration Hub includes numerous features to make it easy for organizations to plan, execute and track migrations. For example, it provides journey templates to offer guidance on the recommended tasks for all migration phases, customizable step-by-step runbooks to execute various subtasks, and predefined workflow templates to accelerate migration and enhance user experiences. By leveraging the guidance, templates and runbooks, businesses can speed up project planning and reduce dependency on outside cloud consultants.
Users can import information about on-premises servers and applications, and discover applications to determine which ones can be migrated and modernized. Another option is to use discovery tools like AWS Discovery Agent or the agentless AWS Discovery Collector for VMware environments if a deeper discovery process is required.
A network visualization feature enables users to quickly identify servers and associated dependencies, identify server roles, and group servers into applications. Doing so can help to accelerate migration planning. To build a migration and modernization strategy for on-premises or AWS applications, AWS Migration Hub provides Strategy Recommendations, a feature that analyzes applications and determines the optimal migration strategies.
Once the migration begins, users can use the AWS Migration Hub dashboard to view the migration status and metrics. The dashboard is particularly useful to track the progress of rehost and replatform migrations, and to identify and troubleshoot issues.
For incremental application refactoring to microservices, AWS Migration Hub provides a chargeable Refactor Spaces feature that removes the undifferentiated work of building and operating AWS infrastructure, minimizes the risk of evolving applications into microservices, and bridges networking across AWS accounts. Moreover, Refactor Spaces maintains the transparency of the underlying architecture changes by providing an application proxy.
Start a migration with AWS Migration Hub
To help users get started with a migration using AWS Migration Hub, the tool prompts them to choose a home region from the AWS Management Console. The home region is where the migration tracking data will be stored. That said, an AWS login is not required to start the AWS migration; applications can also be migrated outside the AWS Console.
Whether or not a login is used, the AWS Migration Hub prompts users to provide information about their existing environment and to specify their migration goals. After doing this, they can either select a built-in journey template or customize it to define their end-to-end migration project.
Prior to migration, users can perform discovery on local resources using a discovery tool. The tools -- Agentless Collector, Discovery Agent and Migration Evaluator -- are available on the Discovery Tools page of the AWS Migration Hub console navigation pane. After choosing a discovery tool, users can view detailed information about discovered servers and explore server network connections.
It's important to authorize the chosen migration tool to communicate the migration status to Migration Hub in the home region. Without this authorization, AWS Migration Hub will not track the migration.
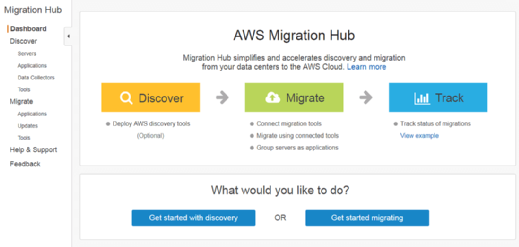
Users can get started with AWS Migration Hub at the dashboard.
Resource discovery prior to migration helps to build a business case for migrating and to build a detailed and systematic migration plan. However, discovery is an optional process, so users can start a migration without it. If they choose to bypass the discovery process and migrate immediately, all application and database servers will appear as resources in AWS Migration Hub as the migration takes place.
During migration, the servers being migrated appear in the Servers page, which can be accessed from the AWS Migration Hub console navigation pane under Discover. To simplify migration tracking, it's useful to group servers as applications. This can be done from the servers list or from the network diagram.
Once AWS Application Discovery Service collects data, it stores it in a repository, which AWS Migration Hub accesses. The service then relays that data to the user, who can examine technical specifications along with other performance information.
Whichever discovery option a user chooses, they must populate a servers list before grouping servers into an application. After the list populates, the user selects the resources to group into an application. All AWS Identity and Access Management users within the same account can view each other's applications.
Track a migration with AWS Migration Hub
AWS Migration Hub tracks migration progress status and the details of each server grouped to the application. Specifically, the migration tool communicates the status to AWS Migration Hub at key points during the migration.
Users can track migration status by following this procedure:
- Navigate to Dashboard in the navigation pane of the Migration Hub console.
- Select the migration application under Most Recently Updated Applications.
- The status will show as Not Started, In Progress or Completed.
- Users can manually change the status from Not Started to In Progress or from In Progress to Completed.
AWS Migration Hub displays the migration status of applications in its console. Each migrating resource shows its status within a diagram and a table. Possible status levels are as follows:
- In progress, replication starting.
- In progress, replication complete.
- Completed, Amazon Machine Image created.
Once migration is finished, AWS Migration Hub will also display data on the newly created resources.
AWS Migration Hub only tracks resources that are in an AWS repository and are migrated with supported tools. Unsupported tools will not report resource statuses back to AWS Migration Hub.
AWS Migration Hub pricing
AWS Migration Hub is free to use for these purposes:
- Collecting and storing discovery data in the home region.
- Planning a migration to AWS.
- Tracking an in-progress migration.
However, organizations can incur costs for using migration tools and for any resources consumed on AWS. Migration Hub's Refactor Spaces is also chargeable on a pay-as-you-use basis at $0.000002 per request. In addition, there are charges for AWS services provisioned by Refactor Spaces, but there are no upfront costs or minimum fees for using Refactor Spaces. AWS also provides a free tier that lets users try Refactor Spaces with 2,160 free environment hours per month for 90 days.
Organizations should take stock of their applications and modernize them where appropriate as part of a cloud migration. Learn about the benefits of modernizing apps and be aware of the potential pitfalls.