business metric (original) (raw)
By
Published: Mar 28, 2022
What is a business metric?
A business metric is a quantifiable measure businesses use to track, monitor and assess the success or failure of various business processes. The main point of using business metrics is to communicate an organization's progress toward certain long- and short-term objectives. Tracking costs and cost management is often a goal of using these metrics.
Effective use of business metrics often requires input from key stakeholders as to which metrics are relevant to their lines of business. Some organizations outline business metrics in their mission statements. Doing that requires buy-in from all levels of the company. Other organizations simply incorporate them into their general workflows.
Some examples of how different lines of business use metrics are the following:
- Marketing departments track metrics pertaining to the success of campaigns and statistics that characterize their reach.
- Sales teams monitor leads, using lead generation and lead scoring. They also track new opportunities and the amount of potential business at various stages of the pipeline.
- Business executives may focus on the overall financial statistics of their company that show revenue, profit, loss, cash flow and bottom line results.
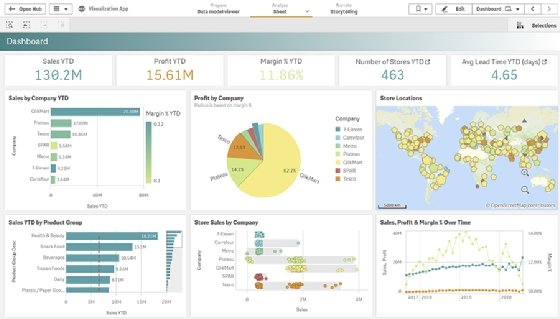
A sales dashboard can provide data on sales, profits, margins and other sales-related metrics broken out by companies or retail outlets.
What makes business metrics important?
Business metrics contribute to a business achieving its strategic and fiscal goals. They help business owners and managers make better decisions and assess the effectiveness of their business operations. They are also used to address specific interests of the business's stakeholders.
Metrics make business insights quantifiable. Business managers can use those insights to develop and improve business strategies.
However, business metrics mean nothing without context attached to them; companies view metrics through the lens of existing benchmarks, practices and objectives. Metrics can be incorporated into a strategy to improve business practices and objectives and optimize performance.
There are key metrics attached to every part of a business, including sales, marketing and finance. Choosing which metrics to track depends on a business's needs, objectives and its industry. There are some metrics -- such as employee engagement and retention -- that apply to businesses in most industries.
Business metrics are important because they do the following:
- provide actionable insights about business performance and goals;
- give employees an understanding of what's important to the business and stakeholders;
- measure performance;
- highlight issues related to a business's strategy and methods; and
- provide stakeholders with insight into a company's performance over time.
Various units in a business will focus on different performance metrics.
Examples of business metrics
Metrics can be categorized by the area of business they pertain to. Some of these metrics overlap or could fall into more than one category.
An example of a key business metric that applies to most businesses is sales revenue. In a B2C context, sales revenue is the income generated from all customer purchases minus the cost of returned or undeliverable items. Sales revenue is tied to such factors as advertising campaigns, price changes and seasonal changes.
Other important metrics include the following:
Sales metrics
- Sales cycle length is the amount of time it takes for a customer to move from the beginning stage to the end stage of a purchase process or a deal. This metric can help sales teams remove obstacles that get in the way of efficient processes.
- Average selling price is the average dollar amount made from each sale or transaction.
- Average profit margin is calculated by dividing net income by net sales. A stable or increasing average profit margin over time is a good indicator of a successful business. The average profit margin differs from the net profit margin, which is all expenses, including interest and taxes, subtracted from revenue.
- Average purchase value is the average value of each transaction processed. This metric helps with developing revenue projections and forecasting.
Financial metrics
- Monthly profit or loss is a measure of revenue less fixed and variable operation costs paid regularly each month. These costs can include rent, insurance, mortgage payments, taxes, salaries and utilities.
- Overhead costs refer to fixed costs -- such as salaries and rents -- that do not depend on the level of goods or services the business produces. Overhead costs generally are not affected by how much a business earns or grows, so they must be tracked separately.
- Size of gross margin is calculated by a company's total sales revenue minus its cost of goods sold, divided by the total sales revenue and then converted into a percentage. The higher the gross margin, the more money an organization keeps on each dollar of sales to service its other costs and potentially yield higher profits. Companies track margins to improve efficiency and find opportunities to lower costs, thereby increasing their margins.
Marketing metrics
- Conversion rate measures the percentage of potential customers, such as website visitors, that make a purchase or take some other action that benefits a business. In the case of website visitors, this might mean engaging with a certain feature on the website. For potential customers, examples of desired actions include purchasing products or making service commitments. Conversion rates are calculated by dividing the number of customers that took an action by the total number of customers and multiplying the result by 100 to get the percentage.
- SEO metrics assess how well online content performs on search engines. Such metrics look at indicators such as keyword ranking, click-through rate, bounce rate and domain authority.
- Website traffic measures the number of visitors to a site or sessions it gets in a certain time period. Businesses often break out that data by the sources that drive visitors to their website and compare the sources to see which are directing the most traffic. Marketing teams may want to see organic traffic, referrals from other websites or social media, and back links from other websites.
Software as a service (SaaS) metrics
- Customer loyalty and retention is a SaaS metric that measures how companies attract customers, get them to buy something and keep buying. The goal is to develop long-term, profitable relationships to boost sales. Companies gather feedback from customers via surveys, direct feedback and other types of analysis to improve service offerings, customer satisfaction and loyalty and retention among the customer base.
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC) includes all activities pertaining to marketing and sales processes and campaigns. CAC is determined by dividing the total acquisition expense by the total new customers over a given period of time.
- Churn rate focuses on lost customers and the costs to acquire them. Churn rate is seen as a solid indicator of a rising cost of customer acquisition and a lowering of the average customer lifetime value.
- Session duration is the total amount of time users use a digital product or service.
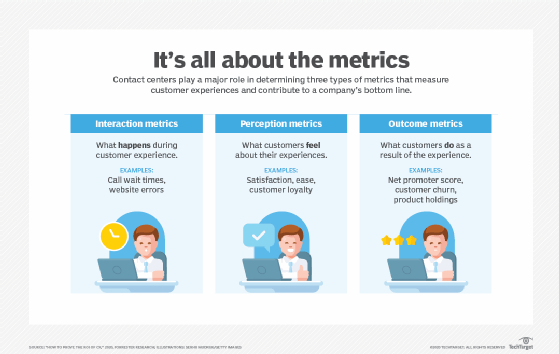
Business metrics used to assess contact center performance are a critical part of evaluating the customer experience.
Workforce metrics
- Time worked per process is a way of assessing how much labor costs a business on a per project or process basis. Calculating this metric is straightforward: Determine the minutes, hours or days spent on a process, making sure to subtract time taken for breaks or to work on other projects.
- Productivity ratios determine how productive a company's employees are. It is calculated by dividing a department's revenue by the number of its employees and comparing that number to industry benchmarks to gauge staff effectiveness. This metric can be applied to almost any aspect of the business.
- Employee engagement measures the positive emotional involvement an employee has with their organization that ultimately increases employee satisfaction. gamification platforms and enterprise social collaboration products can positively influence employee engagement, and can be used to measure it as well through passively collected data. Surveys are another common way to gather data on employee engagement.
- Employee retention rate measures how long employees stay at an organization on average. Employee experience and engagement are key factors related to retention.
Product performance metrics
- Inventory size is a count of the business's assets that are ready to sell or will be ready to sell at any given time. Businesses must constantly track inventory to account for how much product they have to sell. This metric is a key part of inventory management, because it is likely to represent a company's primary source of revenue.
- Variable cost percentage is a measure of one of the components of total cost -- the other is fixed costs. Variable costs include the items that will increase with each sale, such as the cost of raw materials, labor, shipping and anything pertaining to the production or delivery of sold goods and services.
- Daily active user to monthly active user ratio is a measure of the frequency with which users engage with a product. The ratio represents the portion of users that engage with a product or service every single day. It is often abbreviated as DAU/MAU.On-time project delivery tracks the rate of on-time delivery of a project over time.
How do business metrics and key performance indicators compare?
Business metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are not the same. Some similarities and differences include the following:
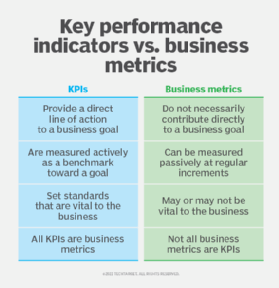
KPIs and business metrics are often considered similar, but they have different uses and business goals.
- Application. The key difference between business metrics and KPIs is how they apply to the business. A business metric often applies broadly across a business; KPIs target certain areas or departments.
- Orientation. Key business performance metrics focus on helping achieve a business goal with a tangible result or outcome. Conversely, business metrics don't need a target. A business metric is simply a measurement of performance that may or may not lead to an outcome.
- Timing. Business metrics are generally measured at regular intervals to mark performance. KPIs are often used as benchmarks on the way to achieving a goal, but they aren't necessarily measured at regular intervals.
- Overlap. Business metrics and KPIs are not mutually exclusive. A KPI can be a type of business metric that has a more specific, performance-oriented goal. They are metrics that directly contribute to the success or failure of a business.
Measuring page views is a useful marketing business metric to see how a particular marketing effort is contributing to performance. Although it has value, a measurement of page views alone is not a KPI because it does not relate directly to achieving a strategic business outcome.
Measuring organic search leads is a KPI because it is directly tied to a specific business outcome -- increasing revenue.
Choosing the right KPIs and business metrics can be tricky. Learn which metrics businesses using public clouds should track and some tools to use.
Continue Reading About business metric
- Ultimate guide to business intelligence in the enterprise
- 10 DevSecOps metrics that actually measure success
- How to create security metrics business leaders care about
- Data governance metrics: Data quality, data literacy and more
- Which data center KPIs are most useful?
 What is cost per sale (pay per sale)?
What is cost per sale (pay per sale)?  By: Katie Terrell Hanna
By: Katie Terrell Hanna  What are social media metrics?
What are social media metrics?  By: Paul Kirvan
By: Paul Kirvan  Customer success vs. account management: How do they differ?
Customer success vs. account management: How do they differ?  By: Tim Murphy
By: Tim Murphy  What is days sales outstanding (DSO)?
What is days sales outstanding (DSO)?