What is a cloud contact center? (original) (raw)
A cloud contact center is an internet-hosted service, typically managed by a third party, that handles all inbound and outbound customer communications for an organization.
Cloud contact centers eliminate the need for an organization to have its own on-premises software, hardware and infrastructure. This makes them more cost-effective than using a traditionally hosted contact center.
A cloud contact center platform includes core call center functionality, such as call routing and reporting. It also includes routing of other transactions from digital channels -- such as email and text messages -- workforce optimization tools and chatbots.
The primary benefit of cloud-based systems is their flexibility in terms of enabling remote work, scalable infrastructure and integration of multiple communication channels -- all without needing on-premises infrastructure. Customer service organizations also have easy access to technology, enabling a better customer experience (CX).
Cloud contact centers are also similar in concept to contact center as a service (CCaaS). A cloud contact center refers to any contact center hosted on cloud infrastructure. CCaaS, on the other hand, is a specific implementation of a cloud contact center. The term CCaaS typically characterizes a cloud contact center based on a subscription model that's hosted by a third party. In CCaaS, customers can lease hardware assets from a provider instead of owning the hardware themselves.
What is an omnichannel cloud contact center?
Omnichannel refers to a fully integrated approach to customer service, where all communication channels are interconnected. These channels often include communication avenues such as phone, text, email, social media and web or application-based chats. The omnichannel approach emphasizes integrating these channels so contact center agents can interact with customers across different channels using a single platform.
Cloud contact centers typically provide an omnichannel approach. They operate as a centralized communication hub where agents can access and respond to customer inquiries across different channels.
Customers might not use a single-channel approach when interacting with an organization. They might start a phone call and move to a mobile app during an interaction, for example. The transition between channels for the customer and customer data should be smooth and consistent, which is how omnichannel approaches help.
Features of cloud contact centers
The following key features of a cloud platform make it an attractive option for many customer service organizations:
- Advanced contact routing. This routes customer inquiries -- regardless of the channel used -- to the appropriate agent.
- Reporting. Real-time dashboards and after-the-fact reporting monitor and evaluate contact center operations.
- Integrated voice response. This helps route calls to appropriately skilled agents, provides important messages to callers and supports self-service functionality.
- Workforce optimization. This provides add-on modules that enhance the contact center's operation, including workforce management, quality monitoring and gamification.
- Speech analytics. This analyzes voice interactions to perform a root cause analysis of phone calls, provide additional quality monitoring and identify calls with specific attributes, such as an upset caller.
- Omnichannel support. This provides unified customer interactions through multiple channels.
Key benefits of a cloud-based contact center
There are several benefits of moving to a cloud contact center. Many enhance CX, improve agent productivity, reduce internal resource requirements as well as offer organizations the following benefits.
Simpler infrastructure and lower upfront costs
Organizations require less infrastructure, making it a cost-saving measure. There's no need to purchase any specific hardware, software or other infrastructure to get the system up and running. All that's needed is internet connectivity and adequate bandwidth. Instead of an upfront investment, organizations pay a monthly service fee for the specific features they want to use in the cloud environment.
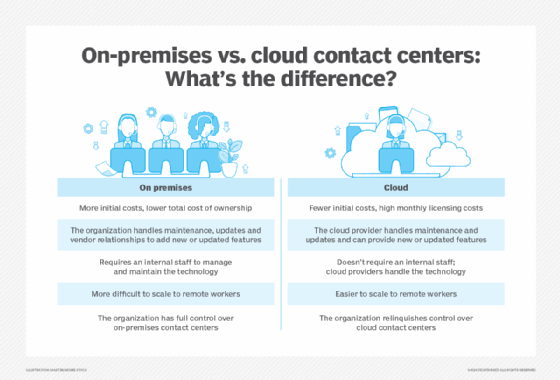
Cloud contact centers are hosted and managed by a third party whereas on-premises contact centers require the hosting organization to maintain the infrastructure.
Embedded multichannel capabilities
Organizations should have an easier transition evolving from a call center to a contact center. Cloud providers have integrated various communications -- such as voice, email, chat and social media -- into their platforms. This enables customers to interact with customer service organizations via the channel of their choice.
In an on-premises environment, channels can be added but could require a software upgrade or integration.
Improved scalability and pay-per-use pricing model
In a cloud environment, contact centers only pay for the resources they use and can scale more easily.
Many organizations can become seasonally busy and traffic can be slow at other times. The ability of organizations to increase or decrease the number of agents is essential. It saves businesses money and can encourage them to improve self-service methods.
Access to state-of-the-art features and capabilities
Organizations have access to new technology as it becomes available on the platform.
Cloud providers are constantly adding new technology to their platforms. This enables contact centers to test these features and capabilities without needing a new vendor to provide the specific feature or capability.
Simpler upgrade process
Organizations that use a cloud platform pay a monthly service fee and receive software upgrades as part of their ongoing service. Upgrades are continuously performed by the cloud vendor with little -- if any -- interruption to service.
In an on-premises environment, upgrades must be scheduled and aren't always included in the license maintenance costs.
Easier remote work
Contact center employees can log in remotely via a browser and perform their work as if they were in the office. The key requirements are having a strong internet connection and the required bandwidth.
Management of critical functions that aren't core competencies
In a cloud environment, the vendor handles many functions that might not be a core competency or function that an organization wants to perform. These functions include items such as system maintenance, business continuity and software support. As a result, there's a reduced need for IT resources and other specialized functions.
Cloud vs. traditional contact centers
A traditional contact center is typically hosted on premises by the organization using it. This means the organization must continually maintain the required infrastructure.
Cloud contact centers, by comparison, are hosted and maintained offsite by a separate provider through the internet. This saves the organization the costs associated with buying, installing and maintaining the infrastructure on premises. This also makes the contact center more scalable, as it can adjust its capacity based on demand.
Why is a cloud contact center important for businesses?
The availability of cloud technology doesn't make on-premises tools obsolete, as many organizations still want control of their systems and data. Others might have significant technology investments and could resist moving to a cloud system.
But, for organizations that must be nimble and continuously pivot to respond to ever-changing customer needs, a cloud system might be the way to go. Cloud contact centers provide the type of flexibility and simple access to advanced technologies that are necessary in this dynamic world.
Should businesses choose a cloud contact center over a cloud call center?
Much like a cloud contact center, a cloud call center is a call center that's hosted by a third party as an internet-hosted service. A cloud call center vendor handles all inbound and outbound customer calls for an organization.
When deciding between a cloud contact center or a cloud call center, the right choice depends on the organization's specific needs. Cloud call center agents focus on voice calls as their primary communication channel. This is ideal for smaller organizations that might not be able to afford the omnichannel functions of contact centers. Cloud call centers can also benefit organizations where phone calls are the predominant form of customer service interactions.
Cloud call centers typically feature call routing, interactive voice response, and call recording and monitoring tools.
Cloud contact centers, on the other hand, provide a more flexible omnichannel approach, which can lead to a better customer experience. They enable customers to interact with an organization through their preferred method and they're optimal for organizations that deal with complex customer inquiries. Cloud contact centers are ideal for businesses that expect growth in digital customer interactions. Contact centers can also typically integrate with customer relationship management (CRM) systems and other tools.
Examples of cloud contact center providers
Examples of cloud contact center vendors from the 2024 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Contact Center as a Service include the following:
- 8x8.
- Amazon Web Services.
- Cisco.
- Content Guru.
- Five9 Inc.
- Genesys Logic Inc.
- Nice Ltd.
- Talkdesk Inc.
- Vonage.
Choosing a cloud contact center vendor
Organizations that want to implement a cloud contact center must carefully consider which vendor matches their business needs, budget and has the features they want. Some key considerations include the following:
- Business needs assessment. Determine what communications channels the business needs, along with the volume of expected customer interactions.
- Features. Organizations must consider the features offered by each vendor. This includes omnichannel customer support, AI and automation, workforce management, CRM integration, skills-based routing, and call recording and monitoring.
- Pricing. Cloud contact center vendors often offer different pricing models, such as a pay-as-you-go, per-user or hybrid model. Consider the upfront and long-term costs of each and if there are any hidden costs associated with each pricing model.
- Scalability. Consider if the vendor can add more agents, support more interactions or integrate communication channels as needed.
- Security and compliance. Ensure the vendor prioritizes data security and any local or regional compliance regulations. Cloud contact center vendors should also have disaster recovery plans in place.
- Support. Ensure the vendor can respond to requests in a timely and effective manner. Check any provided service-level agreements for guarantees on uptimes.
The cost of a cloud contact center
Cloud contact centers offer several different pricing models, which include the following:
- Pay-as-you-go. Charges are based on usage metrics such as the number of calls, minutes or interactions.
- Per-user. This pricing model charges a flat rate either per user or agent.
- Hybrid model. Charges are based on a combination of pay-as-you-go and per-user models. Some services are charged by usage, while others are subscription-based per user.
- Tiered. This model divides prices and features into individual tiers from which an organization can choose.
The different pricing models are designed to accommodate organizations' varying needs and budgets in terms of usage patterns, expected growth and features.
Each cloud contact center platform offers a specific payment model. Learn more about well-known contact center platforms.