What is inventory management? (original) (raw)
By
- Cameron Hashemi-Pour,
- Sarah Amsler, Senior Managing Editor
- Jim O'Donnell, Senior News Writer
Published: Jul 24, 2024
Inventory management is the component of supply chain management that tracks and supervises noncapitalized assets -- or inventory -- and stock items. Inventory management systems oversee the flow of goods from manufacturers to warehouses and from these facilities to the point of sale (POS). A key function of these systems is to keep a detailed record of each new or returned product as it enters or leaves a warehouse or POS.
Organizations from small to large businesses can make use of inventory management to track the flow of goods and inventory turnover. There are numerous inventory management techniques that enable businesses to deliver the right amount of the correct product to the right place on time.
Inventory control is a separate area of inventory management. It focuses on minimizing the total cost of inventory, while maximizing the ability to provide customers with products in a timely manner. In some countries, the two terms are used synonymously.
Why is inventory management important?
Effective inventory management lets businesses balance the amount of inventory they have coming in and going out. The better a business controls its inventory, the more money it can save in business operations.
A business that has too much stock has what's referred to as overstock. Overstocked businesses have money tied up in inventory, limiting cash flow, increasing holding costs and potentially creating a budget deficit. This overstocked inventory, which is also called dead stock, often sits in storage, unable to be sold and eating into the business's profit margin.
But, if a business doesn't have enough inventory, it can result in shortages that negatively affect customer service. Lack of inventory causes delays in responding to customer orders and can result in lost sales. Customers are apt to look elsewhere when told a product isn't in stock and has to be back-ordered.
An inventory management system can help businesses strike the balance between being under- and overstocked for optimal efficiency and profitability.
Key benefits of inventory management
The key benefits of inventory management include the following:
- Reduced costs. There are upfront costs of setting up inventory management systems, processes and software. However, those are outweighed in the long run by lower costs from having the right amounts of inventory on hand and more efficient storage.
- Insight into future trends. Inventory management systems give organizations the tools to analyze sales and predict future trends and customer needs.
- Customer satisfaction. Inventory, transport and delivery tracking are all capabilities of inventory management systems. They result in timely transactions and improved customer experience.
- Optimized storage. Order management is a key part of tracking inventory and identifying products are in danger of spoiling, becoming obsolete or being insufficiently stocked.
- Real-time inventory count. Inventory management software, especially with advanced tracking capabilities that rely on radio frequency identification tags and internet of things (IoT) devices to track goods, can give supply chain and logistics managers real-time data on goods in transit.
- Supply chain relationships. Organizations can establish relationships with suppliers and shippers to keep inventory management running smoothly.
Key challenges of inventory management
Inventory management systems create potential challenges, such as the following:
- Short-term setup costs. These systems come with initial investment and startup costs. These can be especially difficult for small and midsize businesses to handle.
- Data errors. Traditional inventory management software typically involves manual data collection and entry, which can lead to mistakes and inconsistencies.
- Integration complexities. Inventory management platforms must be connected to other existing systems, such as sales and customer relationship management applications, to collect data from them. This often involves complex configurations and requires advanced expertise.
- Large inventories and storage locations. The sheer size of warehouses and other storage locations can make it difficult to sift through products to find what is needed at a given time or even know how much of a product is available.
- Training and user adoption. Training employees to work with the multiple tasks involved in using an advanced inventory management system can be difficult, and users aren't always happy to have to learn a new system.
The inventory management process
Inventory management is a complex process, particularly for larger organizations. However, the steps are essentially the same, regardless of the type or size of organization:
- Delivery. The process starts with goods -- typically raw materials or components -- being delivered to a warehouse receiving area. If the business is a wholesale distributor, the goods delivered are finished products, rather than raw materials or components.
- Storage. Once delivered, raw materials, components or finished products are put in storage. Large organizations typically have more physical space to store raw material and component inventory. Small companies might not have a receiving area, and the goods go directly to stock storage.
- Production. Once they're received and stored, raw materials are pulled from the stock areas as needed and moved to production facilities, where they are made into finished goods.
- Restocking. The finished goods are returned to stock areas where they're held prior to shipment, or they may be shipped directly to customers.
Inventory management uses a variety of data to keep track of the goods as they move through the process, including lot numbers, serial numbers, cost of goods, quantity of goods and the dates when they move through the process.
Inventory management systems
The first inventory management systems were simple spreadsheets that tracked the quantities of goods in a warehouse. They have become more complex systems that go several layers deep and integrate with accounting and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
The systems keep track of goods in inventory, sometimes across several warehousing locations. Inventory management software is used for various functions, such as calculating costs -- often in multiple currencies -- so the organization always has an accurate assessment of the value of the goods and tracking quantities of raw materials and products. These systems also integrate with and pull inventory data from several other systems across the enterprise, such as purchasing, sales, accounting and production systems.
Some inventory management software systems are designed to streamline inventory tracking for large enterprises and can be customized for the requirements and types of inventory an organization uses. Large systems were traditionally run on premises but are now also deployed in public cloud, private cloud and hybrid cloud environments. Small and midsize companies typically don't need such complex and costly systems. They often rely on standalone inventory management products, generally through software-as-a-service applications.
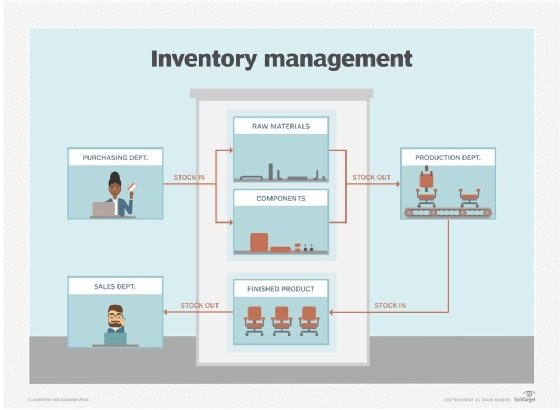
Inventory management software helps businesses track inventory so purchasing departments know what they need to order and sales teams know what is available to sell.
Inventory management techniques
Good inventory management can be achieved with any of several methodologies to keep the right amount of products on hand to fulfill customer demand and operate profitably. This task is particularly complex when organizations must deal with thousands of stock-keeping units that can span multiple warehouses.
Inventory management methodologies include the following:
- Stock review. This is the simplest inventory management methodology and is generally more appealing to smaller businesses. Stock review involves a regular analysis of stock on hand versus projected future needs. It often requires manual data entry, although these systems can be automated. An accurate stock review approach requires that minimum stock levels be defined. Regular inspections determine if stock is below the minimum level or about to go below so supplies can be reordered to meet the minimum levels. Stock review can provide a measure of control over the inventory management process, but it can be labor-intensive and prone to errors.
- Just in time (JIT). Raw materials or components arrive as customers order the finished goods. This method is based on analyzing customer behavior, researching buying patterns, and determining seasonal demand and location-based factors to get an accurate picture of which goods are needed at certain times and places. The advantage of JIT is that customer demand is met in near-real time without needing to keep large quantities of products, raw materials or components on hand. However, it's easy to misread market demand or run into distribution problems with suppliers, which can lead to out-of-stock issues.
- ABC analysis. This approach classifies inventory into three categories that represent the inventory value and quantity of the goods. Category A represents high-value and low-quantity goods, category B represents moderate-value and moderate-quantity goods, and category C represents low-value and high-quantity goods. Inventory management systems manage each category separately. With ABC analysis, it's important to know which items are best sellers in order to keep enough buffer stock on hand. For example, more expensive category A items might take longer to sell, but they don't need to be kept in large quantities. One of the advantages of ABC analysis is that it provides better control over high-value goods. A disadvantage is that it can require considerable resources to continually analyze the inventory levels of all the categories.
- Economic order quantity (EOQ). A formula determines the optimal time to reorder inventory in a warehouse management system. The goal with the EOQ method is to identify the largest number of products to order at any given time. This frees up money that is otherwise tied up in excess inventory and minimizes costs.
- Minimum order quantity (MOQ). The smallest amount of product a supplier is willing to sell is determined. If a business can't purchase the minimum, the supplier doesn't sell it to them. The MOQ method benefits suppliers, letting them quickly get rid of inventory, while weeding out bargain shoppers.
- First in, first out (FIFO). The oldest inventory is sold first to help keep inventory fresh. FIFO is an especially important method for businesses dealing with perishable products that spoil if they aren't sold within a specific time period. It also prevents items from becoming obsolete before a business has the chance to sell them. This typically means keeping older merchandise at the front of shelves and moving new items to the back.
- Last in, first out (LIFO). The newest inventory is typically recorded as sold first. LIFO is a good practice when inflation is an issue, and prices are rising. Because the newest inventory has the highest cost of production, selling it before older inventory means lower profits and less taxable income. LIFO also means the lower cost of older products left on the shelves is what's reported as inventory. However, this is a difficult technique to put into practice, as older items that sit around have a chance of becoming obsolete or spoiled.
- Safety stock. A business sets aside inventory in case of an emergency. The safety stock approach also provides a signal that it's time to reorder merchandise before dipping into the safety stock. It's a good idea for businesses to work safety stock into their warehouse management strategy in case of events that cause supply chain disruptions.
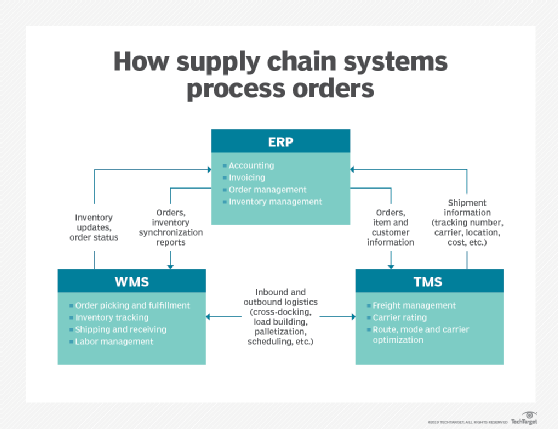
An ERP system coordinates with warehouse management systems and transportation management systems to initiate and track orders, manage inventory and perform accounting functions.
Red flags indicating inventory management issues
When an organization is facing the following issues, they should consider reassessing their inventory management strategies and refining them where needed:
- Frequently incorrect stock amounts. When over- and understocking are no longer just an occasional inconvenience but a regular occurrence, that is a sure sign something is wrong.
- Out-of-date data. An inventory system that isn't based on real-time data is static and becomes quickly outdated. Today's technologies, such as IoT and artificial intelligence (AI), facilitate real-time data collection and analysis.
- Subpar order fulfillment rates. Establishing and analyzing metrics, such as order fulfillment rates, should be a key component of an organization's inventory management process. If those rates fall below a set threshold, it's time to revisit the inventory management strategy.
- Frequent disruptions. When an organization's inventory management processes don't rebound quickly from a warehouse or supply chain disruption, such as equipment failures, it's time to reassess the system.
Both inventory management and inventory control are essential to running a successful direct sales and channel operation. Inventory management is the overall strategy to ensure adequate inventory. Inventory control encompasses the processes and tools used to track existing inventory. Businesses can choose to use an inventory control system on its own, but they are likely to benefit from using both together.
Inventory management
Proper inventory management is a strategy that ensures businesses always have the right amount of inventory at the right time and in the right place. Inventory management tools enable businesses to do the following:
- Calculate safety stock.
- Calculate reorder points.
- Do demand planning and demand forecasting.
- Identify obsolete items.
- Optimize a warehouse layout.
- Identify fill rate percentage.
Inventory control
Inventory control addresses inventory already in a business's possession. It works at the transactional layer of an ERP system and helps businesses do the following:
- Receive inventory.
- Process interbranch transfers.
- Process receipts.
- Pack and ship stock.
- Process customer invoices.
- Process supplier purchase orders.
Examples of inventory management
Examples of inventory management can be found in various industries:
- Retail. A retail chain that sells toys must regularly monitor stock levels of specific toys in warehouses, fulfillment centers and brick-and-mortar stores. Employees use software platforms that track inventory, production, customer orders, shipping and sales data to predict future trends.
- Manufacturing. Procuring raw materials needed to make a product, such as a new car model, is the first step in inventory management at a manufacturing plant. The next step is tracking how much of these materials are used. Finally, the inventory management system helps the manufacturer ensure the right number of cars is produced to meet consumer demand.
- Logistics. A trucking company might use inventory management tracking software and bills of lading to ensure goods are successfully transported to distributors and buyers. Blockchain technology is used to create chains of transactions and document the flow of goods. The different milestones during a typical product delivery -- a finished product leaving a warehouse, being shipped via truck and, ultimately, reaching a buyer -- can be easily tracked with these tools.
Future of inventory management
Industry experts expect a number of future trends to develop:
- Automation. Industry 4.0 technologies, such as AI, machine learning algorithms, IoT, industrial IoT and blockchain, are starting to be used in inventory management to analyze customer data and make predictions. These trends will lead to more advanced inventory software with more automation, letting companies move away from error-prone, manual data entry.
- Lower costs. As AI and machine learning become more widespread, the cost of obtaining this software will decrease. This will make advanced inventory management capabilities available to more companies, including small businesses.
- Advanced AI capabilities. As the retail and manufacturing landscapes become more competitive, advanced capabilities made possible through AI will become more widespread as well. Demand sensing is one such capability. An AI-powered inventory management platform can analyze historical purchase data and economic indicators to proactively sense what goods and services will be in demand to guide inventory strategies.
- Sustainability. Inventory management platforms are also being used for the optimization of sustainability efforts. They will help improve various aspects of operations to enable more recycling and waste reduction.
The use of Industry 4.0 tech in retail, logistics and manufacturing is expanding. Learn about the benefits of AI and other Industry 4.0 tech.
Continue Reading About What is inventory management?
- WMS vs. OMS: Learn the differences between the two systems
- ERP vs. WMS: Which one is right for you?
- Benefits of RFID in supply chain management and logistics
- Why asset management software is more important than ever
- Advantages of using inventory management software
 7 best practices for inventory management
7 best practices for inventory management  By: Paul Maplesden
By: Paul Maplesden  5 important inventory management software features: A list
5 important inventory management software features: A list  By: Reda Chouffani
By: Reda Chouffani  20 common problems with inventory management
20 common problems with inventory management  vendor-managed inventory (VMI)
vendor-managed inventory (VMI)  By: Rahul Awati
By: Rahul Awati