composable infrastructure (original) (raw)
Composable infrastructure is a framework that decouples device resources in order to treat them as services. Physical compute, storage and network fabrics are examples of device resources that can be treated as services.
Benefits of composable infrastructure
The goal of a composable infrastructure is to enable an enterprise data center to use its physical infrastructure in a more cost-effective manner by reducing waste, while reducing the time it takes to deploy a new application. With composable infrastructure, IT administrators don't need to be concerned about the physical location of infrastructure components or physically configure hardware to support specific software applications.
Several vendors, including HP Enterprise and Cisco, have promoted composable infrastructure as a way for internal IT departments to provision workloads as quickly and efficiently as public Cloud services providers, while maintaining control over the infrastructure that supports mission-critical applications in a private cloud setting. In 2018, HPE bought Plexxi, a software-defined networking (SDN) vendor, and eventually developed a composable cloud platform. Dell EMC also developed its own composable infrastructure system, which it refers to as kinetic infrastructure.
The concept of pooling physical infrastructure resources and building infrastructure logically is supported by the popularity of SDN, object storage, converged infrastructure and DevOps.
How composable infrastructure works
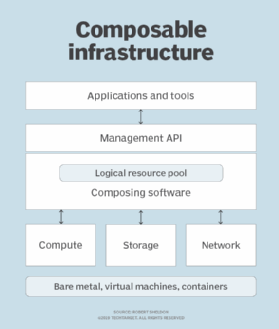
In a composable infrastructure, resources are logically pooled so that administrators don't have to physically configure hardware to support a specific software application. Instead, developers define the application's requirements for physical infrastructure using policies and service profiles. The software then uses application program interface (API) calls to create -- or compose -- the infrastructure it needs to run on bare metal, as a virtual machine or as a container.
A framework defines what the individual objects of composure are, and each object exposes information about itself through a management API. When a software application requests infrastructure to run, available services are located through an automated discovery process, and resources are allocated on demand. When an infrastructure resource is no longer required, it is reappropriated so that it can be allocated to another application.
Standards for composable infrastructure
Because there is no industry standard for deploying a composable infrastructure, individual vendors must determine how to deploy -- or even define -- the infrastructure. Alternate names for composable infrastructure include programmable infrastructure, intelligent infrastructure, software-defined infrastructure, infrastructure as code, decoupled infrastructure and hardware disaggregation.
The lack of standards for composable infrastructure limits the technology's potential. Composable infrastructure should, in theory, be able to support commercial off-the-shelf hardware across multiple locations, but such flexibility is still a long way off. Consequently, there is a higher risk of vendor lock-in.
This was last updated in November 2022
Continue Reading About composable infrastructure
- Everything you need to know about composable infrastructure
- Emerging approaches to HCI for IT services
- Composable infrastructure providers tackle modern workloads
- Composable disaggregated infrastructure right for advanced workloads
- How composable disaggregated infrastructure works
Dig Deeper on Systems automation and orchestration
-
 Composable infrastructure providers tackle modern workloads
Composable infrastructure providers tackle modern workloads  By: Robert Sheldon
By: Robert Sheldon -
 The ephemeral composable stack - Couchbase: all board the unified control plane
The ephemeral composable stack - Couchbase: all board the unified control plane  By: Adrian Bridgwater
By: Adrian Bridgwater -
 How HPE OneView composes, manages Synergy infrastructure
How HPE OneView composes, manages Synergy infrastructure  By: Robert Sheldon
By: Robert Sheldon -
 The state of data center convergence: Past, present and future
The state of data center convergence: Past, present and future  By: Robert Sheldon
By: Robert Sheldon