Build a successful Apache Mesos installation on Linux servers (original) (raw)
Apache Mesos is an open source cluster management tool that abstracts and isolates resources within distributed IT environments. Enterprises use Mesos with, or as an alternative to, Kubernetes for container orchestration in large-scale deployments.
Mesos has a master-agent architecture, in which a master daemon manages agent daemons that run on a cluster node. In this tutorial for Apache Mesos installation, we set up a master on one server and an agent on a second -- but it is possible to run both on one machine. There is no difference in procedure; the only difference is where the master is located when you start the agent.
Readers should expect the build process -- compiling and linking the components of Apache Mesos -- to take about one hour on a two-core machine with 8 GB of memory.
First, avoid these pitfalls
Close any servers and end any running tasks on your machine before you begin compiling the Apache Mesos installation. This process can take 100% of the memory and prevent even SSH login attempts.
All commands must execute via the sudo command, which enables you to act as the administrative root user.
Test frameworks are not critical: It's a complicated process to write a Mesos test framework, and a regular user is unlikely to need one. Instead, IT admins are more likely to use a Mesos framework developed by an established vendor such as Hadoop, Spark or Cassandra.
Apache Mesos installation setup and prerequisites
Mesos runs on most Linux distributions, MacOS and Windows. This tutorial uses Ubuntu 16.04; installation instructions differ for MacOS and Windows.
Open firewall port 5050 on both the master and agent daemons. If you don't have the necessary permissions for that port, use a port that is normally open -- an online port scanner can check for those.
Run all the commands below. If you already have JDK 1.8, skip the step to install the Java development kit, in line two. Check for JDK 1.8 with the java -v command.
sudo apt-get install -y tar wget git
sudo apt-get install -y openjdk-8-jdk
sudo apt-get install -y autoconf libtool
sudo apt-get -y install build-essential python-dev python-six python-virtualenv libcurl4-nss-dev libsasl2-dev libsasl2-modules maven libapr1-dev libsvn-dev zlib1g-dev iputils-ping
Now download and unzip the Apache Mesos installation files. Store these files in the /usr/share folder, which is available to all users.
cd /usr/share/
sudo mkdir mesos
sudo wget http://www.apache.org/dist/mesos/1.7.2/mesos-1.7.2.tar.gz
sudo tar -zxf mesos-1.7.2.tar.gz
cd /usr/share/mesos/mesos-1.7.2
Build the software
You will need to build -- compile and link -- the software. Users can download a binary distribution, but at time of publication, the version number is several iterations behind what is available.
The simple build command, make, starts up the master and agent processes, and the following code should work: Installing the test frameworks that Mesos provides in Python and Java will probably fail.
sudo mkdir build
cd build
../configure
sudo make
An option to speed up the Mesos installation is to use all of the available CPU on the machine and to turn off logging, by adding to the make command:
-j V=0
Install example frameworks
Apache Mesos does not run programs: It runs frameworks, which, in turn, run programs. Install the example frameworks. It will take about an hour to run.
sudo make check
Start Mesos
Complete the installation by starting up the cluster orchestrator. Use an IP address that is accessible from the internet to use a cloud provider and the browser interface: For example, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud usually uses a 172.* address. Amazon networking uses network address translation to expose internal networks to the internet. Don't use the loopback interface 127.0.0.1, as that only works locally.
The next step in this Apache Mesos installation is to start the master daemon:
cd /usr/share/mesos/mesos-1.7.2/build/bin
sudo ./mesos-master.sh --ip=172.31.47.43 --work_dir=/var/lib/mesos
And then start the agent. This step can be done as many times as there are available agents. For a two-server setup, you could install the agent on both the operator server and the master to better emulate a cluster. Agent installation is exactly the same as that for the master, but starts a different program. To start the agent, assign to it the master's IP address and default port, 5050:
cd /usr/share/mesos/mesos-1.7.2/build/bin
sudo ./mesos-master.sh --hostname=(public domain name of you server) --ip=(ip address on your internal network) --work_dir=/var/lib/mesos
Open the browser via the public IP address, for example: http://ec2-35-180-230-169.eu-west-3.compute.amazonaws.com:5050/#/
The browser dashboard displays all agents' statuses; here, one agent is running, and zero tasks are ongoing.
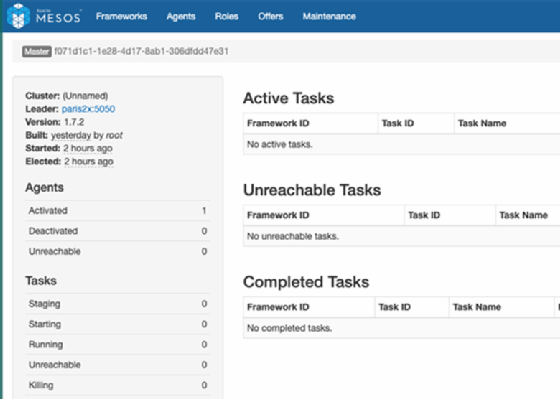
View status reports in the Mesos browser dashboard.
Test the framework
To test your Apache Mesos installation, configure it to run with a cluster-computing framework, such as Apache Spark. Or run any of the three commands listed below, which will configure the build as well, but they work only if the make check command returns a clean compile. The Python example requires Python version 2.7. Spark escapes that concern.
./src/test-framework --master=127.0.0.1:5050
./src/examples/java/test-framework 127.0.0.1:5050
python test_framework.py 172.31.47.43:5050
Establish high availability
High availability enables more than one copy of the master to run so that the system continues to work if a single master fails.
To set up Mesos in high availability mode, first run Apache ZooKeeper, a centralized service for distributed applications that helps maintain configuration information, synchronization and other operational aspects. Then start the masters and agents with the --zk argument: --zk=zk://host1:port1,host2:port2. This command alerts Mesos to the other master instances.