What is a URL (Uniform Resource Locator)? (original) (raw)
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator, also called a web address) is a unique identifier used to locate a resource on the internet. URLs consist of multiple parts -- including a protocol and domain name -- that tell web browsers how and where to retrieve a resource.
End users use URLs by typing them directly into a browser address bar or by clicking a hyperlink found on a webpage, bookmark list, email or another application.
How is a URL structured?
The URL contains the name of the protocol needed to access a resource, as well as a resource name. The first part of a URL identifies what protocol to use as the primary access medium. The second part identifies the IP address or domain name -- and possibly subdomain -- where the resource is located.
URL protocols include HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (HTTP Secure) for web resources, mailto for email addresses, FTP for files on a File Transfer Protocol server and telnet for a session to access remote computers. A colon and two forward slashes follow most URL protocols, but only a colon follows the mailto protocol.
URLs can also specify the following optional information after the domain:
- A path to a specific page or file within a domain.
- A network port to use to make the connection.
- A specific reference point within a file, such as a named anchor in an HTML file.
- A query or search parameters used -- commonly found in URLs for search results.
Importance of URL design
URLs can only be sent over the internet using the ASCII character set. Because URLs often contain non-ASCII characters, the URL must convert into a valid ASCII format. URL encoding replaces unsafe ASCII characters with a percent sign (%) followed by two hexadecimal digits. URLs cannot contain spaces.
URL examples
When designing URLs, there are different theories about how to make the syntax most usable for readers and archivists. For example, the URL's path can include dates, authors and topics in a section referred to as the slug. Consider the URL for this definition:
https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/URL
Look past the HTTPS protocol and the permalink (www.techtarget.com). The file includes two paths (searchnetworking and definition) and the definition title (URL). Though not present in this example, some URL designers choose to add the date of the post, usually as YYYY/MM/DD.
Parts of a URL
Using the URL https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/search/query?q=URL as an example, components of a URL can include the following:
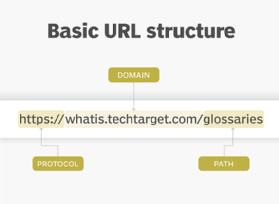
- The protocol or scheme. This is used to access a resource on the internet. Protocols include http, https, ftps, mailto and file. The domain name system name reaches the resource. In this example, the protocol is https.
- Host name or domain name. This is the unique reference that represents a webpage. For this example, it is techtarget.com.
- Subdomain. This precedes the main domain name. In this case, "www" denotes the Word Wide Web. Other subdomain options include "blog," "mail" and "support."
- Port name. These usually aren't visible in URLs, but they're necessary. Ports 80 and 443 are the default ports for web servers, but there are other options. In a URL, ports always follow a colon. For this example, https://www.techtarget.com:443.
- Path. A path refers to a file or location on the web server. For this example, the path is whatis/search/query.
- Query. Found in the URL of dynamic pages, the query consists of a question mark, followed by parameters or the query string. In this example, "?" marks the beginning of the query.
- Parameters. These are pieces of information in a query string of a URL. Multiple parameters can be separated by ampersands (&). In this example, the parameter is "q=URL."
- Fragment. This is an internal page reference, which refers to a section within the webpage. It appears at the end of a URL and begins with a pound sign (#). Although not in the example above, an example could be #history in the URL https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet#History.
Other examples of parts of a URL can include the following:
- The URL mailto:[email protected] initiates a new email addressed to the mailbox "president" in the whitehouse.gov domain.
- The URL ftp://www.companyname.com/whitepapers/widgets.ps specifies FTP use to download a file.
HTTP vs. HTTPS
Computers use both HTTP and HTTPS to retrieve data from web servers to view content in a browser. One difference between them is that HTTPS uses a Secure Sockets Layer certificate to encrypt the end-user and server connection. Another difference is that HTTPS uses TCP/IP port number 443 by default, whereas HTTP uses port 80.
HTTPS is vital to protecting sensitive information -- such as passwords, credit card numbers and identity data -- from unauthorized access.
URL vs. URI
Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) are strings of characters used to identify a resource over a network. A URL is the most common type of URI. URLs are essential to navigating the internet.
URL shorteners
URL shortening is a technique to make a URL substantially shorter in length and still direct to the required page. Shorteners use a redirect on a domain name that is short to achieve this.
Many URL shortener services are available. While many are free, those that offer additional capabilities, such as web analytics, cost money. Companies offering URL shorteners include Rebrandly, Bitly, Short.io, TinyURL and Bl.ink.
Some website hosts, such as GoDaddy.com, offer URL shorteners. Other service providers, including search engines, might not offer URL shorteners. This is because they are often subject to abuse by spammers hiding malware inside shortened URLs.
URL history
Data retention related to web usage is a huge privacy concern. Recently, public demand increased for search engine and application service providers to be transparent in what information they collect, retain and sell.
For example, Google Chrome's privacy policy notes that in basic browser mode, the search engine stores information locally on the system. This information includes browsing history and URLs of pages visited. It also stores a cache of text, images and other resources from those pages.
Google also collects and retains data for various lengths of time. Users can delete some data whenever they want. However, Google deletes some data automatically and retains other data for longer periods of time when necessary.
Editor's note: This definition was updated to improve the reader experience.
This was last updated in August 2024
Continue Reading About What is a URL (Uniform Resource Locator)?
- Are long URLs better for security than short URLs?
- What is a vanity URL (vanity uniform resource locator)?
- Naming and addressing: URIs, URLs
 Top REST API URL naming convention standards
Top REST API URL naming convention standards  By: Raghu Karan Adapala
By: Raghu Karan Adapala  vanity URL (vanity uniform resource locator)
vanity URL (vanity uniform resource locator)  By: Robert Sheldon
By: Robert Sheldon  Secure Sockets Layer certificate (SSL certificate)
Secure Sockets Layer certificate (SSL certificate)  By: Rahul Awati
By: Rahul Awati  DNS over HTTPS (DoH)
DNS over HTTPS (DoH)  By: Brien Posey
By: Brien Posey