transceiver (original) (raw)
What is a transceiver?
A transceiver is a combination transmitter/receiver in a single package. While the term typically applies to wireless communications devices, it can also be used for transmitter/receiver devices in cable or optical fiber systems.
The main functionality of this electronic device is to transmit, as well as receive, different signals.
In local area networks, the transceiver is a part of the network interface card. It can both transmit signals over the network wire and detect electrical signals flowing through the wire. However, some types of networks require an external transceiver.
In wireless communication devices, like smartphones and cordless telephones, the transceiver is built into the mobile device.
What is the difference between a transmitter and a transceiver?
A transmitter is a separate electronic component that generates a radio frequency (RF) current or radio waves. These waves are used in communication systems to transfer data like audio, video, etc.
A transceiver, on the other hand, can both send and receive digital signals.
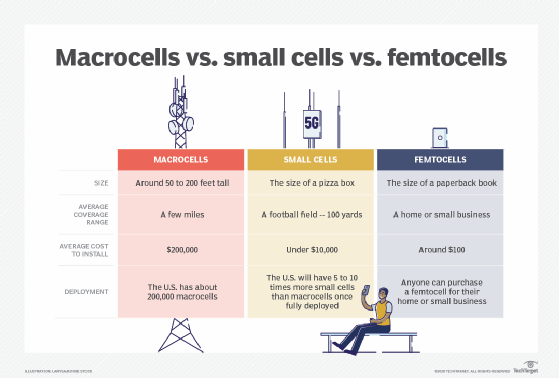
Macrocell, small cell and femtocell cellular base stations are fixed transceivers capable of sending and receiving wireless signals.
How does a radio transceiver work?
In radio communications, the transceiver can work in half-duplex or full-duplex mode:
- Half-duplex transceivers. It can either transmit or receive but not both at the same time. This is because both the transmitter and receiver are connected to the same antenna using an electronic switch. This mode is found in ham radios, walkie-talkies and other single-frequency
- Full-duplex transceivers. The radio transmitter and receiver can work in parallel. Transmission and reception take place on different radio frequencies. This mode is observed in handheld and mobile two-way radios.
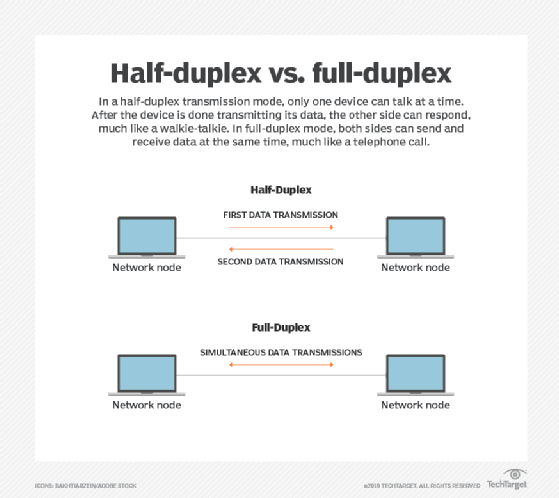
The difference between half-duplex and full-duplex data transmission
What role do transceivers play in a wireless communication network?
The role of a transceiver depends on its type. There are four types of transceivers used in wireless communication systems:
- RF transceivers are used in baseband modems and routers for analog (over the wire) and digital transmission. They are also used in satellite communications networks.
- Optical transceivers employ fiber optic transceiver technology to convert electronic signals into light signals. They are high-speed transmission devices.
- Ethernet transceivers are used to link electronic devices in Ethernet circuitry. They are also known as media access units.
- Wireless transceivers combine technology in Ethernet and RF transponders to improve Wi-Fi transmission speed.
Explore the differences among macrocell, small cell and femtocell base stations, or transceivers, as they relate to 5G cellular wireless communications in the video below.
This was last updated in September 2021
Continue Reading About transceiver
- What is the difference between WLAN and Wi-Fi?
- What's the difference between half-duplex and full-duplex?
- Macrocell vs. small cell vs. femtocell: A 5G introduction
- Prepare your organization for 100G data center Ethernet
 The pros and cons of optical wireless communication
The pros and cons of optical wireless communication  By: Venus Kohli
By: Venus Kohli  5G New Radio (NR)
5G New Radio (NR)  By: Alexander Gillis
By: Alexander Gillis  telecommunications (telecom)
telecommunications (telecom)  By: Wesley Chai
By: Wesley Chai  802.11
802.11  By: Garry Kranz
By: Garry Kranz