CISO (chief information security officer) (original) (raw)
The CISO (chief information security officer) is a senior-level executive responsible for developing and implementing an information security program, which includes procedures and policies designed to protect enterprise communications, systems and assets from both internal and external threats.
In an organization, the CISO ensures information resources and technologies are effectively protected. CISOs oversee the development, implementation and enforcement of security policies. The CISO might also work alongside the chief information officer to procure cybersecurity products and services and to manage disaster recovery and business continuity plans.
The chief information security officer might also be referred to as the chief security architect, the security manager, the corporate security officer or the information security manager, depending on the company's structure and existing titles. When the CISO is also responsible for the overall corporate security of the company -- which includes its employees and facilities -- they might simply be called the chief security officer.
What does a CISO do?
In addition to responding to data breaches and other security incidents, the CISO is tasked with anticipating, assessing and actively managing new and potential cyber threats. The CISO must work with other executives across different departments to align security initiatives with broader business objectives and mitigate the security risks various threats pose to the organization's mission and goals.
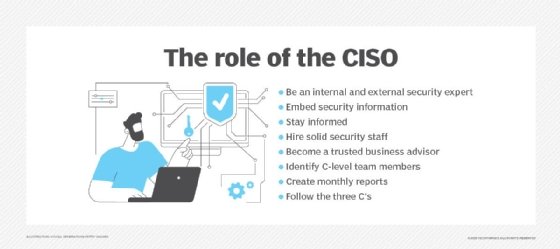
CISOs have a variety of roles and responsibilities surrounding an organization's security implementations.
The chief information security officer's roles and responsibilities include the following:
- Conducting employee security awareness training.
- Developing secure business and communication practices.
- Identifying security objectives and metrics.
- Choosing and purchasing security products from vendors.
- Ensuring that the company is in regulatory compliance with the rules of relevant bodies.
- Enforcing adherence to data security practices.
- Ensuring the company's data privacy is secure.
- Managing the computer security incident response team.
- Conducting electronic discovery and digital forensic investigations.
- Developing cyber resiliency and disaster recovery plans.
- Determining if security strategies are worth the investment financially.
CISO qualifications and certifications
A CISO is typically a skilled leader and manager with a strong understanding of IT and security, who can communicate complicated security concepts to both technical and nontechnical employees. CISOs also require experience in risk management and auditing.
Many companies require CISOs to have a bachelor's degree in cybersecurity or IT, and advanced degrees in business, computer science or engineering.
CISOs also typically have relevant certifications such as those from the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), International Information Systems Security Certification Consortium (ISC2) and the Computing Technology Industry Association (CompTIA). Some of these certifications include the following:
- ISACA Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA).
- ISACA Certified Information Security Manager (CISM).
- ISC2 Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
- ISC2 Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP).
- ISC2 Systems Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP)
- CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst Certification (CySA+).
- CompTIA Network Vulnerability Assessment Professional.
- CompTIA Network Security Professional.
- CompTIA Security Analytics Professional.
- CompTIA IT Operations Specialist.
CISO salary
The average salary in the U.S. for CISOs can vary depending on the group keeping metrics on it. The average range was between 149,000−149,000-149,000−240,000 per year in 2023.
For example, Glassdoor lists the average income for the CISO position in the U.S. in 2023 as 201,820peryear,whereasSalary.comcitestheaveragesalaryas201,820 per year, whereas Salary.com cites the average salary as 201,820peryear,whereasSalary.comcitestheaveragesalaryas241,243 per year. According to Glassdoor, CISOs can earn up to about $407,000 annually. The exact salary of a CISO varies due to several economic and personal factors, including location. Pay might change based on degrees possessed, certifications or time spent in the profession.
With economic uncertainties due to various aspects such as inflation, the growth of security budgets has slowed down in 2023. According to an article from Cybersecuritydive, CISO salaries are increasing, but those increases are slowing down -- stating that the CISO compensation for 2023 was up 11% but down 14% from 2022's average increase.
CISOs must meet the qualifications set out by companies to meet security expectations. Learn more about how to become a CISO.
This was last updated in December 2023
Continue Reading About CISO (chief information security officer)
- Ideal CISO reporting structure is to high-level business leaders
- As a new CISO, the first 100 days on the job are critical
- Reality check: CISO compensation packages run the gamut
- Which type of CISO are you? Company fit matters
- Why organisations need to harmonise their CIO and CISO roles
Dig Deeper on Careers and certifications
- Healthcare CISOs discuss the role's challenges at HIMSS event
 By: Jill McKeon
By: Jill McKeon -
 What are CPE (continuing professional education) credits?
What are CPE (continuing professional education) credits?  By: Rahul Awati
By: Rahul Awati - Cyber workforce must almost double to meet global talent need
 By: Clare McDonald
By: Clare McDonald -
 What a cybersecurity analyst does and how to become one
What a cybersecurity analyst does and how to become one  By: Andrew Froehlich
By: Andrew Froehlich