Pen testing guide: Types, steps, methodologies and frameworks (original) (raw)
Article 1 of 3
Part of: Introduction to penetration testing
Penetration testing helps organizations find security vulnerabilities before hackers do. Uncover details about pen testing steps, methodologies, frameworks and standards.
Penetration testing is a cybersecurity forensics technique used to assess an organization's network perimeter and internal cybersecurity defenses. It involves pen testers hacking into systems and determining where vulnerabilities and weaknesses exist.
The pen testing process not only identifies cybersecurity issues, but also offers recommendations to remediate those issues and verifies the fixes work. Pen tests can save companies thousands or even millions of dollars in lost revenue, ransomware payments and damage to their reputation.
6 steps in a pen test
Pen testing providers may have varying approaches to their tests. In general, the following six activities are involved in conducting a pen test:
- Prepare for the test. Use this phase to gather relevant information, secure approval from management and outline steps for the test.
- Construct a plan. Determine the tools needed to examine the state of the testing candidate. This includes evaluating how security is implemented and where vulnerabilities or alternate access methods may exist.
- Build a team. Gather the appropriate pen testers to conduct the test. In-house and third-party experts may be needed.
- Find the target. Decide what data and systems are being targeted.
- Perform penetration. Use a variety of techniques to bypass the target system's existing security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Establish a foothold position over designated systems and resources, all while trying to remain undetected. Extract data and other evidence for reports.
- Conduct data analysis and reporting. Examine and analyze the data collected during the pen test, and identify remediation steps. Summarize the results of the tests, including what vulnerabilities were detected and exploited and how to fix them, in a report for company management.
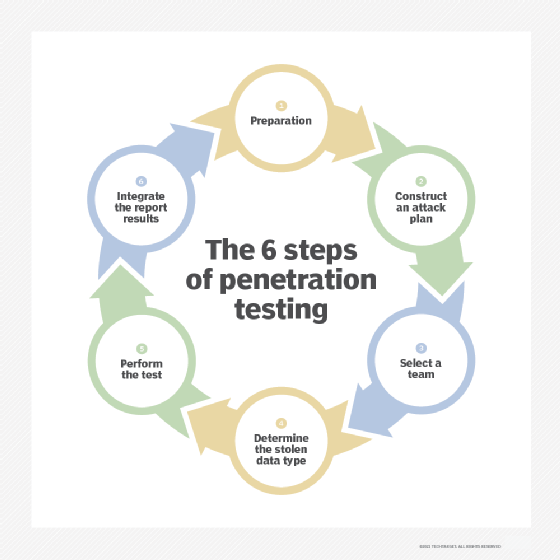
In general, pen tests include at least these six steps.
Types of pen tests and methodologies
There are three general levels of conducting a pen test:
- Black box testing simulates how an experienced threat actor would perform a hack. It starts with no knowledge or understanding of the target's technology infrastructure and security provisions. The goal of this test is to quickly identify easy-to-exploit vulnerabilities.
- Gray box testing takes a black box test a step further. Pen testers typically have some knowledge of the target's systems and security measures. The goal of a gray box test is to learn details about vulnerabilities that can be exploited to a greater level than black box assessments.
- White box testing is the most advanced. This pen test assumes the hacker has detailed knowledge of all aspects of an organization's technology and security infrastructure. White box testers are typically the most experienced pen testing experts. They are tasked with uncovering the tiniest flaws in the security infrastructure. When partnered with system developers and engineers, white box testers can jointly improve an organization's security.
Pen testing results can vary depending on what is tested, as well as whether or not the tester knows anything about the company and if the company knows the test is being conducted. Different kinds of tests include the following:
- External test. Information assets visible to outsiders, such as websites, apps, email and DNSes, are attacked in an attempt to extract data, perform transactions and other activities. The goal is to identify vulnerabilities by outside attack sources.
- Internal test. An internal attack aims to expose what damage could be done if an attacker is already inside the target system. This also covers malicious insiders. Careful screening may help identify employees who are likely to respond to social engineering or phishing attacks.
- Blind test. In this situation, the tester is permitted to obtain publicly available information about the target but has no inside information about the firm or its security resources. By contrast, the target company knows about the attack, including when and where it will occur, and can prepare accordingly. Testers must use all their skills to penetrate the target's defenses.
- Double-blind test. In this test, neither attacker nor target know in advance about the pen test. Testers must, therefore, rely on skills and available tools to achieve success. For the tester, success is penetrating the target's defenses. For the target company, success is preventing the attacker from penetrating its perimeter and defenses.
Pen testing frameworks and standards
Pen testing frameworks and standards provide a blueprint for planning, executing and reporting on cybersecurity vulnerability testing, in addition to activities that collectively provide methodologies for ensuring maximum security. The following are some popular pen testing frameworks and standards:
- Open Source Security Testing Methodology Manual (OSSTMM) provides a detailed approach to all aspects of vulnerability testing and assessment activities. OSSTMM does not advocate a specific approach; rather, it provides best practice guidance on how to achieve successful testing activities.
- NIST's Cybersecurity Framework and other standards, such as Special Publication 800-53A Rev. 5, offer guidance on pen testing and other assessment techniques.
- Penetration Testing Execution Standard (PTES) details all aspects of a pen test. A separate PTES technical guidelines document provides procedures for organizing and executing a pen test.
- OWASP provides detailed guidance on application security and pen testing planning and execution.
Pulling it all together in a pen test report
One of the most important aspects of a pen test is the report. It should be informative and actionable and include the following key points:
- The executive summary explains the purpose and scope of the test, its anticipated benefits and who requested the test.
- The statement of objectives outlines the overall goals of the test -- for example, to identify external threats and vulnerabilities and recommend mitigation actions.
- The methodology describes the overall types of tests and testers -- for example, external test, black box test, in-house testers -- to be used in the test.
- The tools section describes the software tools and nontechnology methods -- for example, social engineering -- needed to achieve results from the test.
- The technical approach section describes the technical approach and structure of the test.
- The attack narrative describes the steps taken, from commencement to conclusion, of the test and includes results of each step.
- The results section summarizes the findings and recommended actions from the pen test. It provides actionable advice on how to achieve the desired results.
Next Steps
Intro: How to use BlackArch Linux for pen testing
Dig Deeper on Threat detection and response
-
 What is penetration testing?
What is penetration testing?  By: Kinza Yasar
By: Kinza Yasar -
 An explanation of pen testing
An explanation of pen testing  By: Tommy Everson
By: Tommy Everson -
 Penetration testing vs. vulnerability scanning: What's the difference?
Penetration testing vs. vulnerability scanning: What's the difference?  By: Kyle Johnson
By: Kyle Johnson -
 cloud penetration testing
cloud penetration testing  By: Char Sample
By: Char Sample
Part of: Introduction to penetration testing
Article 1 of 3