archive (original) (raw)
What is an archive?
An archive is a collection of data moved to a repository for long-term retention, to be kept separate for compliance reasons or moved off primary storage media. It can include a simple list of files or files organized under a directory or catalog structure, depending on how a particular program supports archiving.
Web and file transfer protocol sites that provide downloadable software programs sometimes refer to the list of downloadable files as an archive or archives.
Backup vs. archive
While data backup and archiving are similar, they have distinct differences.
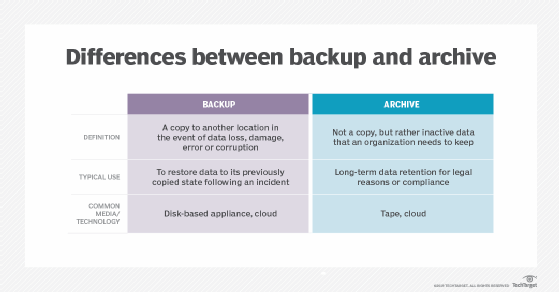
Backups are copies of data stored for the purpose of recovery in the case of corruption or other data loss. These copies are typically created using replication or mirroring and are updated as files change. The storage needs to perform well enough to restore data quickly. Backups are often stored as blocks to facilitate the recovery of large amounts of data at one time.
Archived data is not a copy, but rather inactive and rarely altered data that needs to be retained for long periods of time. Performance is less critical in archive storage. Rather than being stored in blocks, archived data is usually stored as a file or object that can be stored with metadata attached so that granular access to data is possible.
Archive storage options
Archive storage typically needs to be able to store large amounts of data for long periods of time at a low cost. The following storage options are commonly used for archived data:
- Tape. Tape is an effective data storage archival format because of its low cost. However, the time it takes to access data stored on tape is slower than that of other storage options. For that reason, it is most often used as a long-term archival location, where data is unlikely to be accessed.
- Disk. Hard disk drives can be used as archive storage. However, power and cooling of hard disk storage makes this option costly.
- Cloud. The cloud is a favorable archival option because it can easily scale and removes the costs of hardware, power and cooling. However, for large data centers with continuously growing archives, the ongoing costs of cloud storage can start to add up. Some major cloud providers offer cloud archiving platforms that provide slower performance for a lower cost.
- Object. Object storage is an effective archival storage option because it has the ability to store large amounts of metadata, which is essential to easily access data. Object storage is also cheap and can store large amounts of data.
Enterprise data archiving tools
Archiving software enables data to move from production storage to archive storage as needed.
Many archiving software products can automatically offload data to the archived storage location based on user-created policies or as the data becomes less frequently accessed. Some archiving software connects directly to a cloud provider, while other software helps tape or object storage act as an extension of the disk used to store production data.
In many cases, archiving and backup software are integrated. To improve response times when data is accessed, some software also offers the ability to cache segments of archived data on disk, while the majority is stored on object or tape.
Editor's note: This article was revised in 2023 by TechTarget editors to improve the reader experience.
This was last updated in October 2023
Continue Reading About archive
- When long-term data archiving means 'forever'
- Why is a data archive plan important?
- 7 data archiving best practices for backup admins
Dig Deeper on Storage architecture and strategy
-
 Cerabyte brings permanent storage to the U.S.
Cerabyte brings permanent storage to the U.S.  By: Adam Armstrong
By: Adam Armstrong -
 Storage technology explained: Key questions about tape storage By: Stephen Pritchard
Storage technology explained: Key questions about tape storage By: Stephen Pritchard -
 Fujifilm plans to ‘make tape easy’ with Kangaroo SME appliance
Fujifilm plans to ‘make tape easy’ with Kangaroo SME appliance  By: Antony Adshead
By: Antony Adshead -
 New media could bring fresh competition to tape archive market
New media could bring fresh competition to tape archive market  By: Adam Armstrong
By: Adam Armstrong