PSTN vs. VoIP: What's best for your business? (original) (raw)
Unsure of where your organization stands in the PSTN vs. VoIP debate? Use this feature-by-feature comparison to decide whether VoIP or PSTN services fit your organization's needs.
The line is blurring between voice over IP, or VoIP, and the public switched telephone network, or PSTN, as the age of copper lines nears its end of life and telecommunications infrastructure becomes digital. But the PSTN vs. VoIP debate still lingers, as organizations evaluate a migration to IP-based telephony.
Making a decision on whether to move to VoIP or stay on the PSTN requires examining the technology behind the two telephony infrastructures and comparing features.
Traditional PSTN services use dedicated copper lines to deliver voice traffic and circuit switching to connect endpoints during phone calls. Today, PSTN services have become increasingly digital, as new last-mile infrastructure -- such as fiber optic cables -- replaces copper lines. PSTN providers, such as Verizon and AT&T, are also deploying technology, such as Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunking and primary rate interface (PRI), to deliver voice data, according to Irwin Lazar, an analyst at Nemertes Research, based in Mokena, Ill.
VoIP transmits voice traffic over an internet connection or private WAN service and eliminates the need for circuit-switched networks for phone calls. VoIP uses codecs to turn audio into data packets, transmits them across an IP network and turns the packets back into audio on the receiving end of the call. Many organizations get their VoIP services from cloud unified communications providers, such as RingCentral, 8x8 Inc. and Vonage, or from VoIP providers, such as Dialpad, Nextiva and NetFortris.
POTS vs. VoIP vs. PSTN
In the PSTN vs. VoIP debate, PSTN is viewed as more reliable and secure than VoIP networks. PSTN also offers better business continuity, as the connection is not interrupted during a power outage. When VoIP technology first emerged, it was notorious for dropped calls and poor call quality due to jitter and latency. However, the quality and reliability of VoIP services has improved.
Emergency location services are often a challenge for VoIP services, compared with PSTN services. However, in the PSTN vs. VoIP debate, VoIP has its advantages, including lower network infrastructure costs, scalability and advanced features, such as unified communications and app integrations.
Organizations may also have use cases that require them to keep their plain old telephone services (POTS) connection, which requires a PSTN connection. POTS is the most basic form of telephone services, which is analog and copper-based. It has remained largely unchanged, despite the advent of digital telephony.
"The big reason why organizations maintain a POTS line is for services that aren't reliable over an IP PBX," Lazar said. These services include alarm systems, fax services, elevators and other systems that require a direct connection to a monitoring agency or operator.
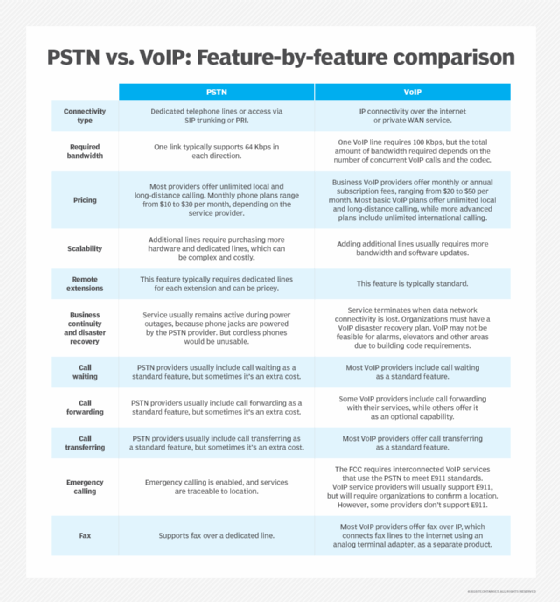
Still unsure where your organization stands in the PSTN vs. VoIP debate? Consider the pros and cons of each technology with this helpful chart.
 By: Joe O’Halloran
By: Joe O’Halloran  What is PSTN (public switched telephone network)?
What is PSTN (public switched telephone network)?  By: Linda Rosencrance
By: Linda Rosencrance  What is telephony?
What is telephony?  By: Paul Kirvan
By: Paul Kirvan