extension (original) (raw)
What is an extension?
An extension typically refers to a file name extension. This suffix is added to the end of a file name, indicating its format. For example, the .doc or .docx extension specifies a Microsoft Word document. The latter was introduced in 2007 and is a more modern version of the .doc format.
There are thousands of file extensions related to different types of software, data and files. Common extensions include the following:
- .py. Python file that is a type of file or Python script that runs on a Python interpreter, a program that reads and executes the Python code.
- .txt. Text file that is essentially a basic text file format that different types of text editors can open.
- .xls/.xlsx. Microsoft Excel spreadsheet created by Microsoft Excel software. Like .docx, .xlsx is also a more modern version of .xls.
- .ppt/.pptx. Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation created by Microsoft PowerPoint presentation software.
- .jpg/.jpeg. Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) image, a standard format for image files, such as photos.
- .png. Portable Network Graphics (PNG), another standard image file format often used for images requiring transparency.
- .gif. Graphics Interchange Format (GIF), which is used for image files and supports both static and animated images.
- .pdf. Portable Document Format (PDF), a file format created by Adobe and used to open documents that are meant to look the same on all devices and software.
- .mp3. MPEG-1 Audio Layer-3 (MP3), a standard format for audio files, especially music.
- .mp4. MPEG-4 Video (MP4), a standard format for video files.
- .exe. Executable file (EXE file), which is a file that contains a program that can run on Microsoft Windows.
- .zip. Compressed archive file used to compress and archive multiple files or folders.
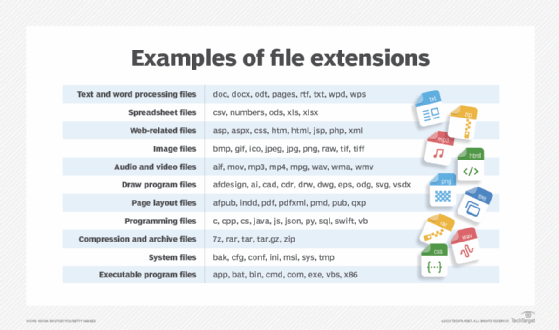
Thousands of file extensions related to different types of software, data and files exist.
What is a file extension?
A file extension enables a file's format to be described as part of its name so that users can understand the type of file without having to open it or trying to use it. The file name extension also helps an application recognize a file that it can work with.
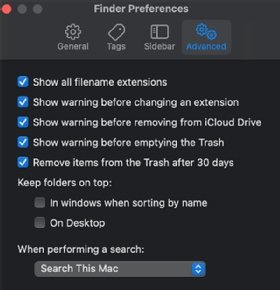
Enabling the display of file extensions on a Mac
In software systems, an extension can sometimes refer to a plugin or add-on that extends the software's capabilities. For example, these are often used in web browsers, text editors, development environments and other software to add new features or functionality.
Some file extensions are specific to certain operating systems (OSes). For example, EXE files are typically used with Windows, while DMG files are used with macOS for disk images. Apple's macOS does not display file extensions by default. However, it often uses file extensions combined with other mechanisms, such as file type codes, to determine the file type.
It is easy to enable the display of file extensions on a Mac. A user can do so in Finder -- a file manager for Mac devices -- by going to Finder > Preferences > Advanced and then checking the box for Show all filename extensions.
Although showing file extensions by default is not important, they are crucial to ensure compatibility with other systems -- for example, when files are being transferred between different OSes.
What is the HEIC extension?
The High-Efficiency Image Container (HEIC) file extension is a format for storing images that uses the High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) standard. Also known as H.265, HEVC provides more efficient compression than older formats, such as JPEG and Advanced Video Coding. This means HEIC files can store high-quality images using less space, preserving device storage.
See how to check and verify file integrity and how to implement file classification in file servers.
This was last updated in August 2023