What is managed detection and response (MDR)? (original) (raw)
Managed detection and response (MDR) services are a collection of network-, host- and endpoint-based cybersecurity technologies that a third-party provider manages for a client organization. The provider typically installs technology on-premises at the client organization and provides additional external and automated threat-hunting services.
MDR systems improve cybersecurity by searching for threats and responding to them once detected. They also let users connect with the provider's security experts, who can bolster the security skills of the client company's IT department. This makes them ideal for businesses that don't have a designated in-house threat detection team.
Managed detection and response services are becoming more popular partially because of the growing skills gap in cybersecurity. Gartner predicted that, by 2025, 50% of all enterprises will have adopted MDR services.
How does MDR work?
MDR continuously monitors an organization's networks, endpoints and systems. To identify potential security incidents, MDR teams use a combination of automation, machine learning and human expertise, such as threat hunters and security professionals. They also use advanced security and management services, such as security information and event management (SIEM) and extended detection and response (XDR).
When a threat is detected, the first step is to analyze it to determine if it's a false positive. If the threat is real, the MDR team assesses its severity level. The team then works to prevent or defend against the attack, providing security controls or automatically isolating compromised endpoints. The team then issues a report of the incident, including remediation steps, processes and guidance to prevent a subsequent attack.
What are the types of MDR?
Different variations of MDR services provide tailored approaches based on an organization's needs. There are three main variations of MDR:
- Managed endpoint detection and response. MEDR monitors and secures endpoints, such as laptops, mobile devices and servers. It provides deep visibility into endpoint activity to detect and block attacks before they spread across a network.
- Managed network detection and response. MNDR checks network traffic and communication patterns to detect threats across an organization's infrastructure. This approach is ideal for identifying network-specific threats, such as lateral movement within a compromised network.
- Managed extended detection and response. MXDR is an advanced form of MDR that integrates multiple security layers, including endpoint, network and cloud security. MXDR uses data from multiple sources, such as SIEM, security controls and telemetry.
Common features in MDR offerings
MDR systems are relatively new. Each company offers different MDR services. Providers typically focus on either network-, endpoint- or log-based technologies. A network-based MDR platform focuses on threats in a firewall, whereas an endpoint-based product works with antimalware software.
Regardless of the level that the service works at, it unites reports from multiple technologies to perform the following functions:
- Threat detection, in which the security operations center (SOC) continuously monitors data and prioritizes alerts for analysis.
- Threat analysis, in which SOC personnel home in on potential threats and determine the source and scope of the threat.
- Threat response, in which the provider notifies the client of an incident and offers their analysis recommendations for resolving the problem.
- Event triage, in which MDR services categorize and prioritize security events based on their criticality -- by considering various factors, they create a list of security events to ensure that the most crucial incidents receive immediate attention.
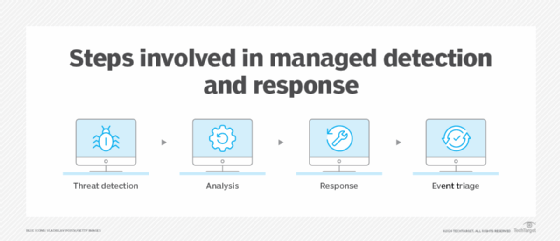
The steps of the managed detection and response process include detection and triage.
Response capability is where there's the most variation among providers. Each provider decides when their work ends and the customer takes on the issue. Some providers might also offer additional features for a price, such as on-premises expert consultation and additional on-premises hardware.
Benefits of MDR
MDR services have an active role in improving a business's information security strategy. They handle threat detection, incident response, continuous monitoring and IT asset analysis.
MDR services mitigate common problems IT departments face and provide several benefits:
- Management of high alert volume. MDR services can help companies manage the sheer volume of cybersecurity alerts that must be checked individually. Too many false alerts can cause alert fatigue among smaller security teams, leading them to neglect other responsibilities.
- Threat analysis. Many alerts don't immediately present themselves as a threat and require thorough analysis to determine their status. MDR services provide advanced analytics tools, threat intelligence and access to security experts to interpret events and provide recommendations for improvement.
- Access to security expertise. In ISC2's 2023 "Cybersecurity Workforce Study," 67% of participants stated their organizations lack the personnel necessary to detect and resolve security problems. Furthermore, 92% of respondents said their organizations have a skills gap, with cloud computing security, artificial intelligence, machine learning and zero-trust adoption among the most prevalent. MDR services can help close the skills gap by providing access to experts, who usually work 24/7 to monitor a network and are available for consultation.
- Endpoint detection and response. Businesses can lack the funds, time or skills to train employees on EDR tools. MDR services come with EDR tools and integrate them into detection, analysis and response processes, eliminating the need for extensive in-house endpoint security.
- Around-the-clock monitoring. MDR vendors guarantee constant surveillance and threat detection by providing customer networks with nonstop protection and monitoring.
- Proactive threat hunting. An organization's security stack can't always detect every security event. However, most MDR providers proactively scan a customer's network and systems for signs of an active attack and take swift action when one is identified.
- Rapid incident response. MDR services offer rapid response times to advanced threats and security incidents. Security teams swiftly detect unusual activities, consistently identify cyberthreats and take prompt action to mitigate them.
- Cloud threat monitoring. MDR services commonly involve monitoring and protecting cloud environments. This is valuable for organizations relying on a cloud infrastructure, ensuring thorough cloud security coverage across multiple platforms.
- Customized security rules and services. MDR services offer personalized security rules tailored to an organization's unique needs. This adaptability enables customized threat detection and response strategies.
What are the challenges of MDR?
As with many anything-as-a-service models that outsource IT processes, customers trade control for convenience and flexible prices. MDR services have some downsides compared to older managed security products and the client's intended use for the services.
Common challenges that come with MDR services include the following:
- Complex deployment. Deploying MDR can be difficult, especially for enterprises with extensive IT environments. Integrating MDR tools and technologies into existing systems and processes involves rigorous planning and coordination.
- Cost considerations. MDR services can pose a financial challenge, especially for small and medium-sized organizations with tight budgets. It is important to evaluate and justify the costs associated with outsourcing MDR services.
- Integration with an existing security infrastructure. To ensure the effectiveness of MDR services, an organization's current security posture should seamlessly integrate with them. This includes network monitoring tools, endpoint protection programs and SIEM systems. However, ensuring consistent compatibility and integration can be challenging.
- Evolving threat landscape. The threat landscape continues to evolve, with new cyberattacks and malware variants emerging regularly. MDR service providers must keep abreast of the latest cybersecurity threats and consistently update their detection and response capabilities to counter threats.
- Inadequate responses. Not all MDR providers are created equal. While some are meticulous in finding and managing threats, others might not be so vigilant. For example, some services might only trigger generic alerts -- "There is a critical alert on your firewall, and you should investigate further" -- after a security event. The businesses using those services must do more troubleshooting and remediation on their own.
MDR vs. classic managed security
MDR and classic managed security services both provide customers with external cybersecurity assistance, but there are some key differences. Classic managed security services vendors -- sometimes called managed security service providers (MSSPs) -- primarily focus on monitoring and managing security tools, such as firewalls and SIEM systems. However, MSSPs don't offer the same level of direct threat detection as MDR services and don't provide incident response.
MDR providers go beyond MSSPs' monitoring capabilities, using machine learning, automation and expert analytics to detect and respond to threats. Many MDR services can be integrated with an organization's MSSP.
Other differences between MDR services and traditional managed security services include the following:
- Compliance. Classic managed security services vendors are typically focused more on compliance reporting and helping businesses meet compliance requirements. MDR services rarely focus on this.
- Log format. MSSPs can generally work with a wider variety of event logs and contexts. MDR providers primarily use the logs that come with their tools.
- Human interaction. MSSPs handle any communication with the provider through online portals and emails. MDR providers have teams of experts, or a SOC, that can be reached through multiple channels in real time.
- Detection methods. Because MDR providers offer human expertise, they can apply deeper analysis to alerts and detect novel threats. MSSPs are less involved in analysis, focusing more on known and frequently occurring threats using a rule-based system.
- Network visibility. MDR providers can detect events and movement within a client network, whereas MSSPs focus mainly on the network perimeter.
- Resource allocation. MDR benefits companies that prefer not to handle security internally and instead use MDR services. However, classic managed security usually requires hiring a security team and administering a SOC.
- Notifications. Notifications are filtered with MDR, saving the team from having to address false positives. In contrast, MSSPs send notifications for every security event, regardless of its nature.
- Monitoring. MDR offers around-the-clock monitoring and cybersecurity solutions, providing continuous surveillance. MSSPs typically provide more constrained monitoring services.
- Technology types. MSSPs are good for managing foundational security technology, such as firewalls, and performing day-to-day security tasks. MDR tools are more specialized services designed to handle complex modern networks and the new vulnerabilities they present.
Each option has strengths and weaknesses. Companies can use both MDR and classic managed security services in tandem to maximize the benefits. Secureworks, Tata Communications and Trustwave are three of the highly rated MSSP providers, according to Gartner.
MDR vs. EDR vs. XDR
EDR and XDR are two distinct threat detection services that are often compared with and integrated into MDR services. EDR focuses on providing deep visibility into endpoint activities and securing endpoints. It's a key component of MDR and MEDR but doesn't provide the same breadth of coverage across networks and other attack surfaces as MDR.
XDR extends beyond endpoint protection by integrating security data across multiple environments, including network, cloud and endpoint layers. MXDR services add continuous monitoring and expert threat response to build upon XDR.
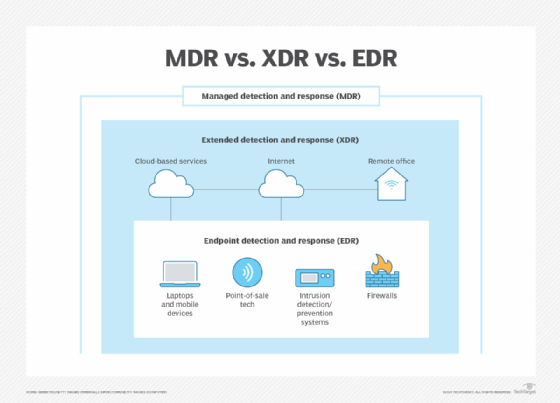
Managed detection and response, extended detection and response, and endpoint detection and response are similar services often used under the MDR umbrella.
MDR vs. SIEM
SIEM is another distinct service that can be used in tandem with MDR. It collects and analyzes security data from sources such as logs and events. While this can help provide insights into potential security incidents, SIEM systems don't respond to those threats.
MDR services, on the other hand, actively monitor and respond to threats in real time. They often use SIEM data for threat detection, along with expert analysis and automated threat mitigation.
How to choose an MDR service
When choosing a provider, customers should consider the following:
- Organizational size. When looking for MDR providers, the size of the organization matters. For example, larger organizations might have more complex networks and a higher volume of security events. Therefore, they should look for an MDR provider capable of promptly scaling, detecting and responding to incidents.
- Level of skill and competency. It's critical to select a provider with experience and knowledge in cybersecurity. Customers should also look for a company that provides onboarding assistance and client success services.
- Technology and tools. The type of technology an MDR provider uses is an important factor to consider, along with how up to date it is with the latest security tools. The type of security tools an MDR provider uses provides insight into its capability and competence.
- Adherence to compliance. By understanding and verifying the compliance regulations that an MDR provider adheres to, an organization can make informed decisions, reduce regulatory risks and ensure that the chosen provider aligns with the specific requirements of its industry and geographic location.
- Transparent communication. Effective communication is critical in the customer-MDR provider interaction. Customers should inquire about the provider's communication channels and protocols during regular operations and incident response. Transparency in communication is also vital, as the provider should be able to explain the steps of the MDR service and offer updates on the progress of the security measures.
- Security outcomes. Organizations should ensure the MDR service aligns with their specific goals, such as mitigating cybersecurity risks and improving overall network security.
- Attack surface coverage. Organizations should ensure that the service covers all potential attack surfaces, including endpoints, networks and cloud workloads.
- Expertise of the provider. The best MDR providers employ experienced threat hunters with a comprehensive understanding of ransomware, emerging threats and extended detection.
- Integration. Organizations should ensure that the MDR service can integrate smoothly with their existing systems and that data is integrated between shared systems.
- Automation. Organizations should look for services with a high degree of automation, enabling faster threat detection and response times.
- Service customization. The service should be flexible enough to meet an organization's needs, such as accommodating customer security requirements or integrating with SIEM systems.
A well-engineered MDR system can offer numerous benefits to any organization. Learn how to select the right MDR service and what to expect from an MDR provider.
This was last updated in November 2024