menu (original) (raw)
What is menu?
A menu is a set of options presented to the user of a computer application to help them find information or execute a function. Menus are common in GUIs provided in OSes such as Windows and macOS. They're also used in speech recognition and on internet websites and web pages.
Menu explained
A menu is essentially a graphical control element that accesses various elements on a GUI. It provides users with options and built-in commands to access the features or functionalitieso of an application or program, whether it's web-based or on the user's system.
All menus contain an organized set of items located in a menu bar for easy navigation through the different levels or features of a program. A menu can also be structured as a submenu, depending on its complexity and command structure.
In general, menu-driven applications are user-friendly since they present options in a simple visual format. Additionally, menus organize and categorize the top content of the program to make it easy for users to access various features as per their needs.
How to access a menu
A menu is also known as a file menu or a file, edit, view menu because these are often the first three options in a drop-down menu, particularly in Windows-based programs. A user can access a program menu via a keyboard shortcut by clicking a mouse or through other input devices. When a selection is made, the menu item is highlighted.
When using a mouse, the mouse pointer must target a menu option. Left-clicking on the option will either execute that command or open a subset of options. For example, to open a new file in Windows Word, the user would click on the File option followed by the Open option. Similarly, to change the layout of the open page, a user would click on the View option and then select the required layout option under the View menu: read mode, print layout and web layout.
Types of menus
There are many types of menus. Here's a list of the most popular ones.
Pop-up menu
A pop-up menu, also known as a context menu or shortcut menu, is hidden and doesn't appear until the user right-clicks on a specific selection. The menu appears over the application and is oriented vertically while the user clicks on an item. It then disappears from the screen.
In Windows environments, pop-up menus can be programmatically invoked or invoked automatically by right-clicking on the mouse. In the latter case, the menu is tied to a window or control, which means each window and control can have its own pop-up menu.
Pop-up menus shouldn't be confused with pop-up ads that often appear on some commercial websites.
Graphical drop-down menu
In a graphical drop-down menu, clicking on an item -- which could be text, button or icon -- causes a list of new items to appear. One example can be seen by clicking on text such as "File" or "Edit" in the horizontal list at the top of the screen in a Windows application. If there are no sub-items, clicking on the item will simply execute the indicated function.
Cascading menu
A cascading menu is one of the most common menu systems for OSes, programs and websites. It displays submenus when an item is selected on the main menu.
In older Windows versions like Windows XP, the Programs submenus of the Start menu begin to cascade to the right, regardless of which option is selected. For example, selecting the Accessories menu will cascade a submenu that lists options such as Communications, Entertainment, Games and Calculator. Clicking on any of these options may open another submenu, which will cascade to the right.
The advantage of a cascading menu is that the user can easily narrow down the list of possible options, suboptions, sub-suboptions and so on before selecting the desired option.
On websites, cascading menus are usually presented as a series of drop-down lists. To start with, only the top-level drop-down list is populated and enabled. The other lists are either empty or grayed out, meaning they can't be selected. Once the user selects an option in the top-level list, the list at the next level gets activated. The process continues until the user arrives at the required option.
Pull-down menu
Also known as a drop-down menu, the pull-down menu is a popular choice for GUIs. When a user clicks on a menu title, the menu items will appear to drop down from that position and be displayed on the screen. Users can then select the required option by clicking the menu item or holding the mouse button down.
Moving bar menu
In a moving bar menu, the user selects options by moving a highlighted bar over them. The menu bar can be moved with a mouse, or by using the arrow keys or Tab key on a keyboard.
Tear-off menu
In a tear-off menu, the menu can be moved to another place on the screen from where it was first displayed. Usually, this menu is moved from the top portion of the window to the left, right or bottom of the same window.
Menu in speech-driven systems
In speech-driven systems, a menu is presented as a set of audible choices to which the user can respond by pressing a button or speaking aloud. This menu type is common in telephone answering systems, automated customer service programs, and interactive voice response systems. Users may select items several times as they drill down to reach the desired department or access the required information.
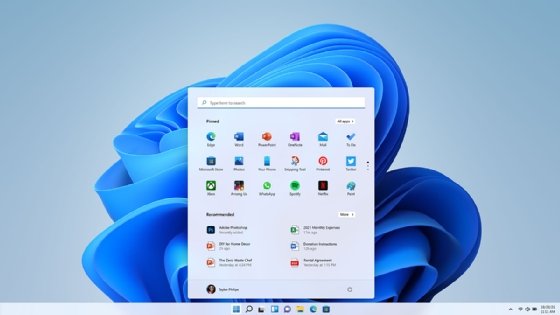
Windows 11 Start menu.
Menu-driven programs vs. command-driven programs
In a command-driven program or system, the user must enter the command instead of selecting from a prebuilt list. These commands usually take a specific form or syntax and may consist of words, numbers, special characters or some combination thereof.
A menu-based program includes a GUI, while a command-based program provides a command-line interface. The CLI was a standard way for users to interact with programs before GUIs became popular.
Menu-driven systems are easier to learn and use since users simply select an option from a list to perform a specific action. However, such programs aren't as flexible as command-driven programs.
On the other hand, command-driven programs are harder to learn and use. Nonetheless, the CLI approach is preferred by technical professionals looking for high-speed performance or a Multitasking environment where they don't have to navigate through multiple icons or choices and can continue to work uninterrupted.
See also: hierarchical menu, Ctrl-Alt-Delete, mobile user interface, system tray
This was last updated in August 2022