telemetry (original) (raw)
What is telemetry?
Telemetry is the automatic measurement and wireless transmission of data from remote sources. In general, telemetry works in the following way: Sensors at the source measure either electrical data, such as voltage and current, or physical data, such as temperature and pressure. Electronic devices then send this data to remote locations for monitoring and analysis.
Software developers and IT administrators use telemetry to remotely monitor the health, security and performance of applications and application components in real time. They use telemetry to measure startup and processing times, crashes, user behavior and resource use, and to assess the state of a system.
Telemetry is also used to gather information in fields such as meteorology, agriculture, defense and healthcare.
How does telemetry work?
Telemetry measures electrical or physical data with a telemeter, which is a tool to measure various metrics such as pressure, speed and temperature. These measurements are converted into electrical voltages, then a multiplexer combines these voltages, along with timing data, into a data stream for transmission to a remote receiver. The receiver separates the data stream into its original components, and the data is displayed and processed according to user specifications.
Telemetry data can be transferred using analog or digital electronic devices. Applications using the technology include measuring and transmitting data from internet of things (IoT) sensors located in automobiles, smart meters, power sources, robots and even wildlife. Telemetry sends data using computer networks, satellites, cable, and infrared and ultrasonic technologies.
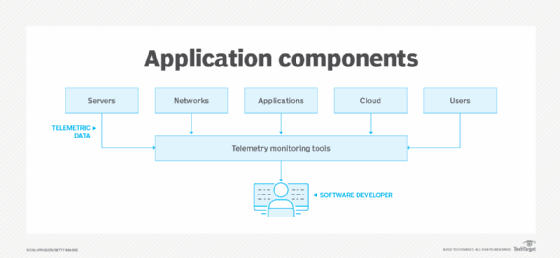
Telemetric data is gathered from multiple components to inform software developers.
Ways telemetry is used
In software development, telemetry systems are used with an end user's permission to remotely monitor the security, health and performance of applications. The information developers get from these systems provides insights into how their applications are performing without the need of feedback from users.
Telemetry is also used in the following fields:
- Meteorology. Weather balloons and other meteorological devices use telemetry system to collect and transmit meteorological data such as temperature and barometric pressure.
- Agriculture. Wireless weather stations and sensors gather data on the environment, such as temperature, humidity and solar radiation, that helps farmers make decisions about what and when to plant crops.
- Space exploration and defense. NASA and the U.S. military use telemetry to monitor the location, performance and health of satellites, spacecraft and aircraft.
- Healthcare. Individuals with heart conditions or other medical issues use telemetry devices to monitor heart rate, blood pressure and other vital statistics. This use of telemetry in healthcare is sometimes referred to as biotelemetry.
Types of telemetry monitoring
In software development, telemetry is measured using IT monitoring tools. These tools track the following components of an application:
Servers
In IT infrastructure, monitoring servers is critical to ensuring application performance. Server metrics include the following:
- Processor use. Overuse of the central processing unit (CPU) indicates an application is forcing the computer to do more work than it can handle. A CPU that isn't used to full capacity may mean network requests are not going through or features of the application are not being used.
- Server statistics. These stats indicate whether issues with CPU use are the fault of out-of-date or failing servers, or they're a problem with the application itself. Metrics to keep an eye on are servers being oversubscribed in virtualization, CPU, physical memory or the input/output load over time.
- User activity and requests. This data gives insight into server performance and use.
Network
Networks are also important to monitor. The following four parameters should be tracked:
- Bandwidth capacity defines how the network is used while it runs applications.
- Application use reveals potential performance and functionality issues such as delays in data being sent between a computer and web browser.
- Network ports handle network requests, so monitoring them helps keep an eye out for security breaches and routing delays.
- Storage should be tracked to see if it is near capacity or has poor data retrieval speeds. Under-used storage might mean a data backup system has failed.
Applications
The most important metrics in application telemetry are the following:
- Database access. Monitoring the number of open database connections is important because, as they grow, they can slow performance.
- Database processing. Here, telemetry monitors the number of database queries, response times and the amount of data passed between an application and database.
- Errors. Telemetry monitors for unusual activity, requests and database errors that might indicate an application failure or security breach.
- Application key performance indicators (KPIs). Telemetry of application KPIs is an important part of understanding the customer and user experience (UX) of an application. Application KPIs can measure metrics, such as transactions per second, request throughput and latency. For example, in e-commerce, KPIs measure sales and database growth.
- DevOps activity. Application monitoring also involves tracking DevOps activity such as application deployments and software development.
Cloud
Telemetry in the cloud includes monitoring the following:
- cloud availability
- internet routing
- energy consumption
- utilization
- request latency
Users
User telemetry involves gaining insights into application performance from the user's point of view. Instead of approaching telemetry from the system's components, user telemetry monitors UX. This means an application is analyzed from the user-facing side to detect problems and symptoms before users do.
Benefits of telemetry
In software development, the benefits of telemetry include the following four:
- Remote feedback. Admins are able to gather information in real time from any remote location without interacting with users.
- Performance monitoring. Telemetry gives real-time insight into the performance of applications. Admins use this feedback to ensure their systems are working properly.
- Activity monitoring. UX and application experience is monitored. This includes metrics such as the frequency with which users engage, how long, what features they engage with most, device configurations and the cause of crashes. Knowing the faults and weaknesses of an application enables developers to improve systems in real time or update them in the future.
- Security. Telemetry is important to network analytics, providing key security information that can help admins act before a breach occurs.
Drawbacks and challenges of telemetry
The following are three key challenges with telemetry systems:
- Data access. Telemetry is only as good as the data the system is able to gather. End users may turn off telemetry for privacy reasons, limiting the pool of users providing data.
- Data deluge. The increase in the number of IoT devices that gather telemetry data has led to systems generating more data than analysts can handle.
- Legacy issues. Older devices and applications don't always support telemetry. For network monitoring, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) technology is an alternative. SNMP works better with older devices that do not support telemetry.
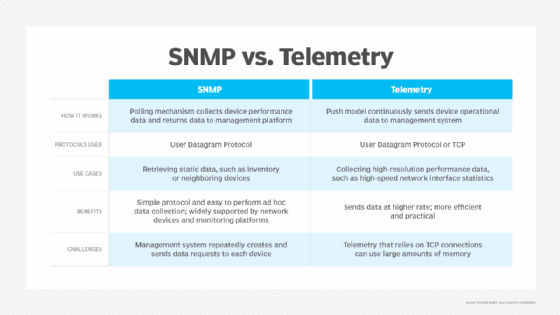
Telemetry is often compared to SNMP for network monitoring.
Telemetry monitoring tools
The most common monitoring tools include the following:
- Dashboards provide system telemetry data in real time.
- Log parsing translates log files used by Log Management
- Business intelligence delivers data about security incidents and trends, such as seasonal variations, to drive better business decisions.
- Automation tools automatically detect security risks and other problems.
- Security analytics gathers data, such as suspicious user, network and database activity.
History of telemetry
Telemetry began in 1763 with mercury pressure gauges. These early telemeters let engine conductors monitor the pressure in Watt steam engines from a close distance. Telemetry expanded in the 1800s and was used to relay and receive communications through Samuel Morse's telegraph machine.
In 1912, the first telemetry application in Chicago used telephone lines to transmit operational data from a power plant to a central office. Because telemetry was originally used in projects like this, the first telemetry systems were called supervisory systems. However, the buildup to World War II found electric telemeters in wider use. Following the war, telemeters became commercially available and were used for espionage throughout the Cold War.
In 1960, the interrogation-reply principle was developed, which enabled a more selective transmission of data upon request. At that time, a telemetry transmitter consisted of a set of measuring instruments, an encoder that translated instrument readings into analog or digital signals, a modulator and a wireless transmitter with an antenna. The receiver consisted of an antenna, a set of radio-frequency amplifiers, a demodulator and recording devices. Mainframe computers were used to process and store the received information.
Telemetry is used by IT admins to collect and analyze data. Learn how telemetry is changing the future of observability for cloud native apps.
This was last updated in December 2022