uploading (original) (raw)
What is uploading?
Uploading is the transmission of data from a local device to a remote device. Typically, the remote device is a larger server. From a user's point of view, to upload a file is to send it to another computer, and to download a file is to receive it. Generally speaking, to upload a file is to transfer a copy of it to a server.
Uploading is most used for transferring files over a network, especially over the internet. Usually, this is done from a client computer to a server.
What is the difference between uploading and downloading?
Both uploads and downloads are transfers of data from one computer to another. The difference between uploading and downloading is if the data is being sent or received from the user's perspective.
In an upload, the user initiates the transfer of data from the device they are using to another device they are not currently interacting with. In a download, the user initiates a transfer of data from the computer they are not interacting with to their local device. While not a hard-and-fast rule, if the data is moving between two peer client devices or between two pieces of local data storage, such as from a compact disc to a hard disk drive, it would be called transferring data and not downloading.
It's a matter of perspective. An upload from the sending device is a download to the receiving device. So, it's important to consider the context and who is sending or receiving when choosing whether to say upload or download.
To illustrate, imagine a user wanted to send a picture on an iPhone to a friend using AirDrop. They would be uploading the picture to their friend. Their friend would be downloading the picture from them.
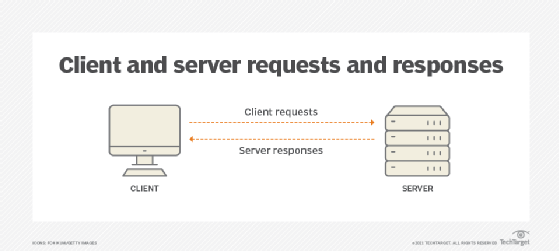
Uploading usually occurs between a client computer and a server.
How do you upload?
There are many ways and protocols used to upload data; choosing the correct method depends on where the data is stored and how it is used:
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP) has historically been one of the simplest ways to upload a file to a server. It uses a program to log on to a server and to transfer the files.
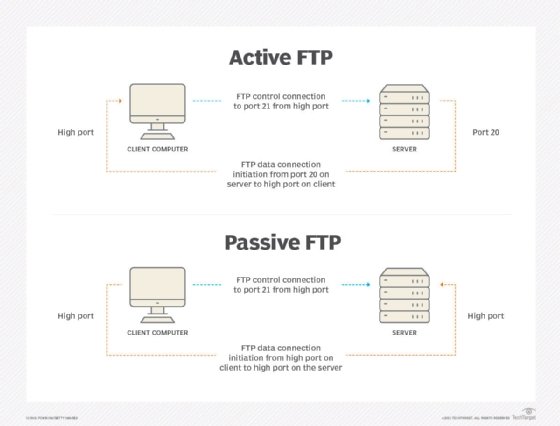
FTP is a simple way to upload a file to a server. - Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) uses the same protocol as browsing websites to send the file data. Many applications that upload data use HTTP as the underlying protocol. For example, dragging a file into a web browser to upload and the Dropbox sync feature use HTTP.
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) uses special clients and protocols to send and receive files without a central host. A popular P2P protocol is BitTorrent.
- E-mail uses a central server. So, any files attached to an email must first be uploaded to the server before they can be downloaded by the recipient. This is often done automatically by the email client.
What is upload speed?
Upload speed is a measure of how much data can be transferred from a user's device to an arbitrary internet location in a second. It is typically measured in megabits per second. The higher the number, the faster the connection. The maximum capacity to transfer data of a wired or wireless network in a certain amount of time is referred to as bandwidth.
For most home or personal internet connections, the upload speed is lower than the download. This may be because the equipment to send data at high speeds is prohibitively costly or bulky to install at the end user's location. So, downloads are prioritized by the internet service provider. This is called an asymmetrical internet connection. Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, cellular, cable and satellite internet typically have asymmetric upload and download speeds.
This is usually acceptable because, for most people, they need to download far more data than they need to upload. For example, in a typical video call or conference, the user only needs to upload one small video of themselves, while simultaneously downloading many other videos of all the other participants.
Businesses may benefit from having the same upload speed as their download; this is called having a symmetrical internet connection. Businesses often need to send and receive large files equally. Additionally, a business may need to run a server on its premises that uploads to other clients out on the internet. Many other modern uses also rely on fast upload speeds, such as cloud computing, internet of things data logging to a central server and big data services. Fiber optic internet connections usually have symmetrical upload and download speeds.
Learn about the 12 most used network protocols, as well as their purposes and use cases. See how to calculate network bandwidth requirements.
This was last updated in June 2023