Iberian Peninsula (original) (raw)
A peninsula is a piece of land almost surrounded by water and connected to the mainland on at least one side. Thus, it is a landform extending from a mainland into a water body such as an ocean or sea.
Europe is one of the world’s largest peninsulas and the only one with a continental status. It is the world’s 5th largest continent by area, covering approximately 9.9 million km2. Europe is made up of several other smaller peninsulas. However, the four largest peninsulas in Europe are Italian, Balkan, Iberian, and Scandinavian Peninsulas. The Iberian Peninsula is the continent’s second-largest peninsula after the Scandinavian Peninsula.
Where Is The Iberian Peninsula?
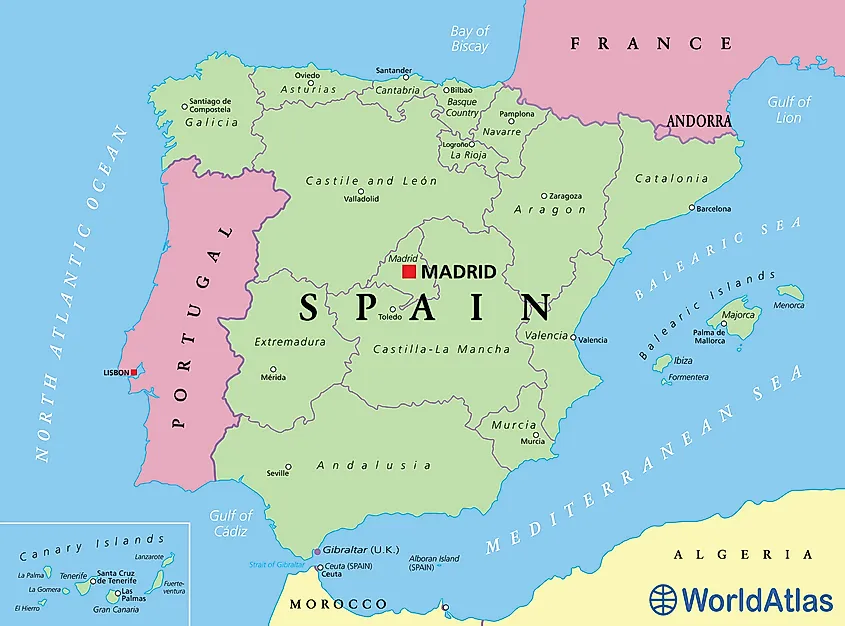
Iberian Peninsula Map
The Iberian Peninsula is located on Europe’s southwestern tip. It is part of the southern Europe peninsula, which comprises three peninsulas; Iberian, Balkan, and Italian peninsulas. The Iberian is the westernmost peninsula of the three peninsulas. The Iberian Peninsula’s southern tip is separated from the Africa continent by the narrow Strait of Gibraltar. At the narrowest point, the peninsula is only 8 kilometers from Africa, specifically Morocco.
The Iberian Peninsula covers approximately 583,256 km2, accounting for about 5.9% of Europe’s total area. It extends from Punta de Tarifa on the extreme south to Punta de Estaca de Bares on the northern extremity. From the west, the peninsula begins at Cabo da Roca and extends to Cap de Creus in the east. It forms an irregular octagonal shape resembling an ox-hide.
Iberian Peninsula Countries
| Country or territory | Capital | Area | Mainland population | % area of Iberian Peninsula |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andorra | Andorra la Vella | 468 km2 (181 sq mi) | 84,082 | 0.1 |
| France (part of the French department of Pyrénées-Orientales) | Paris | 539 km2 (208 sq mi) | 12,035 | 0.1 |
| Gibraltar (British Overseas Territory) | — | 7 km2 (2.7 sq mi) | 29,431 | < 0.1 |
| Portugal | Lisbon | 89,015 km2 (34,369 sq mi) | ca. 10,047,083 | 15.3 |
| Spain | Madrid | 492,175 km2 (190,030 sq mi) | ca. 43,731,572 | 84.5 |
The Iberian Peninsula is separated from the rest of Europe by the Pyrenees mountain range located between France and Spain. The peninsula is mainly occupied by Spain and Portugal. However, it also comprises Andorra, part of Southern France (part of the French department of Pyrénées-Orientales), and Gibraltar (British overseas territory).
Spain’s European continental territory is located entirely on the peninsula. It also occupies much of the landform, including the northwest, east, and central parts. Spain accounts for 84.5% of the peninsula’s total area or 492,175 square kilometers. It is bordered to the northwest and west by Portugal, north by Andorra and Southern France, and south by Gibraltar.
Portugal is the peninsula’s largest country. It occupies 15.3% of the peninsula or 89,015 square kilometers. It is bordered to the east and north by Spain. Andorra is located entirely on the Iberian Peninsula. It is the peninsula’s smallest country, covering 468 square kilometers. France is represented on the peninsula by the Pyrenees-Orientales and accounts for about 0.1% of the total area or 539 square kilometers. Gibraltar, located on the southern tip, occupies only 7 square kilometers on the peninsula
Origin Of Name
The name “Iberian” is often used to refer to Portugal and Spain. This name is linked to the Ebro River, also known as Hiberus in Latin and Iberos in ancient Greek. River Ebro runs on the north and northeastern part of the peninsula, particularly Spain, and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. The Greeks referred to Spain as Hiberia because of River Ebro and those living along the river bank as Iberians.
It is unclear what the word “Hiber” or “Iber” mean. However, according to the Basque speakers, the word “ibar” means “watered meadow” or “valley,” while “ibai” stands for “river.” But, there is no evidence linking the two Basque words to River Ebro. Jean-Baptiste Bory de Saint-Vincent coined the name “Iberian Peninsula” in 1823.
Important Geographical Features
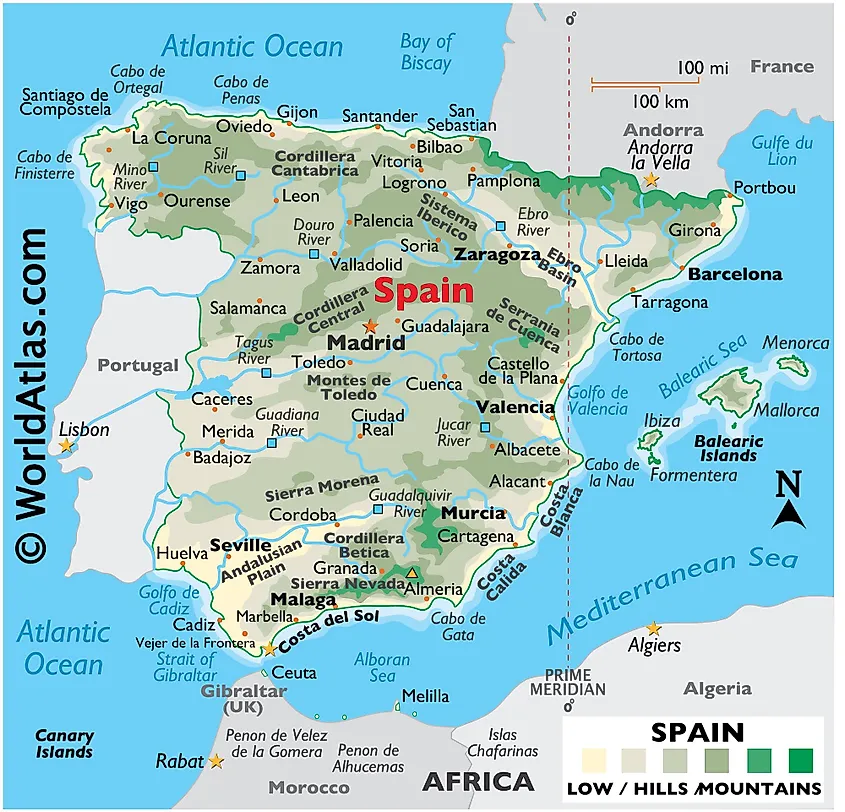
Physical map of Spain in the Iberian Peninsula showing the major physical features.
The Iberian Peninsula lies between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean and is separated from France by the Pyrenees mountain range. It features some of Europe’s important geographical features such as rivers, mountains, and coastal plains.
About 75% of the peninsula’s total area is Meseta Central, also known as Inner Plateau. This massive plateau occupies the peninsula’s central part and rises between 610 and 760 meters above sea level. It is crossed by Sistema Central mountain range, leaving Submeseta Sur and Submeseta Norte to the south and north respectively. It is the source of most rivers that flow throughout the peninsula.
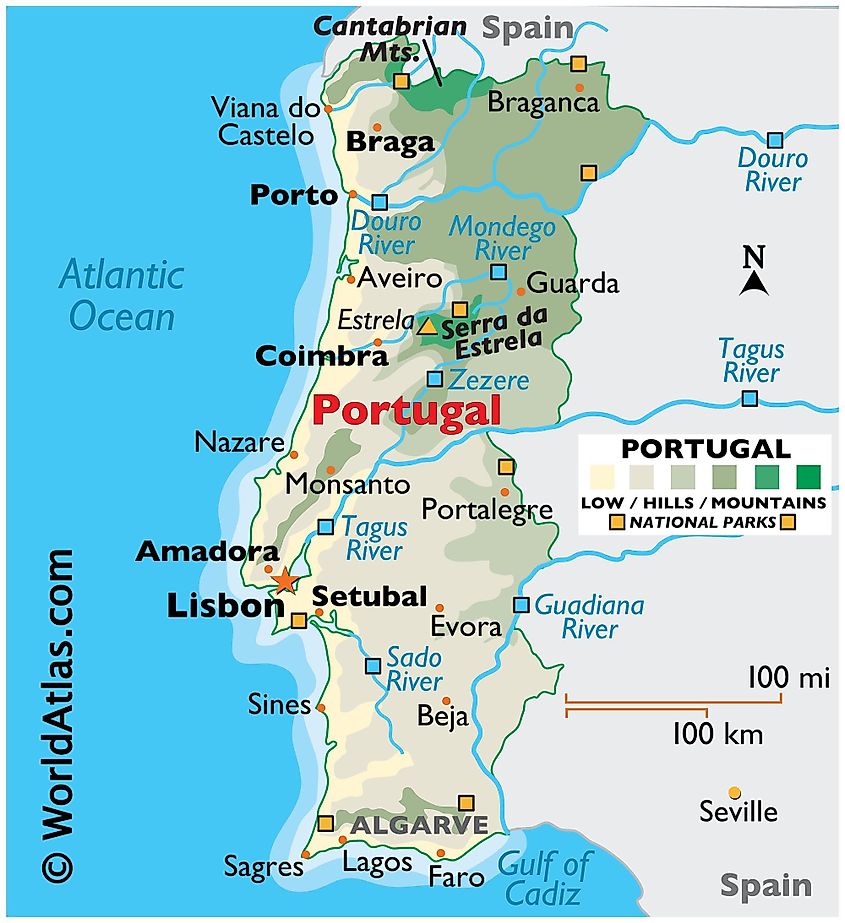
Physical map of Portugal in the Iberian Peninsula showing the major physical features.
The Iberian Peninsula is a largely mountainous region, with several mountain systems. The Pyrenees mountain range is located at the border between Spain and France. Aneto, the highest mountain in the Pyrenees, is located in Spain. The Cantabrian Mountains stretch over 300 kilometers along the northern coast, with Torre de Cerrado as the highest peak. On the peninsula’s central part, the mountain systems include the Sistema Central and Sistema Iberico. Other mountain systems are Montes de Toledo, Sierra Morena, and Baetic System.
Several rivers flow through the Peninsula, including Tagus, Douro, Ebro, and Guadiana. At 1,007 kilometers, Tagus is Iberian’s longest river. It originates in Monte Universales and forms the border between Spain and Portugal. Guadiana River also forms the border between the two countries, separating Andalucia and Extremadura (Spain) from Algarve and Alentejo (Portugal). The Iberian Peninsula also has a coastline of about 3,313 kilometers, of which 1,653 kilometers are on the Atlantic Ocean and 1,660 kilometers on the Mediterranean Sea.
Climate
The Iberian Peninsula experiences two main climate types. The oceanic climate, dominant along the Atlantic coastal regions, is characterized by cool summers and relatively even temperatures. The other climate experienced on the peninsula is the Mediterranean climate, characterized by varying temperatures and precipitation. Central Spain experiences a semi-arid climate, while the Sierra Nevada region experiences a desert climate.
Plants And Animals

Forest landscape in Verdes refuge, with the Allons river, Coristanco, Galicia, Spain
The Iberian Peninsula is one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots. However, the various regions within the peninsula are characterized by distinct flora and fauna. About 27% of Spain’s total area is a protected area. It is home to about 9,000 vascular plants, of which about 25% are endemic. Plains, plateaus, and valleys across the peninsula host the semi-deciduous forests that are dominated by carob, cork oak, holm oak, and wild olive. Laurisilva rainforests are only restricted to the peninsula and contain the endemic Laurisilva species. Higher altitudes are dominated by Pyrenean oak, juniper, and scots pine.

Red deer at Lousã Mountain, Coimbra, Portugal.
Over 70,000 animal species are found on the Iberian Peninsula, with invertebrates accounting for the largest proportion. Some of the native species include Pyrenean desman, shrew, and European hedgehog. Other species include Eurasian beaver, Alpine marmot, the European rabbit, Iberian lynx, Italian wolf, and Eurasian lynx. The peninsula is also a popular stopover for most migratory birds because it is Africa and Northern Europe’s closest stopover.
History Of Human Settlement In the Iberian Peninsula
Humans have been living on the Iberian Peninsula since over 1.2 million years ago. Neanderthals occupied the peninsula around 200,000 BP. However, early modern humans migrated to the peninsula approximately 40,000 years ago from Southern France. The Roman army occupied the peninsula around 213 BC after successfully fighting the Carthaginians. However, it took Rome 200 years to defeat the Iberians and Celtic and annex the peninsula. Thereafter, Hispania Province was established. The Romans occupied the Iberian Peninsula for 600 years.
The Germanic people, including Vandals, Suebi, and Alans began settling on the peninsula around the 5th century. The Visigoths arrived much later and occupied the whole of the peninsula, expelling other tribes except the Suebi people. However, around 584, they took control of the Suebi Kingdom, including Bracara (Braga).
In the early 8th century, Muslims, led by Tariq Ibn Ziyad conquered and occupied the peninsula except for the northern kingdom. The Muslims named the peninsula “Al-Andalus,” meaning “land of the Vandals.” The Muslim population included Arabs, Muladi, and Berbers. By the end of Muslim dominance on the peninsula (end of 15th century), the Iberian Peninsula had an estimated population of about 6.5 million people.
Important Population Centers
| Metropolitan region | State | Population (2019) |
|---|---|---|
| Madrid | Spain | 6,641,649 |
| Barcelona | Spain | 5,575,204 |
| Lisbon | Portugal | 2,846,332 |
| Valencia | Spain | 2,540,588 |
| Seville | Spain | 1,949,640 |
| Alicante-Elche | Spain | 1,862,780 |
| Porto | Portugal | 1,722,374 |
| Málaga-Marbella | Spain | 1,660,985 |
| Murcia-Cartagena | Spain | 1,487,663 |
| Cádiz | Spain | 1,249,739 |
| Bilbao | Spain | 1,137,191 |
| A Coruña | Spain | 1,122,006 |
| Oviedo-Gijón | Spain | 1,022,205 |
The Iberian Peninsula has an estimated population of 53 million people and is dominated by three main metropolises; Lisbon, Barcelona, and Madrid. Madrid is the largest metropolitan region, with a population of 6.6 million people. Barcelona has a population of about 5.6 million, while Lisbon has 2.8 million people. Portugal’s other populous city is Porto, with 1.7 million people. Valencia and Seville in Spain have a combined population of 4.5 million people.
Economy

Fish traps in red, green and blue and typical fishing boats in the port of Cascais, traditional fishing village in Portugal.
The peninsula’s economy largely depends on the economy of Spain and Portugal. These countries have some of the thriving industries in Europe, including fishing, tourism, and mining. Because of the long coastline, fishing is a popular economic activity, with major catches including tuna and sardines. Processed fish products from Spain and Portugal are exported to the global market through several companies, including Ramirez.
Portugal is the world’s leading producer of carob and cork. Besides, it also produces barley, corn, and wheat. Spain’s traditional agricultural products include cereal grains, vegetables, citrus fruits, and olive oil.
The Iberian Peninsula is one of the world’s most visited places. In 2017, Spain recorded over 80 million visitors, making it the 2nd most-visited country. Madrid is the home to World Tourism Organization. Portugal receives over 20 million visitors annually, making it one of the world’s most-visited countries.
Significant European minerals come from the peninsula. Portugal is notable for copper Uranium, and tin. It also has vast coal and iron reserves. Spain is one of the top renewable energy producers. Overall, the Iberian Peninsula countries have a combined GDP of over $1.6 trillion.