Generate an Explainability Report with the Automobile dataset using Contextual AI — Contextual AI documentation (original) (raw)
This notebook demonstrates how to generate an explainability report using the Contextual AI compiler.
Motivation¶
When it comes to putting your machine learning model into production, one may need to consider the following:
- How can you compare newly trained models with previous versions?
- How can you present your new model’s results to non-technical users (e.g. managers, business developers) in an intuitive manner?
- How can you establish trust between your machine learning model and its end-users?
The Contextual AI project attempts to address these questions by providing interpretability and explanations throughout the lifecycle of a ML solution, including: 1. The data itself, allowing for robust data validation and intuitive visualisations 2. The training/validation processes of model, allowing users to understand how well the model trained and which features were important 3. The predictions, allowing for users to understand why a model exhibited particular behavior
For more details, please refer to our whitepaper
Steps¶
- Train a model on the automobile dataset
- Evaluate the model’s performance with Contextual AI report
1. Performance Model Training¶
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import warnings
1.1 Loading Data¶
data = pd.read_csv("Automobile_data.csv") data.describe
<bound method NDFrame.describe of symboling normalized-losses make fuel-type aspiration
0 3 ? alfa-romero gas std
1 3 ? alfa-romero gas std
2 1 ? alfa-romero gas std
3 2 164 audi gas std
4 2 164 audi gas std
.. ... ... ... ... ...
200 -1 95 volvo gas std
201 -1 95 volvo gas turbo
202 -1 95 volvo gas std
203 -1 95 volvo diesel turbo
204 -1 95 volvo gas turbo
num-of-doors body-style drive-wheels engine-location wheel-base ... \0 two convertible rwd front 88.6 ... 1 two convertible rwd front 88.6 ... 2 two hatchback rwd front 94.5 ... 3 four sedan fwd front 99.8 ... 4 four sedan 4wd front 99.4 ... .. ... ... ... ... ... ... 200 four sedan rwd front 109.1 ... 201 four sedan rwd front 109.1 ... 202 four sedan rwd front 109.1 ... 203 four sedan rwd front 109.1 ... 204 four sedan rwd front 109.1 ...
engine-size fuel-system bore stroke compression-ratio horsepower \0 130 mpfi 3.47 2.68 9.0 111 1 130 mpfi 3.47 2.68 9.0 111 2 152 mpfi 2.68 3.47 9.0 154 3 109 mpfi 3.19 3.4 10.0 102 4 136 mpfi 3.19 3.4 8.0 115 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... 200 141 mpfi 3.78 3.15 9.5 114 201 141 mpfi 3.78 3.15 8.7 160 202 173 mpfi 3.58 2.87 8.8 134 203 145 idi 3.01 3.4 23.0 106 204 141 mpfi 3.78 3.15 9.5 114
peak-rpm city-mpg highway-mpg price0 5000 21 27 13495 1 5000 21 27 16500 2 5000 19 26 16500 3 5500 24 30 13950 4 5500 18 22 17450 .. ... ... ... ... 200 5400 23 28 16845 201 5300 19 25 19045 202 5500 18 23 21485 203 4800 26 27 22470 204 5400 19 25 22625
[205 rows x 26 columns]>
1.2 Quick Check¶
symboling 0 normalized-losses 0 make 0 fuel-type 0 aspiration 0 num-of-doors 0 body-style 0 drive-wheels 0 engine-location 0 wheel-base 0 length 0 width 0 height 0 curb-weight 0 engine-type 0 num-of-cylinders 0 engine-size 0 fuel-system 0 bore 0 stroke 0 compression-ratio 0 horsepower 0 peak-rpm 0 city-mpg 0 highway-mpg 0 price 0 dtype: int64
1.3 Feature quantity engineering¶
#normalized-losses a=data[data['normalized-losses']!='?'] b=(a['normalized-losses'].astype(int)).mean() data['normalized-losses']=data['normalized-losses'].replace('?',b).astype(int)
#num-of-doors a=data[data['body-style']=='sedan'] a['num-of-doors'].value_counts() a=data['num-of-doors'].map({'two':2,'four':4,'?':4}) data['num-of-doors']=a
#price a=data[data['price']!='?'] b=(a['price'].astype(int)).mean() data['price']=data['price'].replace('?',b).astype(int)
#horse power a=data[data['horsepower']!='?'] b=(a['horsepower'].astype(int)).mean() data['horsepower']=data['horsepower'].replace('?',b).astype(int)
#bore a=data[data['bore']!='?'] b=(a['bore'].astype(float)).mean() data['bore']=data['bore'].replace('?',b).astype(float)
#stroke a=data[data['stroke']!='?'] b=(a['stroke'].astype(float)).mean() data['stroke']=data['stroke'].replace('?',b).astype(float)
#peak-rpm a=data[data['peak-rpm']!='?'] b=(a['peak-rpm'].astype(float)).mean() data['peak-rpm']=data['peak-rpm'].replace('?',b).astype(float)
#num-of-cylinders a=data['num-of-cylinders'].map({'four':4,'five':5,'six':6,'?':4}) data['num-of-doors']=a
data.describe()
| symboling | normalized-losses | num-of-doors | wheel-base | length | width | height | curb-weight | engine-size | bore | stroke | compression-ratio | horsepower | peak-rpm | city-mpg | highway-mpg | price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 194.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 | 205.000000 |
| mean | 0.834146 | 122.000000 | 4.304124 | 98.756585 | 174.049268 | 65.907805 | 53.724878 | 2555.565854 | 126.907317 | 3.329751 | 3.255423 | 10.142537 | 104.253659 | 5125.369458 | 25.219512 | 30.751220 | 13207.126829 |
| std | 1.245307 | 31.681008 | 0.679289 | 6.021776 | 12.337289 | 2.145204 | 2.443522 | 520.680204 | 41.642693 | 0.270844 | 0.313597 | 3.972040 | 39.519219 | 476.979093 | 6.542142 | 6.886443 | 7868.768212 |
| min | -2.000000 | 65.000000 | 4.000000 | 86.600000 | 141.100000 | 60.300000 | 47.800000 | 1488.000000 | 61.000000 | 2.540000 | 2.070000 | 7.000000 | 48.000000 | 4150.000000 | 13.000000 | 16.000000 | 5118.000000 |
| 25% | 0.000000 | 101.000000 | 4.000000 | 94.500000 | 166.300000 | 64.100000 | 52.000000 | 2145.000000 | 97.000000 | 3.150000 | 3.110000 | 8.600000 | 70.000000 | 4800.000000 | 19.000000 | 25.000000 | 7788.000000 |
| 50% | 1.000000 | 122.000000 | 4.000000 | 97.000000 | 173.200000 | 65.500000 | 54.100000 | 2414.000000 | 120.000000 | 3.310000 | 3.290000 | 9.000000 | 95.000000 | 5200.000000 | 24.000000 | 30.000000 | 10595.000000 |
| 75% | 2.000000 | 137.000000 | 4.000000 | 102.400000 | 183.100000 | 66.900000 | 55.500000 | 2935.000000 | 141.000000 | 3.580000 | 3.410000 | 9.400000 | 116.000000 | 5500.000000 | 30.000000 | 34.000000 | 16500.000000 |
| max | 3.000000 | 256.000000 | 6.000000 | 120.900000 | 208.100000 | 72.300000 | 59.800000 | 4066.000000 | 326.000000 | 3.940000 | 4.170000 | 23.000000 | 288.000000 | 6600.000000 | 49.000000 | 54.000000 | 45400.000000 |
1.4 Understanding the range of important features¶¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.style.use('seaborn') import seaborn as sns
data[['engine-size','peak-rpm','curb-weight','horsepower','price','highway-mpg']].hist(figsize=(10,8),bins=6,color='g',linewidth='3',edgecolor='k') plt.tight_layout()
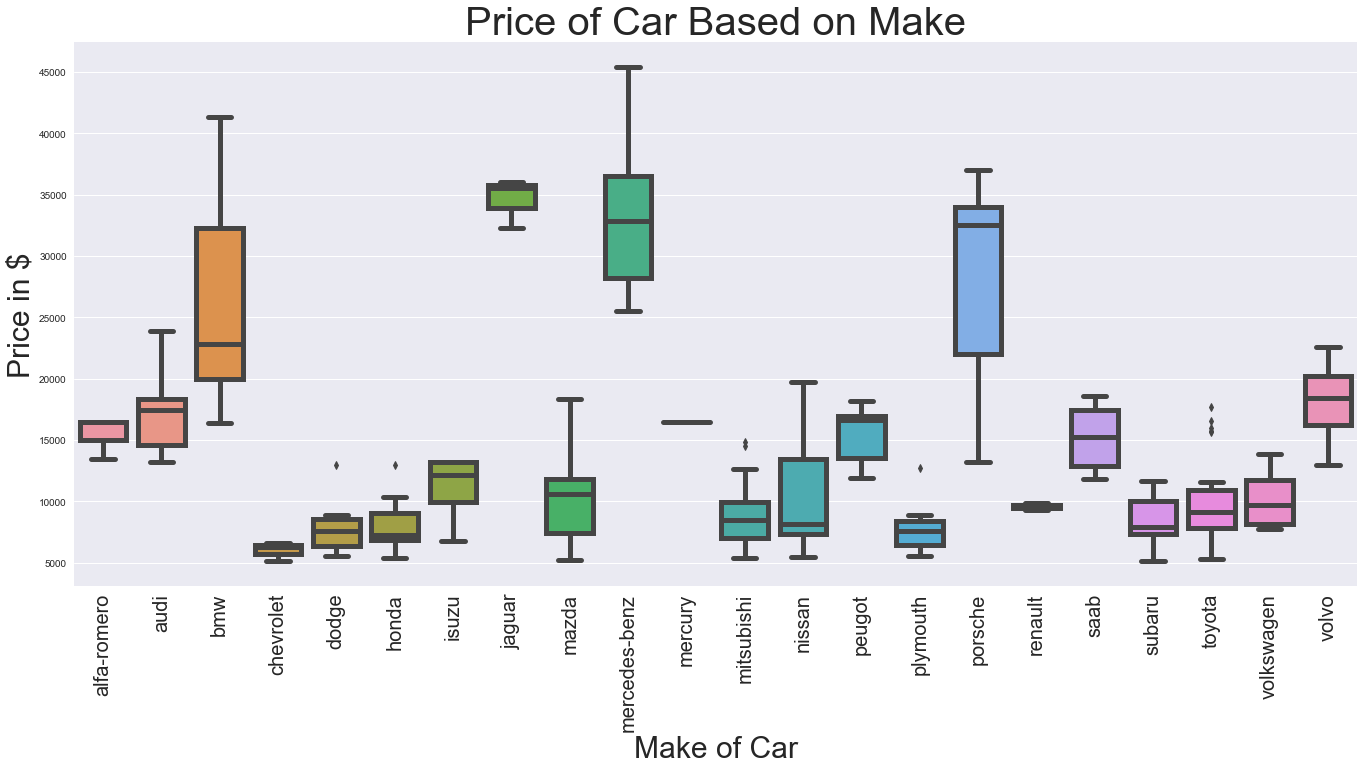
1.5 Getting the Price of car based on make¶
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize']=(23,10) ax = sns.boxplot(x="make", y="price", data=data,width=0.8,linewidth=5) ax.set_xlabel('Make of Car',fontsize=30) ax.set_ylabel('Price in $',fontsize=30) plt.title('Price of Car Based on Make',fontsize=40) ax.tick_params(axis='x',labelsize=20,rotation=90)
1.6 Data split¶
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x = data[['curb-weight','engine-size','horsepower','width']] y = data['price']
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2)
x_train.to_csv("train_data.csv", index=False) x_train.head()
| curb-weight | engine-size | horsepower | width | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 165 | 2265 | 98 | 112 | 64.0 |
| 41 | 2465 | 110 | 101 | 65.2 |
| 120 | 1967 | 90 | 68 | 63.8 |
| 161 | 2122 | 98 | 70 | 64.4 |
| 140 | 2240 | 108 | 73 | 63.8 |
1.7 Model Training¶
import pickle from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier model = DecisionTreeClassifier() model.fit(x_train,y_train)
pkl = open('model.pkl', 'wb') pickle.dump(model, pkl) model = None
1.5 ML load model and evaluation¶
model_pkl = open('model.pkl', 'rb') model = pickle.load(model_pkl)
accuracy = round(model.score(x_train, y_train) * 100, 2) print("Model Accuracy: ", accuracy)
2. Involve Contextual AI complier¶
import os import sys sys.path.append('../../../') from xai.compiler.base import Configuration, Controller
2.1 Specify config file¶
json_config = 'basic-report.json'
2.2 Initial compiler controller with config¶
controller = Controller(config=Configuration(json_config)) print(controller.config)
{'name': 'Report for Automobile Dataset', 'overview': True, 'content_table': True, 'contents': [{'title': 'Feature Importance Analysis', 'desc': 'This section provides the analysis on feature', 'sections': [{'title': 'Feature Importance Ranking', 'component': {'_comment': 'refer to document section xxxx', 'class': 'FeatureImportanceRanking', 'attr': {'trained_model': 'model.pkl', 'train_data': 'train_data.csv'}}}]}, {'title': 'Data Statistics Analysis', 'desc': 'This section provides the analysis on data', 'sections': [{'title': 'Simple Data Statistic', 'component': {'_comment': 'refer to document section xxxx', 'class': 'DataStatisticsAnalysis', 'attr': {'data': 'Automobile_data.csv'}}}]}], 'writers': [{'class': 'Pdf', 'attr': {'name': 'automobile-basic-report'}}]}
2.2 Finally compiler render¶
../../../xai/data/helper.py:189: UserWarning: Warning: the feature [price] is suspected to be identifiable feature. [Examples]: ['13495', '16500', '16500', '13950', '17450']
'[Examples]: %s\n' % (column, col_data.tolist()[:5]))
Result¶
print("report generated : %s/automobile-basic-report.pdf" % os.getcwd())
report generated : /Users/i062308/Development/Explainable_AI/tutorials/compiler/automobile/automobile-basic-report.pdf