Encrypting Amazon Aurora resources - Amazon Aurora (original) (raw)
Amazon Aurora can encrypt your Amazon Aurora DB clusters. Data that is encrypted at rest includes the underlying storage for DB clusters, its automated backups, read replicas, and snapshots.
Amazon Aurora encrypted DB clusters use the industry standard AES-256 encryption algorithm to encrypt your data on the server that hosts your Amazon Aurora DB clusters. After your data is encrypted, Amazon Aurora handles authentication of access and decryption of your data transparently with a minimal impact on performance. You don't need to modify your database client applications to use encryption.
Note
For encrypted and unencrypted DB clusters, data that is in transit between the source and the read replicas is encrypted, even when replicating across AWS Regions.
Topics
- Overview of encrypting Amazon Aurora resources
- Encrypting an Amazon Aurora DB cluster
- Determining whether encryption is turned on for a DB cluster
- Availability of Amazon Aurora encryption
- Encryption in transit
- Limitations of Amazon Aurora encrypted DB clusters
Overview of encrypting Amazon Aurora resources
Amazon Aurora encrypted DB clusters provide an additional layer of data protection by securing your data from unauthorized access to the underlying storage. You can use Amazon Aurora encryption to increase data protection of your applications deployed in the cloud, and to fulfill compliance requirements for encryption at rest. For an Amazon Aurora encrypted DB cluster, all DB instances, logs, backups, and snapshots are encrypted. For more information about the availability and limitations of encryption, see Availability of Amazon Aurora encryption and Limitations of Amazon Aurora encrypted DB clusters.
Amazon Aurora uses an AWS Key Management Service key to encrypt these resources. AWS KMS combines secure, highly available hardware and software to provide a key management system scaled for the cloud. You can use an AWS managed key, or you can create customer managed keys.
When you create an encrypted DB cluster, you can choose a customer managed key or the AWS managed key for Amazon Aurora to encrypt your DB cluster. If you don't specify the key identifier for a customer managed key, Amazon Aurora uses the AWS managed key for your new DB cluster. Amazon Aurora creates an AWS managed key for Amazon Aurora for your AWS account. Your AWS account has a different AWS managed key for Amazon Aurora for each AWS Region.
To manage the customer managed keys used for encrypting and decrypting your Amazon Aurora resources, you use the AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS).
Using AWS KMS, you can create customer managed keys and define the policies to control the use of these customer managed keys. AWS KMS supports CloudTrail, so you can audit KMS key usage to verify that customer managed keys are being used appropriately. You can use your customer managed keys with Amazon Aurora and supported AWS services such as Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, and Amazon Redshift. For a list of services that are integrated with AWS KMS, see AWS Service Integration. Some considerations about using KMS keys:
- Once you have created an encrypted DB instance, you can't change the KMS key used by that DB instance. Therefore, be sure to determine your KMS key requirements before you create your encrypted DB instance.
If you must change the encryption key for your DB cluster, create a manual snapshot of your cluster and enable encryption while copying the snapshot. For more information, see re:Post Knowledge article. - If you copy an encrypted snapshot, you can use a different KMS key to encrypt the target snapshot than the one that was used to encrypt the source snapshot.
- You can't share a snapshot that has been encrypted using the AWS managed key of the AWS account that shared the snapshot.
- Each DB instance in the DB cluster is encrypted using the same KMS key as the DB cluster.
- You can also encrypt a read replica of an Amazon Aurora encrypted cluster.
Important
Amazon Aurora can lose access to the KMS key for a DB cluster when you disable the KMS key. In these cases, the encrypted DB cluster goes intoinaccessible-encryption-credentials-recoverable state. The DB cluster remains in this state for seven days, during which the instance is stopped. API calls made to the DB cluster during this time might not succeed. To recover the DB cluster, enable the KMS key and restart this DB cluster. Enable the KMS key from the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI, or RDS API. Restart the DB cluster using the AWS CLI command start-db-cluster or AWS Management Console.
The inaccessible-encryption-credentials-recoverable state only applies to DB clusters that can stop. This recoverable state is not applicable to instances that can't stop, such as clusters with cross-Region read replicas. For more information, see Limitations for stopping and starting Aurora DB clusters.
If the DB cluster isn't recovered within seven days, it goes into the terminalinaccessible-encryption-credentials state. In this state, the DB cluster is not usable anymore and you can only restore the DB cluster from a backup. We strongly recommend that you always turn on backups for encrypted DB clusters to guard against the loss of encrypted data in your databases.
During the creation of a DB cluster, Aurora checks if the calling principal has access to the KMS key and generates a grant from the KMS key that it uses for the entire lifetime of the DB cluster. Revoking the calling principals access to the KMS key does not affect a running database. When using KMS keys in cross-account scenarios, such as copying a snapshot to another account, the KMS key needs to be shared with the other account. If you create a DB cluster from the snapshot without specifying a different KMS key, the new cluster uses the KMS key from the source account. Revoking access to the key after you create the DB cluster does not affect the cluster. However, disabling the key impacts all DB clusters encrypted with that key. To prevent this, specify a different key during the snapshot copy operation.
For more information about KMS keys, see AWS KMS keys in the_AWS Key Management Service Developer Guide_ and AWS KMS key management.
Encrypting an Amazon Aurora DB cluster
To encrypt a new DB cluster, choose Enable encryption on the console. For information on creating a DB cluster, see Creating an Amazon Aurora DB cluster.
If you use the create-db-cluster AWS CLI command to create an encrypted DB cluster, set the --storage-encrypted parameter. If you use theCreateDBCluster API operation, set theStorageEncrypted parameter to true.
Once you have created an encrypted DB cluster, you can't change the KMS key used by that DB cluster. Therefore, be sure to determine your KMS key requirements before you create your encrypted DB cluster.
If you use the AWS CLI create-db-cluster command to create an encrypted DB cluster with a customer managed key, set the --kms-key-id parameter to any key identifier for the KMS key. If you use the Amazon RDS APICreateDBInstance operation, set the KmsKeyId parameter to any key identifier for the KMS key. To use a customer managed key in a different AWS account, specify the key ARN or alias ARN.
Determining whether encryption is turned on for a DB cluster
You can use the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI, or RDS API to determine whether encryption at rest is turned on for a DB cluster.
To determine whether encryption at rest is turned on for a DB cluster
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console athttps://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/.
- In the navigation pane, chooseDatabases.
- Choose the name of the DB cluster that you want to check to view its details.
- Choose the Configuration tab and check the Encryption value.
It shows either Enabled orNot enabled.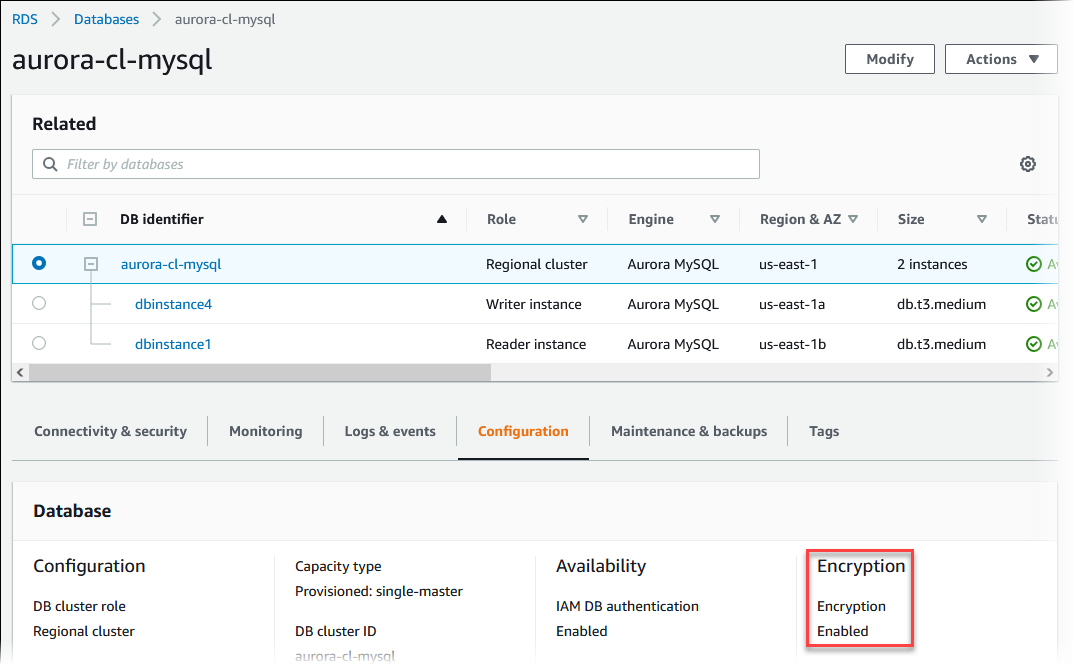
To determine whether encryption at rest is turned on for a DB cluster by using the AWS CLI, call the describe-db-clusters command with the following option:
--db-cluster-identifier– The name of the DB cluster.
The following example uses a query to return eitherTRUE or FALSE regarding encryption at rest for the mydb DB cluster.
Example
aws rds describe-db-clusters --db-cluster-identifier mydb --query "*[].{StorageEncrypted:StorageEncrypted}" --output textTo determine whether encryption at rest is turned on for a DB cluster by using the Amazon RDS API, call the DescribeDBClusters operation with the following parameter:
DBClusterIdentifier– The name of the DB cluster.
Availability of Amazon Aurora encryption
Amazon Aurora encryption is currently available for all database engines and storage types.
Note
Amazon Aurora encryption is not available for the db.t2.micro DB instance class.
Encryption in transit
Encryption at the physical layer
All data flowing accross AWS Regions over the AWS global network is automatically encrypted at the physical layer before it leaves AWS secured facilities. All traffic between AZs is encrypted. Additional layers of encryption, including those listed in this section may provide additional protections.
Encryption provided by Amazon VPC peering and Transit Gateway cross-Region peering
All cross-Region traffic that uses Amazon VPC and Transit Gateway peering is automatically bulk-encrypted when it exits a Region. An additional layer of encryption is automatically provided at the physical layer for all traffic before it leaves AWS secured facilities.
Encryption between instances
AWS provides secure and private connectivity between DB instances of all types. In addition, some instance types use the offload capabilities of the underlying Nitro System hardware to automatically encrypt in-transit traffic between instances. This encryption uses Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data (AEAD) algorithms, with 256-bit encryption. There is no impact on network performance. To support this additional in-transit traffic encryption between instances, the following requirements must be met:
- The instances use the following instance types:
- General purpose: M6i, M6id, M6in, M6idn, M7g
- Memory optimized: R6i, R6id, R6in, R6idn, R7g, X2idn, X2iedn, X2iezn
- The instances are in the same AWS Region.
- The instances are in the same VPC or peered VPCs, and the traffic does not pass through a virtual network device or service, such as a load balancer or a transit gateway.
Limitations of Amazon Aurora encrypted DB clusters
The following limitations exist for Amazon Aurora encrypted DB clusters:
- You can't turn off encryption on an encrypted DB cluster.
- You can't create an encrypted snapshot of an unencrypted DBcluster.
- A snapshot of an encrypted DB cluster must be encrypted using the same KMS key as the DB cluster.
- You can't convert an unencrypted DB cluster to an encrypted one. However, you can restore an unencrypted snapshot to an encrypted Aurora DB cluster. To do this, specify a KMS key when you restore from the unencrypted snapshot.
- You can't create an encrypted Aurora Replica from an unencrypted Aurora DB cluster. You can't create an unencrypted Aurora Replica from an encrypted Aurora DB cluster.
- To copy an encrypted snapshot from one AWS Region to another, you must specify the KMS key in the destination AWS Region. This is because KMS keys are specific to the AWS Region that they are created in.
The source snapshot remains encrypted throughout the copy process.Amazon Aurora uses envelope encryption to protect data during the copy process. For more information about envelope encryption, see Envelope encryption in the AWS Key Management Service Developer Guide. - You can't unencrypt an encrypted DB cluster. However, you can export data from an encrypted DB cluster and import the data into an unencrypted DB cluster.