Introduction to Java UDFs | Snowflake Documentation (original) (raw)
You can write the handler for a user-defined function (UDF) in Java. Topics in this section describe how to design and write a Java handler. You’ll also find examples.
For an introduction to UDFs, including a list of languages in which you can write a UDF handler, refer to User-defined functions overview.
Once you have a handler, you create the UDF with SQL. For information on using SQL to create or call a UDF, refer toCreating a user-defined function or Executing a UDF.
Snowflake currently supports writing UDFs in the following versions of Java:
- 11.x
- 17.x
How a Java handler works¶
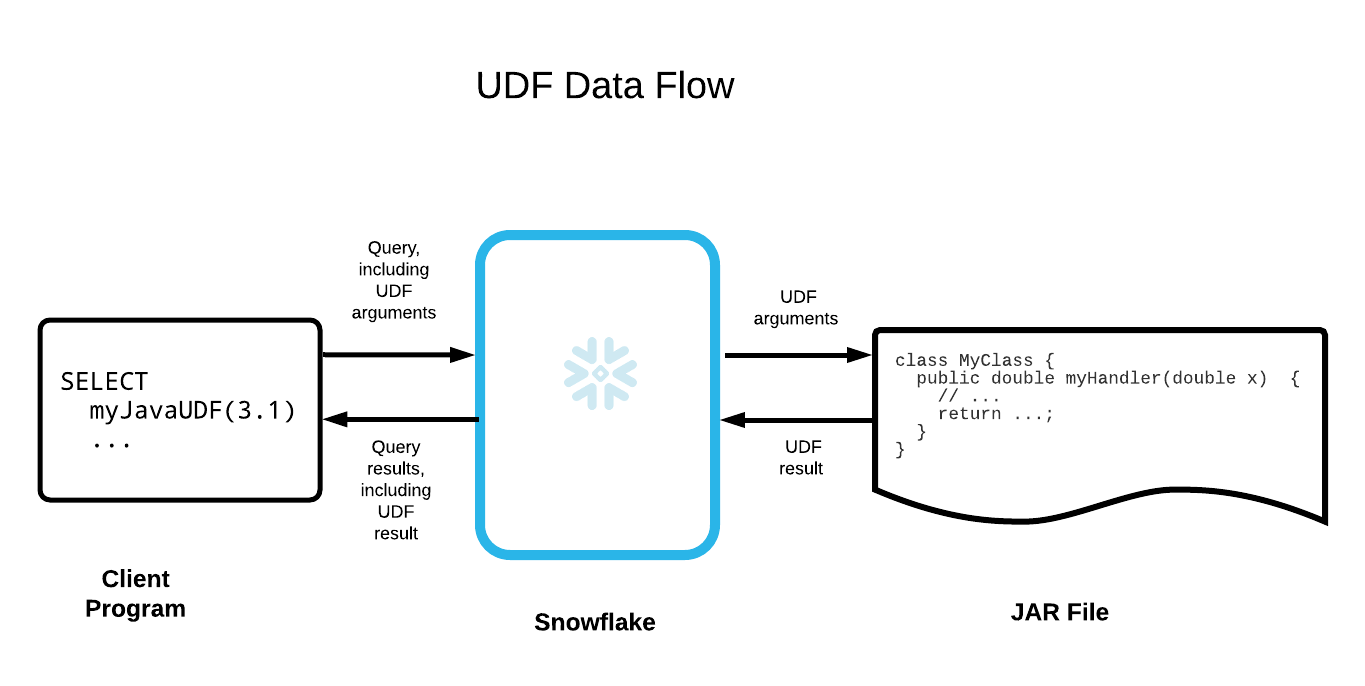
When a user calls a UDF, the user passes UDF’s name and arguments to Snowflake. Snowflake calls the associated handler code (with arguments, if any) to execute the UDF’s logic. The handler method then returns the output to Snowflake, which passes it back to the client.
For each row passed to a UDF, the UDF returns either a scalar (i.e. single) value or, if defined as a table function, a set of rows.
Java UDFs can contain both new code and calls to existing libraries, allowing you both flexibility and code reuse. For example, if you already have data analysis code in Java, then you can probably incorporate that into a Java UDF.
Below is a simplified illustration of the data flow:
Example¶
Code in the following example creates a UDF called echo_varchar with a handler method TestFunc.echoVarchar. The Java argument and return types are converted to and from SQL by Snowflake according to mappings described inSQL-Java Data Type Mappings.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION echo_varchar(x VARCHAR) RETURNS VARCHAR LANGUAGE JAVA CALLED ON NULL INPUT HANDLER = 'TestFunc.echoVarchar' TARGET_PATH = '@~/testfunc.jar' AS 'class TestFunc { public static String echoVarchar(String x) { return x; } }';
Design considerations¶
Keep in mind the following for designing a useful handler.
- General considerations. For considerations common to UDFs and procedures, refer toDesign Guidelines and Constraints for Functions and Procedures.
- SQL-Java type mapping. When exchanging argument and return values with a UDF, Snowflake converts between the handler language and SQL. For more information on choosing data types for your handler code, refer to Choosing your data types.
- Code packaging. You can make your handler code available either in-line with the CREATE FUNCTION statement or on a stage as compiled code in a JAR. For more information on the difference, refer to Keeping handler code in-line or on a stage.
- Code optimization. For information about optimizing your handler code, such as when the code handles state shared across rows, refer toOptimizing initialization and controlling global state in scalar UDFs.
- Best practices. For information about best practices, refer to Following best practices andSecurity Practices for UDFs and Procedures.
Handler coding¶
From basics to detailed examples, the following topics describe how to write a UDF handler in Java.
- Java class definition. You write the logic for a UDF in a Java class. For more about how Snowflake interacts with your code, refer toDesigning the class.
- Error handling. For information about how Snowflake surfaces errors generated by handlers, refer toHandling errors.
- Tabular return values. You can return tabular values as well as scalar (single) values from a UDF. For information on how to write a handler that returns tabular values, refer to Tabular Java UDFs (UDTFs).
- Logging and event tracing. For information on capturing log and trace data as your handler code executes, refer toLogging, tracing, and metrics.
- Dependencies. You can make dependences available to your code at run time by uploading them to a stage. For more informaiton, refer to Making dependencies available to your code.
- Handler files organization. If you intend to package compiled handler code into a JAR file, organize and build your code using the suggestions in Organizing your files.
- Code examples For a range of handler examples in Java, refer to Java UDF handler examples.