debug-io, error-output, query-io, standard-input, standard-output, trace-output (original) (raw)
ANSI Common Lisp  21 Streams
21 Streams  21.2 Dictionary of Streams
21.2 Dictionary of Streams
| 21.2.53 *debug-io*, *error-output*, *query-io*, *standard-input*, *standard-output*, *trace-output* | Variable |
|---|
Value Type:
For *standard-input*: an input stream
For *error-output*, *standard-output*, and *trace-output*: an output stream.
For *debug-io*, *query-io*: a bidirectional stream.
Initial Value:
implementation-dependent, but it must be an open _stream_that is not a _generalized synonym stream_to an _I/O customization variables_but that might be a generalized synonym stream to the value of some I/O customization variable. The initial value might also be a _generalized synonym stream_to either the symbol *terminal-io* or to the _stream_that is its value.
Description:
These variables are collectively called the_standardized_ I/O customization variables. They can be bound or assigned in order to change the default destinations for input and/or output used by various standardized operators and facilities.
The value of *debug-io*, called debug I/O, is a stream to be used for interactive debugging purposes.
The value of *error-output*, called error output, is a stream to which warnings and non-interactive error messages should be sent.
The value of *query-io*, called query I/O, is a bidirectional _stream_to be used when asking questions of the user. The question should be output to this stream, and the answer read from it.
The value of *standard-input*, called standard input, is a stream that is used by many _operators_as a default source of input when no specific input _stream_is explicitly supplied.
The value of *standard-output*, called standard output, is a stream that is used by many _operators_as a default destination for output when no specific output _stream_is explicitly supplied.
The value of *trace-output*, called trace output, is the stream on which traced functions (see trace) and the time macro print their output.
Examples:
(with-output-to-string (error-output)
(warn "this string is sent to error-output"))
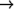 "Warning: this string is sent to error-output
" ;The exact format of this string is implementation-dependent.
"Warning: this string is sent to error-output
" ;The exact format of this string is implementation-dependent.
(with-input-from-string (standard-input "1001")
(+ 990 (read))) 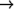 1991
1991
(progn (setq out (with-output-to-string (standard-output)
(print "print and format t send things to")
(format t "standard-output now going to a string")))
:done)
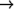 :DONE
out
:DONE
out
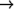 "
"print and format t send things to" standard-output now going to a string"
"
"print and format t send things to" standard-output now going to a string"
(defun fact (n) (if (< n 2) 1 (* n (fact (- n 1)))))
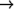 FACT
(trace fact)
FACT
(trace fact)
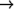 (FACT)
;; Of course, the format of traced output is implementation-dependent.
(with-output-to-string (trace-output)
(fact 3))
(FACT)
;; Of course, the format of traced output is implementation-dependent.
(with-output-to-string (trace-output)
(fact 3))
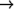 "
1 Enter FACT 3
| 2 Enter FACT 2
| 3 Enter FACT 1
| 3 Exit FACT 1
| 2 Exit FACT 2
1 Exit FACT 6"
"
1 Enter FACT 3
| 2 Enter FACT 2
| 3 Enter FACT 1
| 3 Exit FACT 1
| 2 Exit FACT 2
1 Exit FACT 6"
See Also:
*terminal-io*,synonym-stream,time,trace, Chapter 9 Conditions, Chapter 23 Reader, Chapter 22 Printer
Notes:
The intent of the constraints on the initial _value_of the I/O customization variables is to ensure that it is always safe to bind or assign such a variable to the value of another I/O customization variable, without unduly restricting implementation flexibility.
It is common for an implementation to make the initial values of *debug-io* and *query-io*be the same stream, and to make the initial values of *error-output* and *standard-output*be the same stream.
The functions y-or-n-p and yes-or-no-p use _query I/O_for their input and output.
In the normal Lisp read-eval-print loop, input is read from standard input. Many input functions, including read and read-char, take a stream argument that defaults to standard input.
In the normal Lisp read-eval-print loop, output is sent to standard output. Many output functions, including print and write-char, take a stream argument that defaults to standard output.
A program that wants, for example, to divert output to a file should do so by binding *standard-output*; that way error messages sent to*error-output* can still get to the user by going through*terminal-io* (if *error-output* is bound to *terminal-io*), which is usually what is desired.
Allegro CL Implementation Details:
None.