define-condition (original) (raw)
ANSI Common Lisp  9 Conditions
9 Conditions  9.2 Dictionary of Conditions
9.2 Dictionary of Conditions
| 9.2.29 define-condition | Macro |
|---|
Syntax:
define-condition name ({parent-type}*) ({slot-spec}*) {option}*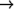 name
name
| slot-spec::= | slot-name | (slot-name 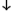 slot-option) slot-option) |
|---|
| slot-option::= | [[{:reader symbol}* | |
|---|---|
{:writer 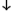 function-name}* | function-name}* | |
|
| {:accessor symbol}* | | |
{:allocation 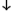 allocation-type} | allocation-type} | |
|
| {:initarg symbol}* | | |
| {:initform form} | | |
| {:type type-specifier}]] |
| option::= | [[(:default-initargs . initarg-list) | |
|---|---|
| (:documentation string) | | |
| (:report report-name)]] |
| allocation-type::= | :instance | :class |
|---|
Arguments and Values:
name - a symbol.
parent-type - a symbol naming a condition type. If no parent-types are supplied, the parent-types default to (condition).
default-initargs - a list of keyword/value pairs.
Slot-spec -- the name of a slot or a _list_consisting of the slot-name followed by zero or more slot-options.
Slot-name -- a slot name (a symbol), the list of a slot name, or the list of slot name/slot form pairs.
Option -- Any of the following:
- :reader
:reader can be supplied more than once for a given _slot_and cannot be nil. - :writer
:writer can be supplied more than once for a given _slot_and must name a generic function. - :accessor
:accessor can be supplied more than once for a given _slot_and cannot be nil. - :allocation
:allocation can be supplied once at most for a given slot. The default if :allocation is not supplied is :instance. - :initarg
:initarg can be supplied more than once for a given slot. - :initform
:initform can be supplied once at most for a given slot. - :type
:type can be supplied once at most for a given slot. - :documentation
:documentation can be supplied once at most for a given slot. - :report
:report can be supplied once at most.
Description:
define-condition defines a new condition type called name, which is a subtype of the type or types named by_parent-type_. Each parent-type argument specifies a direct _supertype_of the new condition. The new conditioninherits slots and methods from each of its directsupertypes, and so on.
If a slot name/slot form pair is supplied, the slot form is a form that can be evaluated by make-condition to produce a default value when an explicit value is not provided. If no slot form is supplied, the contents of the _slot_is initialized in an implementation-dependent way.
If the type being defined and some other type from which it inherits have a slot by the same name, only one slot is allocated in the_condition_, but the supplied slot form overrides any slot form that might otherwise have been inherited from a parent-type. If no slot form is supplied, the inherited slot form (if any) is still visible.
Accessors are created according to the same rules as used by defclass.
A description of slot-options follows:
- :reader
The :reader slot option specifies that an unqualified method is to be defined on the generic function named by the argument to :reader to read the value of the given slot. - The :initform slot option is used to provide a default initial value form to be used in the initialization of the slot. This_form_ is evaluated every time it is used to initialize the slot. The_lexical environmentin which this form is evaluated is the lexicalenvironment_ in which the define-conditionform was evaluated. Note that the lexical environment refers both to variables and to_functions. For local slots, the dynamic environment is the dynamicenvironment_in which make-condition was called; for shared slots, the _dynamic environment_is the dynamic environment in which thedefine-condition form was evaluated.
No implementation is permitted to extend the syntax of define-conditionto allow (slot-name form) as an abbreviation for(slot-name :initform form). - :initarg
The :initarg slot option declares an initialization argument named by its symbol argument and specifies that this initialization argument initializes the given slot. If the initialization argument has a value in the call to initialize-instance, the value is stored into the given slot, and the slot's :initform slot option, if any, is not evaluated. If none of the initialization arguments specified for a given slot has a value, the slot is initialized according to the:initform slot option, if specified. - :type
The :type slot option specifies that the contents of the_slot_ is always of the specified type. It effectively declares the result type of the reader generic function when applied to an object of this condition type. The consequences of attempting to store in a_slot_ a value that does not satisfy the type of the slot is undefined. - :default-initargs
This option is treated the same as it would be defclass. - :documentation
The :documentation slot option provides a _documentation string_for the slot. - :report
Condition reporting is mediated through the print-objectmethod for the condition type in question, with *print-escape*always being nil. Specifying (:report report-name)in the definition of a condition type C is equivalent to:
(defmethod print-object ((x c) stream)
(if print-escape (call-next-method) (report-name x stream)))
If the value supplied by the argument to :report (report-name) is a symbol or a lambda expression, it must be acceptable to function. (function report-name)is evaluated in the current lexical environment. It should return a functionof two arguments, a condition and a stream, that prints on the stream a description of the condition. This function is called whenever thecondition is printed while *print-escape* is nil.
If report-name is a string, it is a shorthand for
(lambda (condition stream)
(declare (ignore condition))
(write-string report-name stream))
This option is processed after the new condition type has been defined, so use of the slot accessors within the :report function is permitted. If this option is not supplied, information about how to report this type of condition is inherited from the parent-type.
The consequences are unspecifed if an attempt is made to read a slot that has not been explicitly initialized and that has not been given a default value.
The consequences are unspecified if an attempt is made to assign the_slots_ by using setf.
If a define-condition form appears as a top level form, the compiler must make name recognizable as a valid type name, and it must be possible to reference the condition type as the_parent-type_ of another condition type in a subsequentdefine-condition form in the file being compiled.
Examples:
The following form defines a condition of type peg/hole-mismatch which inherits from a condition type called blocks-world-error:
(define-condition peg/hole-mismatch (blocks-world-error) ((peg-shape :initarg :peg-shape :reader peg/hole-mismatch-peg-shape) (hole-shape :initarg :hole-shape :reader peg/hole-mismatch-hole-shape)) (:report (lambda (condition stream) (format stream "A ~A peg cannot go in a ~A hole." (peg/hole-mismatch-peg-shape condition) (peg/hole-mismatch-hole-shape condition)))))
The new type has slots peg-shape and hole-shape, so make-condition accepts :peg-shape and :hole-shape keywords. The readers peg/hole-mismatch-peg-shape and peg/hole-mismatch-hole-shapeapply to objects of this type, as illustrated in the :report information.
The following form defines a condition type named machine-errorwhich inherits from error:
(define-condition machine-error (error) ((machine-name :initarg :machine-name :reader machine-error-machine-name)) (:report (lambda (condition stream) (format stream "There is a problem with ~A." (machine-error-machine-name condition)))))
Building on this definition, a new error condition can be defined which is a subtype of machine-error for use when machines are not available:
(define-condition machine-not-available-error (machine-error) () (:report (lambda (condition stream) (format stream "The machine ~A is not available." (machine-error-machine-name condition)))))
This defines a still more specific condition, built upon machine-not-available-error, which provides a slot initialization form for machine-name but which does not provide any new slots or report information. It just gives the machine-name slot a default initialization:
(define-condition my-favorite-machine-not-available-error (machine-not-available-error) ((machine-name :initform "mc.lcs.mit.edu")))
Note that since no :report clause was given, the information inherited from machine-not-available-error is used to report this type of condition.
(define-condition ate-too-much (error)
((person :initarg :person :reader ate-too-much-person)
(weight :initarg :weight :reader ate-too-much-weight)
(kind-of-food :initarg :kind-of-food
:reader :ate-too-much-kind-of-food)))
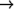 ATE-TOO-MUCH
(define-condition ate-too-much-ice-cream (ate-too-much)
((kind-of-food :initform 'ice-cream)
(flavor :initarg :flavor
:reader ate-too-much-ice-cream-flavor
:initform 'vanilla ))
(:report (lambda (condition stream)
(format stream "
ATE-TOO-MUCH
(define-condition ate-too-much-ice-cream (ate-too-much)
((kind-of-food :initform 'ice-cream)
(flavor :initarg :flavor
:reader ate-too-much-ice-cream-flavor
:initform 'vanilla ))
(:report (lambda (condition stream)
(format stream "A ate too much ~A ice-cream"
(ate-too-much-person condition)
(ate-too-much-ice-cream-flavor condition)))))
A" *)
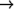 ATE-TOO-MUCH-ICE-CREAM
(make-condition 'ate-too-much-ice-cream
:person 'fred
:weight 300
:flavor 'chocolate)
ATE-TOO-MUCH-ICE-CREAM
(make-condition 'ate-too-much-ice-cream
:person 'fred
:weight 300
:flavor 'chocolate)
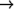 #<ATE-TOO-MUCH-ICE-CREAM 32236101>
(format t "
#<ATE-TOO-MUCH-ICE-CREAM 32236101>
(format t "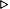 FRED ate too much CHOCOLATE ice-cream
FRED ate too much CHOCOLATE ice-cream
 NIL
NIL
See Also:
make-condition, defclass, Section 9.1 Condition System Concepts
Allegro CL Implementation Details:
None.