Determining the Class Precedence List (original) (raw)
ANSI Common Lisp  4 Types and Classes
4 Types and Classes  4.3 Classes
4.3 Classes
4.3.5 Determining the Class Precedence List
The defclass form for a class provides a total ordering on that class and its direct superclasses. This ordering is called the local precedence order. It is an ordered list of the_class_ and its direct superclasses. The**class precedence list** for a class C is a total ordering on_C_ and its superclasses that is consistent with the_local precedence orders_ for each of C and its superclasses.
A class precedes its direct superclasses, and a direct superclass precedes all other direct superclasses specified to its right in the superclasses list of the defclass form. For every class C, define
RC={(C,C1),(C1,C2), ... ,(Cn-1,Cn)} where C1, ... ,Cn are the direct superclasses of C in the order in which they are mentioned in the defclass form. These ordered pairs generate the total ordering on the class C and its direct_superclasses_.
Let SC be the set of C and its superclasses. Let R be
The set R might or might not generate a partial ordering, depending on whether the Rc, c 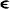 SC, are consistent; it is assumed that they are consistent and that R generates a partial ordering. When the Rc are not consistent, it is said that R is inconsistent.
SC, are consistent; it is assumed that they are consistent and that R generates a partial ordering. When the Rc are not consistent, it is said that R is inconsistent.
To compute the class precedence list for C, topologically sort the elements of SC with respect to the partial ordering generated by R. When the topological sort must select a class from a set of two or more classes, none of which are preceded by other classes with respect to R, the class selected is chosen deterministically, as described below.
If R is inconsistent, an error is signaled.
4.3.5.1 Topological Sorting
4.3.5.2 Examples of Class Precedence List Determination