OWL-ViT (original) (raw)
Overview
The OWL-ViT (short for Vision Transformer for Open-World Localization) was proposed in Simple Open-Vocabulary Object Detection with Vision Transformers by Matthias Minderer, Alexey Gritsenko, Austin Stone, Maxim Neumann, Dirk Weissenborn, Alexey Dosovitskiy, Aravindh Mahendran, Anurag Arnab, Mostafa Dehghani, Zhuoran Shen, Xiao Wang, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Kipf, and Neil Houlsby. OWL-ViT is an open-vocabulary object detection network trained on a variety of (image, text) pairs. It can be used to query an image with one or multiple text queries to search for and detect target objects described in text.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
Combining simple architectures with large-scale pre-training has led to massive improvements in image classification. For object detection, pre-training and scaling approaches are less well established, especially in the long-tailed and open-vocabulary setting, where training data is relatively scarce. In this paper, we propose a strong recipe for transferring image-text models to open-vocabulary object detection. We use a standard Vision Transformer architecture with minimal modifications, contrastive image-text pre-training, and end-to-end detection fine-tuning. Our analysis of the scaling properties of this setup shows that increasing image-level pre-training and model size yield consistent improvements on the downstream detection task. We provide the adaptation strategies and regularizations needed to attain very strong performance on zero-shot text-conditioned and one-shot image-conditioned object detection. Code and models are available on GitHub.
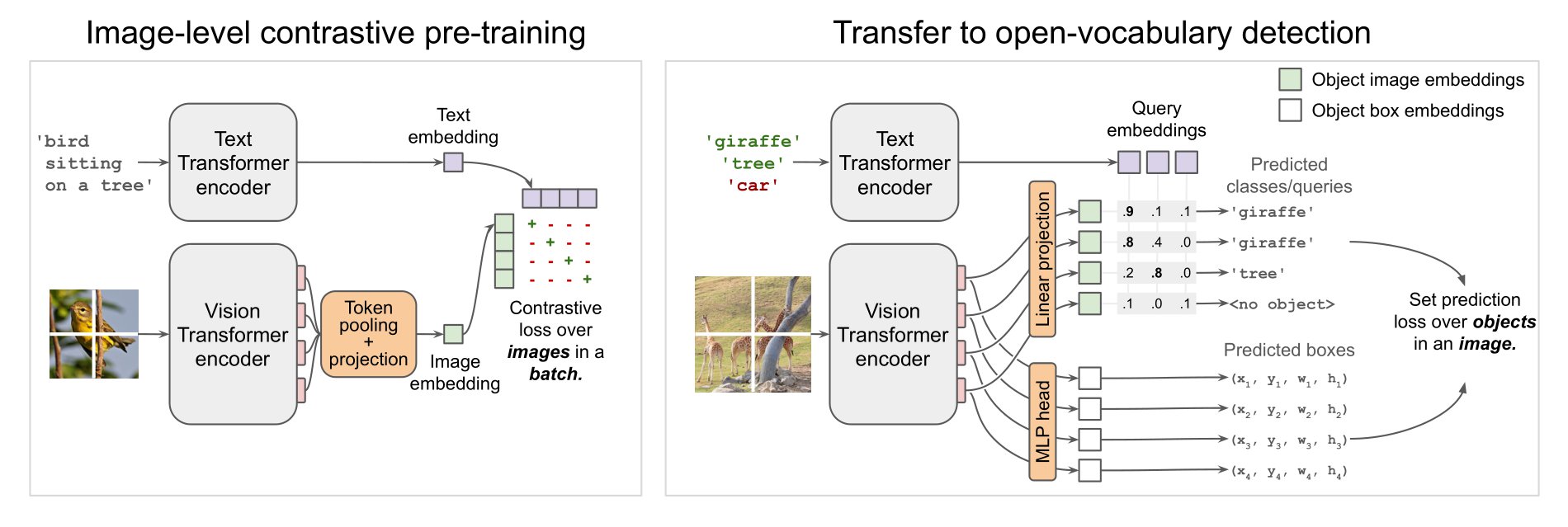 OWL-ViT architecture. Taken from the original paper.
OWL-ViT architecture. Taken from the original paper.
This model was contributed by adirik. The original code can be found here.
Usage tips
OWL-ViT is a zero-shot text-conditioned object detection model. OWL-ViT uses CLIP as its multi-modal backbone, with a ViT-like Transformer to get visual features and a causal language model to get the text features. To use CLIP for detection, OWL-ViT removes the final token pooling layer of the vision model and attaches a lightweight classification and box head to each transformer output token. Open-vocabulary classification is enabled by replacing the fixed classification layer weights with the class-name embeddings obtained from the text model. The authors first train CLIP from scratch and fine-tune it end-to-end with the classification and box heads on standard detection datasets using a bipartite matching loss. One or multiple text queries per image can be used to perform zero-shot text-conditioned object detection.
OwlViTImageProcessor can be used to resize (or rescale) and normalize images for the model and CLIPTokenizer is used to encode the text. OwlViTProcessor wraps OwlViTImageProcessor and CLIPTokenizer into a single instance to both encode the text and prepare the images. The following example shows how to perform object detection using OwlViTProcessor and OwlViTForObjectDetection.
import requests from PIL import Image import torch
from transformers import OwlViTProcessor, OwlViTForObjectDetection
processor = OwlViTProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") model = OwlViTForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg" image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw) texts = [["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"]] inputs = processor(text=texts, images=image, return_tensors="pt") outputs = model(**inputs)
target_sizes = torch.Tensor([image.size[::-1]])
results = processor.post_process_object_detection(outputs=outputs, target_sizes=target_sizes, threshold=0.1) i = 0
text = texts[i] boxes, scores, labels = results[i]["boxes"], results[i]["scores"], results[i]["labels"] for box, score, label in zip(boxes, scores, labels): ... box = [round(i, 2) for i in box.tolist()] ... print(f"Detected {text[label]} with confidence {round(score.item(), 3)} at location {box}") Detected a photo of a cat with confidence 0.707 at location [324.97, 20.44, 640.58, 373.29] Detected a photo of a cat with confidence 0.717 at location [1.46, 55.26, 315.55, 472.17]
Resources
A demo notebook on using OWL-ViT for zero- and one-shot (image-guided) object detection can be found here.
OwlViTConfig
class transformers.OwlViTConfig
( text_config = None vision_config = None projection_dim = 512 logit_scale_init_value = 2.6592 return_dict = True **kwargs )
Parameters
- text_config (
dict, optional) — Dictionary of configuration options used to initialize OwlViTTextConfig. - vision_config (
dict, optional) — Dictionary of configuration options used to initialize OwlViTVisionConfig. - projection_dim (
int, optional, defaults to 512) — Dimensionality of text and vision projection layers. - logit_scale_init_value (
float, optional, defaults to 2.6592) — The initial value of the logit_scale parameter. Default is used as per the original OWL-ViT implementation. - return_dict (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether or not the model should return a dictionary. IfFalse, returns a tuple. - kwargs (optional) — Dictionary of keyword arguments.
OwlViTConfig is the configuration class to store the configuration of an OwlViTModel. It is used to instantiate an OWL-ViT model according to the specified arguments, defining the text model and vision model configs. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the OWL-ViTgoogle/owlvit-base-patch32 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
from_text_vision_configs
( text_config: Dict vision_config: Dict **kwargs ) → OwlViTConfig
An instance of a configuration object
Instantiate a OwlViTConfig (or a derived class) from owlvit text model configuration and owlvit vision model configuration.
OwlViTTextConfig
class transformers.OwlViTTextConfig
( vocab_size = 49408 hidden_size = 512 intermediate_size = 2048 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 8 max_position_embeddings = 16 hidden_act = 'quick_gelu' layer_norm_eps = 1e-05 attention_dropout = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 initializer_factor = 1.0 pad_token_id = 0 bos_token_id = 49406 eos_token_id = 49407 **kwargs )
Parameters
- vocab_size (
int, optional, defaults to 49408) — Vocabulary size of the OWL-ViT text model. Defines the number of different tokens that can be represented by theinputs_idspassed when calling OwlViTTextModel. - hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 512) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers and the pooler layer. - intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 2048) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder. - num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder. - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 8) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder. - max_position_embeddings (
int, optional, defaults to 16) — The maximum sequence length that this model might ever be used with. Typically set this to something large just in case (e.g., 512 or 1024 or 2048). - hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"quick_gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new""quick_gelu"are supported. - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-05) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers. - attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities. - initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. - initializer_factor (
float, optional, defaults to 1.0) — A factor for initializing all weight matrices (should be kept to 1, used internally for initialization testing). - pad_token_id (
int, optional, defaults to 0) — The id of the padding token in the input sequences. - bos_token_id (
int, optional, defaults to 49406) — The id of the beginning-of-sequence token in the input sequences. - eos_token_id (
int, optional, defaults to 49407) — The id of the end-of-sequence token in the input sequences.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of an OwlViTTextModel. It is used to instantiate an OwlViT text encoder according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the OwlViTgoogle/owlvit-base-patch32 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
from transformers import OwlViTTextConfig, OwlViTTextModel
configuration = OwlViTTextConfig()
model = OwlViTTextModel(configuration)
configuration = model.config
OwlViTVisionConfig
class transformers.OwlViTVisionConfig
( hidden_size = 768 intermediate_size = 3072 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 12 num_channels = 3 image_size = 768 patch_size = 32 hidden_act = 'quick_gelu' layer_norm_eps = 1e-05 attention_dropout = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 initializer_factor = 1.0 **kwargs )
Parameters
- hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 768) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers and the pooler layer. - intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 3072) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder. - num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder. - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder. - num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — Number of channels in the input images. - image_size (
int, optional, defaults to 768) — The size (resolution) of each image. - patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 32) — The size (resolution) of each patch. - hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"quick_gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new""quick_gelu"are supported. - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-05) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers. - attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities. - initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. - initializer_factor (
float, optional, defaults to 1.0) — A factor for initializing all weight matrices (should be kept to 1, used internally for initialization testing).
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of an OwlViTVisionModel. It is used to instantiate an OWL-ViT image encoder according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the OWL-ViTgoogle/owlvit-base-patch32 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
from transformers import OwlViTVisionConfig, OwlViTVisionModel
configuration = OwlViTVisionConfig()
model = OwlViTVisionModel(configuration)
configuration = model.config
OwlViTImageProcessor
class transformers.OwlViTImageProcessor
( do_resize = True size = None resample = <Resampling.BICUBIC: 3> do_center_crop = False crop_size = None do_rescale = True rescale_factor = 0.00392156862745098 do_normalize = True image_mean = None image_std = None **kwargs )
Parameters
- do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to resize the shorter edge of the input to a certainsize. - size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to {“height” — 768, “width”: 768}): The size to use for resizing the image. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. Ifsizeis a sequence like (h, w), output size will be matched to this. Ifsizeis an int, then image will be resized to (size, size). - resample (
int, optional, defaults toResampling.BICUBIC) — An optional resampling filter. This can be one ofPIL.Image.Resampling.NEAREST,PIL.Image.Resampling.BOX,PIL.Image.Resampling.BILINEAR,PIL.Image.Resampling.HAMMING,PIL.Image.Resampling.BICUBICorPIL.Image.Resampling.LANCZOS. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to crop the input at the center. If the input size is smaller thancrop_sizealong any edge, the image is padded with 0’s and then center cropped. - crop_size (
int, optional, defaults to {“height” — 768, “width”: 768}): The size to use for center cropping the image. Only has an effect ifdo_center_cropis set toTrue. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to rescale the input by a certain factor. - rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults to1/255) — The factor to use for rescaling the image. Only has an effect ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether or not to normalize the input withimage_meanandimage_std. Desired output size when applying center-cropping. Only has an effect ifdo_center_cropis set toTrue. - image_mean (
List[int], optional, defaults to[0.48145466, 0.4578275, 0.40821073]) — The sequence of means for each channel, to be used when normalizing images. - image_std (
List[int], optional, defaults to[0.26862954, 0.26130258, 0.27577711]) — The sequence of standard deviations for each channel, to be used when normalizing images.
Constructs an OWL-ViT image processor.
This image processor inherits from ImageProcessingMixin which contains most of the main methods. Users should refer to this superclass for more information regarding those methods.
preprocess
( images: Union do_resize: Optional = None size: Optional = None resample: Resampling = None do_center_crop: Optional = None crop_size: Optional = None do_rescale: Optional = None rescale_factor: Optional = None do_normalize: Optional = None image_mean: Union = None image_std: Union = None return_tensors: Union = None data_format: Union = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'> input_data_format: Union = None )
Parameters
- images (
ImageInput) — The image or batch of images to be prepared. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False. - do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_resize) — Whether or not to resize the input. IfTrue, will resize the input to the size specified bysize. - size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.size) — The size to resize the input to. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toself.resample) — The resampling filter to use when resizing the input. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_center_crop) — Whether or not to center crop the input. IfTrue, will center crop the input to the size specified bycrop_size. - crop_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.crop_size) — The size to center crop the input to. Only has an effect ifdo_center_cropis set toTrue. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_rescale) — Whether or not to rescale the input. IfTrue, will rescale the input by dividing it byrescale_factor. - rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults toself.rescale_factor) — The factor to rescale the input by. Only has an effect ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_normalize) — Whether or not to normalize the input. IfTrue, will normalize the input by subtractingimage_meanand dividing byimage_std. - image_mean (
Union[float, List[float]], optional, defaults toself.image_mean) — The mean to subtract from the input when normalizing. Only has an effect ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue. - image_std (
Union[float, List[float]], optional, defaults toself.image_std) — The standard deviation to divide the input by when normalizing. Only has an effect ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue. - return_tensors (
strorTensorType, optional) — The type of tensors to return. Can be one of:- Unset: Return a list of
np.ndarray. TensorType.TENSORFLOWor'tf': Return a batch of typetf.Tensor.TensorType.PYTORCHor'pt': Return a batch of typetorch.Tensor.TensorType.NUMPYor'np': Return a batch of typenp.ndarray.TensorType.JAXor'jax': Return a batch of typejax.numpy.ndarray.
- Unset: Return a list of
- data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional, defaults toChannelDimension.FIRST) — The channel dimension format for the output image. Can be one of:ChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format.ChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.- Unset: defaults to the channel dimension format of the input image.
- input_data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
Prepares an image or batch of images for the model.
post_process_object_detection
( outputs threshold: float = 0.1 target_sizes: Union = None ) → List[Dict]
Parameters
- outputs (
OwlViTObjectDetectionOutput) — Raw outputs of the model. - threshold (
float, optional) — Score threshold to keep object detection predictions. - target_sizes (
torch.TensororList[Tuple[int, int]], optional) — Tensor of shape(batch_size, 2)or list of tuples (Tuple[int, int]) containing the target size(height, width)of each image in the batch. If unset, predictions will not be resized.
A list of dictionaries, each dictionary containing the scores, labels and boxes for an image in the batch as predicted by the model.
Converts the raw output of OwlViTForObjectDetection into final bounding boxes in (top_left_x, top_left_y, bottom_right_x, bottom_right_y) format.
post_process_image_guided_detection
( outputs threshold = 0.0 nms_threshold = 0.3 target_sizes = None ) → List[Dict]
Parameters
- outputs (
OwlViTImageGuidedObjectDetectionOutput) — Raw outputs of the model. - threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — Minimum confidence threshold to use to filter out predicted boxes. - nms_threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.3) — IoU threshold for non-maximum suppression of overlapping boxes. - target_sizes (
torch.Tensor, optional) — Tensor of shape (batch_size, 2) where each entry is the (height, width) of the corresponding image in the batch. If set, predicted normalized bounding boxes are rescaled to the target sizes. If left to None, predictions will not be unnormalized.
A list of dictionaries, each dictionary containing the scores, labels and boxes for an image in the batch as predicted by the model. All labels are set to None asOwlViTForObjectDetection.image_guided_detection perform one-shot object detection.
Converts the output of OwlViTForObjectDetection.image_guided_detection() into the format expected by the COCO api.
OwlViTFeatureExtractor
Preprocess an image or a batch of images.
( outputs target_sizes ) → List[Dict]
Parameters
- outputs (
OwlViTObjectDetectionOutput) — Raw outputs of the model. - target_sizes (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, 2)) — Tensor containing the size (h, w) of each image of the batch. For evaluation, this must be the original image size (before any data augmentation). For visualization, this should be the image size after data augment, but before padding.
A list of dictionaries, each dictionary containing the scores, labels and boxes for an image in the batch as predicted by the model.
Converts the raw output of OwlViTForObjectDetection into final bounding boxes in (top_left_x, top_left_y, bottom_right_x, bottom_right_y) format.
( outputs threshold = 0.0 nms_threshold = 0.3 target_sizes = None ) → List[Dict]
Parameters
- outputs (
OwlViTImageGuidedObjectDetectionOutput) — Raw outputs of the model. - threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — Minimum confidence threshold to use to filter out predicted boxes. - nms_threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.3) — IoU threshold for non-maximum suppression of overlapping boxes. - target_sizes (
torch.Tensor, optional) — Tensor of shape (batch_size, 2) where each entry is the (height, width) of the corresponding image in the batch. If set, predicted normalized bounding boxes are rescaled to the target sizes. If left to None, predictions will not be unnormalized.
A list of dictionaries, each dictionary containing the scores, labels and boxes for an image in the batch as predicted by the model. All labels are set to None asOwlViTForObjectDetection.image_guided_detection perform one-shot object detection.
Converts the output of OwlViTForObjectDetection.image_guided_detection() into the format expected by the COCO api.
OwlViTProcessor
class transformers.OwlViTProcessor
( image_processor = None tokenizer = None **kwargs )
Parameters
- image_processor (OwlViTImageProcessor, optional) — The image processor is a required input.
- tokenizer ([
CLIPTokenizer,CLIPTokenizerFast], optional) — The tokenizer is a required input.
Constructs an OWL-ViT processor which wraps OwlViTImageProcessor and CLIPTokenizer/CLIPTokenizerFastinto a single processor that interits both the image processor and tokenizer functionalities. See the__call__() and decode() for more information.
This method forwards all its arguments to CLIPTokenizerFast’s batch_decode(). Please refer to the docstring of this method for more information.
This method forwards all its arguments to CLIPTokenizerFast’s decode(). Please refer to the docstring of this method for more information.
post_process_image_guided_detection
( *args **kwargs )
This method forwards all its arguments to OwlViTImageProcessor.post_process_one_shot_object_detection. Please refer to the docstring of this method for more information.
OwlViTModel
class transformers.OwlViTModel
( config: OwlViTConfig )
Parameters
- config (OwlViTConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( input_ids: Optional = None pixel_values: Optional = None attention_mask: Optional = None return_loss: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_base_image_embeds: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. SeePreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details. What are input IDs? - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.What are attention masks?
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. - return_loss (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the contrastive loss. - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTOutput or a tuple oftorch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.owlvit.configuration_owlvit.OwlViTConfig'>) and inputs.
- loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenreturn_lossisTrue) — Contrastive loss for image-text similarity. - logits_per_image (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(image_batch_size, text_batch_size)) — The scaled dot product scores betweenimage_embedsandtext_embeds. This represents the image-text similarity scores. - logits_per_text (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(text_batch_size, image_batch_size)) — The scaled dot product scores betweentext_embedsandimage_embeds. This represents the text-image similarity scores. - text_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size * num_max_text_queries, output_dim) — The text embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of OwlViTTextModel. - image_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, output_dim) — The image embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output ofOwlViTVisionModel. - text_model_output (Tuple
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — The output of the OwlViTTextModel. - vision_model_output (
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — The output of the OwlViTVisionModel.
The OwlViTModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
from PIL import Image import requests from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTModel
model = OwlViTModel.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg" image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw) inputs = processor(text=[["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"]], images=image, return_tensors="pt") outputs = model(**inputs) logits_per_image = outputs.logits_per_image
probs = logits_per_image.softmax(dim=1)
get_text_features
( input_ids: Optional = None attention_mask: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → text_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size * num_max_text_queries, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. SeePreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details. What are input IDs? - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_max_text_queries, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.What are attention masks?
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
text_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
The text embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of OwlViTTextModel.
The OwlViTModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTModel
model = OwlViTModel.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") inputs = processor( ... text=[["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], ["photo of a astranaut"]], return_tensors="pt" ... ) text_features = model.get_text_features(**inputs)
get_image_features
( pixel_values: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → image_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
image_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
The image embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of OwlViTVisionModel.
The OwlViTModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
from PIL import Image import requests from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTModel
model = OwlViTModel.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg" image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw) inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt") image_features = model.get_image_features(**inputs)
OwlViTTextModel
class transformers.OwlViTTextModel
( config: OwlViTTextConfig )
forward
( input_ids: Tensor attention_mask: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size * num_max_text_queries, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. SeePreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details. What are input IDs? - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_max_text_queries, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.What are attention masks?
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple oftorch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.owlvit.configuration_owlvit.OwlViTTextConfig'>) and inputs.
- last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. - pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state of the first token of the sequence (classification token) after further processing through the layers used for the auxiliary pretraining task. E.g. for BERT-family of models, this returns the classification token after processing through a linear layer and a tanh activation function. The linear layer weights are trained from the next sentence prediction (classification) objective during pretraining. - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).
Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs. - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).
Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The OwlViTTextModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTTextModel
model = OwlViTTextModel.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") inputs = processor( ... text=[["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], ["photo of a astranaut"]], return_tensors="pt" ... ) outputs = model(**inputs) last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output
OwlViTVisionModel
class transformers.OwlViTVisionModel
( config: OwlViTVisionConfig )
forward
( pixel_values: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple oftorch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.owlvit.configuration_owlvit.OwlViTVisionConfig'>) and inputs.
- last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. - pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state of the first token of the sequence (classification token) after further processing through the layers used for the auxiliary pretraining task. E.g. for BERT-family of models, this returns the classification token after processing through a linear layer and a tanh activation function. The linear layer weights are trained from the next sentence prediction (classification) objective during pretraining. - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).
Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs. - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).
Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The OwlViTVisionModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
from PIL import Image import requests from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTVisionModel
model = OwlViTVisionModel.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg" image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model(**inputs) last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output
OwlViTForObjectDetection
class transformers.OwlViTForObjectDetection
( config: OwlViTConfig )
forward
( input_ids: Tensor pixel_values: FloatTensor attention_mask: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTObjectDetectionOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. - input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size * num_max_text_queries, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. SeePreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details. What are input IDs?. - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_max_text_queries, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.What are attention masks?
- output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the last hidden state. Seetext_model_last_hidden_stateandvision_model_last_hidden_stateunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTObjectDetectionOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTObjectDetectionOutput or a tuple oftorch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.owlvit.configuration_owlvit.OwlViTConfig'>) and inputs.
- loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsare provided)) — Total loss as a linear combination of a negative log-likehood (cross-entropy) for class prediction and a bounding box loss. The latter is defined as a linear combination of the L1 loss and the generalized scale-invariant IoU loss. - loss_dict (
Dict, optional) — A dictionary containing the individual losses. Useful for logging. - logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches, num_queries)) — Classification logits (including no-object) for all queries. - pred_boxes (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches, 4)) — Normalized boxes coordinates for all queries, represented as (center_x, center_y, width, height). These values are normalized in [0, 1], relative to the size of each individual image in the batch (disregarding possible padding). You can use post_process_object_detection() to retrieve the unnormalized bounding boxes. - text_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_max_text_queries, output_dim) — The text embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of OwlViTTextModel. - image_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, patch_size, patch_size, output_dim) — Pooled output of OwlViTVisionModel. OWL-ViT represents images as a set of image patches and computes image embeddings for each patch. - class_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches, hidden_size)) — Class embeddings of all image patches. OWL-ViT represents images as a set of image patches where the total number of patches is (image_size / patch_size)**2. - text_model_output (Tuple
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — The output of the OwlViTTextModel. - vision_model_output (
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — The output of the OwlViTVisionModel.
The OwlViTForObjectDetection forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
import requests from PIL import Image import torch from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTForObjectDetection
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32") model = OwlViTForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch32")
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg" image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw) texts = [["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"]] inputs = processor(text=texts, images=image, return_tensors="pt") outputs = model(**inputs)
target_sizes = torch.Tensor([image.size[::-1]])
results = processor.post_process_object_detection( ... outputs=outputs, threshold=0.1, target_sizes=target_sizes ... )
i = 0
text = texts[i] boxes, scores, labels = results[i]["boxes"], results[i]["scores"], results[i]["labels"]
for box, score, label in zip(boxes, scores, labels): ... box = [round(i, 2) for i in box.tolist()] ... print(f"Detected {text[label]} with confidence {round(score.item(), 3)} at location {box}") Detected a photo of a cat with confidence 0.707 at location [324.97, 20.44, 640.58, 373.29] Detected a photo of a cat with confidence 0.717 at location [1.46, 55.26, 315.55, 472.17]
image_guided_detection
( pixel_values: FloatTensor query_pixel_values: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTImageGuidedObjectDetectionOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. - query_pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values of query image(s) to be detected. Pass in one query image per target image. - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTImageGuidedObjectDetectionOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.owlvit.modeling_owlvit.OwlViTImageGuidedObjectDetectionOutput or a tuple oftorch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.owlvit.configuration_owlvit.OwlViTConfig'>) and inputs.
- logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches, num_queries)) — Classification logits (including no-object) for all queries. - target_pred_boxes (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches, 4)) — Normalized boxes coordinates for all queries, represented as (center_x, center_y, width, height). These values are normalized in [0, 1], relative to the size of each individual target image in the batch (disregarding possible padding). You can use post_process_object_detection() to retrieve the unnormalized bounding boxes. - query_pred_boxes (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches, 4)) — Normalized boxes coordinates for all queries, represented as (center_x, center_y, width, height). These values are normalized in [0, 1], relative to the size of each individual query image in the batch (disregarding possible padding). You can use post_process_object_detection() to retrieve the unnormalized bounding boxes. - image_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, patch_size, patch_size, output_dim) — Pooled output of OwlViTVisionModel. OWL-ViT represents images as a set of image patches and computes image embeddings for each patch. - query_image_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, patch_size, patch_size, output_dim) — Pooled output of OwlViTVisionModel. OWL-ViT represents images as a set of image patches and computes image embeddings for each patch. - class_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches, hidden_size)) — Class embeddings of all image patches. OWL-ViT represents images as a set of image patches where the total number of patches is (image_size / patch_size)**2. - text_model_output (Tuple
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — The output of the OwlViTTextModel. - vision_model_output (
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — The output of the OwlViTVisionModel.
The OwlViTForObjectDetection forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
import requests from PIL import Image import torch from transformers import AutoProcessor, OwlViTForObjectDetection
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch16") model = OwlViTForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("google/owlvit-base-patch16") url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg" image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw) query_url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000001675.jpg" query_image = Image.open(requests.get(query_url, stream=True).raw) inputs = processor(images=image, query_images=query_image, return_tensors="pt") with torch.no_grad(): ... outputs = model.image_guided_detection(**inputs)
target_sizes = torch.Tensor([image.size[::-1]])
results = processor.post_process_image_guided_detection( ... outputs=outputs, threshold=0.6, nms_threshold=0.3, target_sizes=target_sizes ... ) i = 0
boxes, scores = results[i]["boxes"], results[i]["scores"] for box, score in zip(boxes, scores): ... box = [round(i, 2) for i in box.tolist()] ... print(f"Detected similar object with confidence {round(score.item(), 3)} at location {box}") Detected similar object with confidence 0.856 at location [10.94, 50.4, 315.8, 471.39] Detected similar object with confidence 1.0 at location [334.84, 25.33, 636.16, 374.71]