Compare Code Mappings of Simulink Models - MATLAB & Simulink (original) (raw)
The Simulink® Comparison Tool is an interactive tool for identifying and comparing differences between Simulink models. You can use the tool to compare the code mappings of models. TheComparison Tool shows mapping differences under Code Mappings, organized by mapping type.
Each mapping type that is different between the models appears as a subtree underCode Mappings. The blocks that contain the differences in this mapping type appear within the type subtree (not necessarily as immediate descendents). For example, the comparison in this screenshot shows that there are differences in the mapping types Embedded Coder C - Data Interface and Simulink Coder C. The differences of the first type are in the Outport blockout_1, and the differences of the second type are in theInport block in_1.

Unsupported mapping types, which refer to mapping categories not fully recognized by the tool (and therefore not fully detailed), are also displayed underCode Mappings if they contain differences, but as empty labels. Blocks with differences in unsupported mapping types do not appear in the comparison tool.

This table shows supported and unsupported mapping types.
| Mapping Type | Target Description | Supported by Comparison Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Simulink Coder C | GRT-based system target file (grt.tlc) with C language | Supported |
| Embedded Coder C - Data Interface | ERT-based system target file (ert.tlc) with C language and data interface configuration | |
| Embedded Coder C - Service Interface | ERT-based system target file (ert.tlc) with C language and service interface configuration | |
| Embedded Coder C++ Class | ERT-based system target file (ert.tlc) with C++ language | Not supported |
| AUTOSAR Classic | AUTOSAR Classic system target file (autosar.tlc) with C language | |
| AUTOSAR Adaptive | AUTOSAR Adaptive system target file (autosar_adaptive.tlc) with C++ language | |
| DDS (Data Distribution Service) | ERT-based system target file (ert.tlc) with C++ language |
As with other types of blocks displayed in the Comparison Tool, when you select a block with mapping difference, the difference is shown in the lower panes of the tool.
Compare Model Mapping with Comparison Tool
This example shows how to use the Comparison Tool to compare the code mappings of two models. The two models, mapDiff1 and mapDiff2, are identical except for a few differences.
Store the names of the models in variables.
model_1 = "mapDiff1"; model_2 = "mapDiff2";
Model Description
The two models have identical structure: a root-level input port connected to a Bias block, which is connected to a root-level output port.

Each model has two predefined sets of code mapping configurations:
- Simulink Coder C
- Embedded Coder C - Data Interface
The models are identical, except for these differences:
| Block | Compared Element | Type of Mapping | Value in mapDiff1 | Value in mapDiff2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias | Bias parameter | Not a mapping element | 1 | 2 |
| Root-level inport | Storage class | Simulink Coder C | ImportedExtern | ExportedGlobal |
| Root-level outport | Storage class | Embedded Coder C - Data Interface | BitField | Struct |
Open Comparison Tool
Enter this command in the Command Window to open the Comparison Tool:
The left and right panes of the tool show the first and second models, respectively. Each model is displayed in the form of a structured tree. Identical blocks do not appear in the structured trees. Blocks with elements that are different in the models appear as leaves. To learn more about how to use the Comparison Tool, see Understand Simulink Model Comparison Changes.
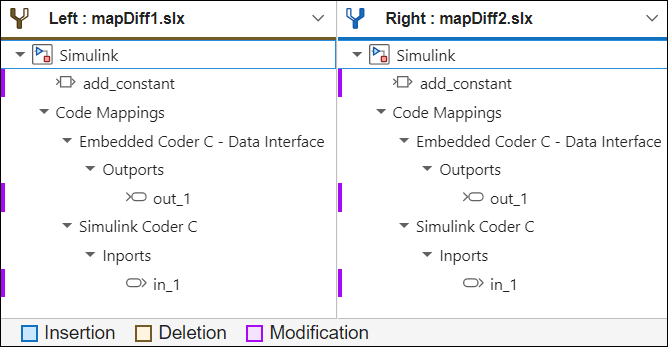
The Comparison Tool shows code mapping differences regardless of whether or not you have the appropriate license to use the displayed mapping types. For example, even if you do not have Embedded Coder™ license you are still able to see the differences in the Embedded Coder mappings elements.
Step Through Code Mapping Differences
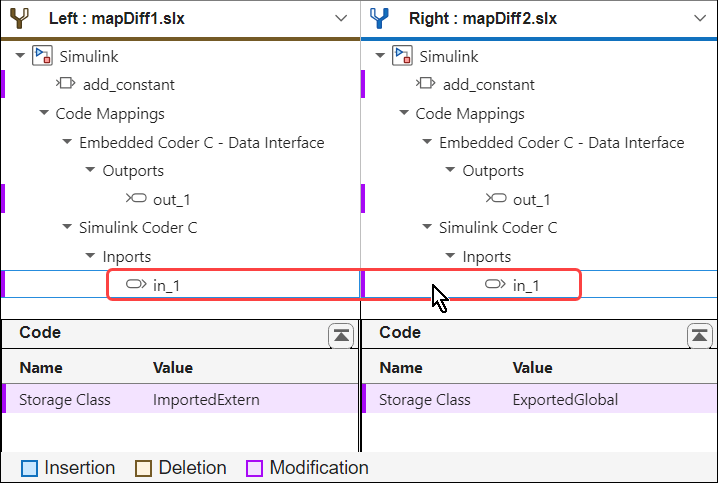
Select the in_1 leaf in the Comparison Tool. The lower panes of the tool display the storage class values of the root-level inport of the models, ImportedExtern on the lower-left pane and ExportedGlobal on the lower-right pane.
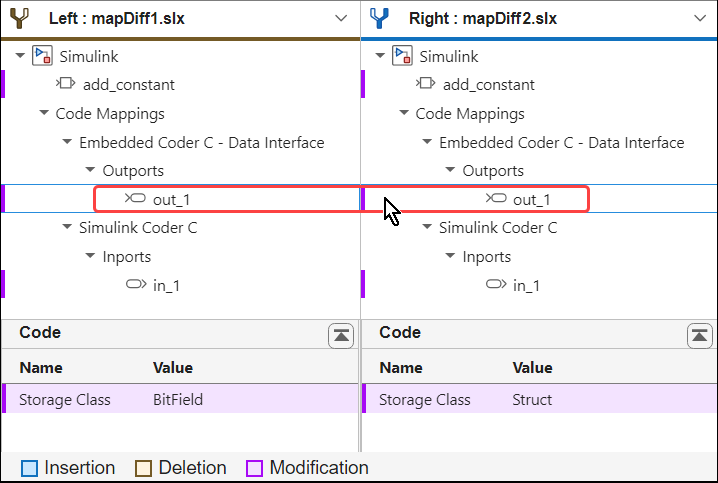
Select the out_1 leaf. The lower panes of the tool now display the storage class values of the root-level output port of the models, Bitfield on the lower-left pane and Struct on the lower-right pane.
Observe Differences in Models
You can optionally open the models to see the differences in them while observing the differences in the Comparison Tool.
Note: To see mapping elements in the models themselves, you do need the appropriate licenses.
If the models are not open, open them by entering these:
open_system(model_1) open_system(model_2)
Select the add_constant leaf in the Comparison Tool. In the lower panes of the Comparison Tool you see the values of the Bias parameter of the Bias block, 1 on the lower-left pane and 2 on the lower-right pane. If Always Highlight is cleared, click Highlight Now to highlight the Bias block in the models. Note that the Bias block itself is highlighted, not the parameter that differs between the models (the Bias parameter in this case).
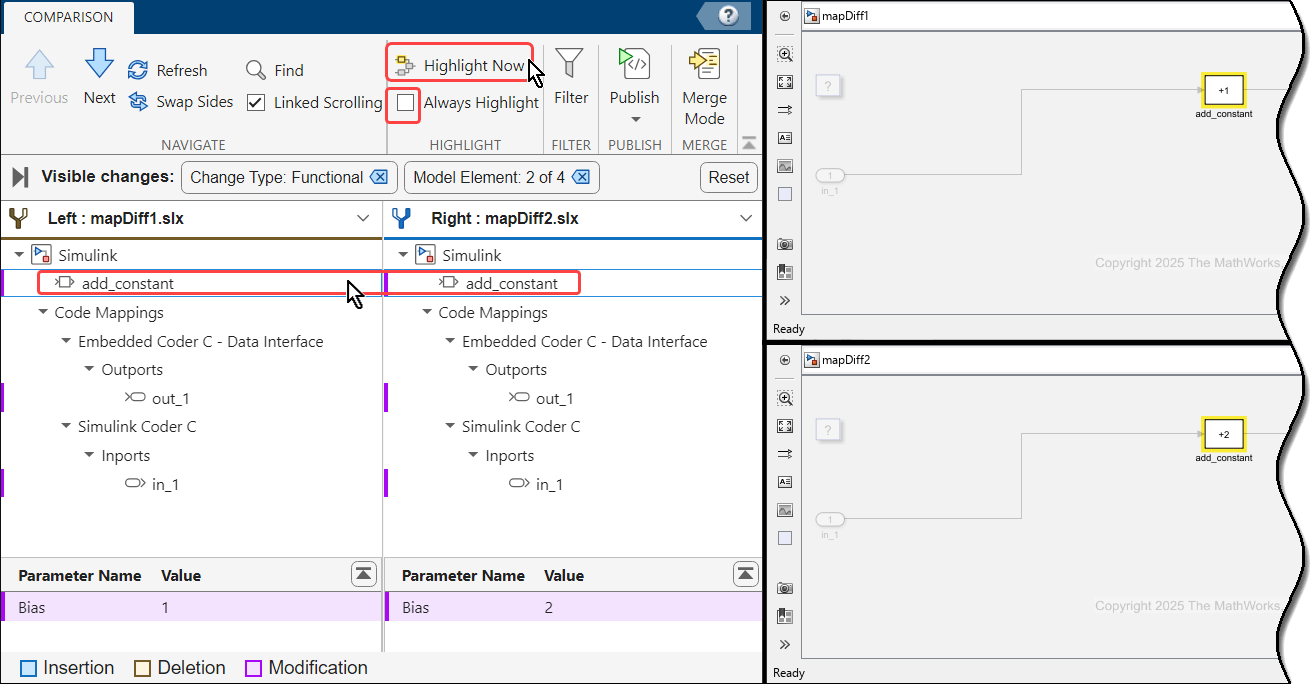
Observe Mapping Element Differences in Models
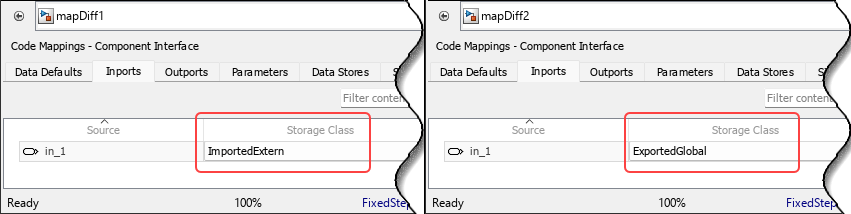
Similar to other differences shown in the Comparison Tool, when you select a block in the structured tree of the tool, the block itself is highlighted in the canvas of the compared models. For example, when you select the in_1 leaf in the Comparison Tool, the root-level Inport block is highlighted in the models. As before, the lower panes of the tool display the Storage Class values of the root-level Inport in_1 of the models, ImportedExtern on the lower-left pane and ExportedGlobal on the lower-right pane.

To see the actual difference (storage class in this case):
- Open the Code Mappings editor (see Open the Code Mappings Editor — C).
- Navigate to the Inports tab.
- Look at the Storage Class value of the (single) entry in the list.
The storage class is ImportedExtern in mapDiff1 and ExportedGlobal in mapDiff2.
Limitations
- The Comparison Tool displays differences between mapping elements that belong to blocks in referenced entities (such as libraries and referenced models) regardless of whether the referenced entity is loaded. But when the referenced entity is not loaded, the Comparison Tool displays the Simulink Identifier of the block instead of its path. This is because the path of unloaded blocks cannot be resolved. These images show how a referenced state is displayed in the tool when the library to which the state belongs is loaded and when the library is not loaded.


To learn more about Simulink Identifiers, see Simulink.ID.getSID. - The Merge Mode of the Comparison Tool does not support resolving and merging code mappings. When you save the resolved model, the tool copies the mappings in the model on the right pane into the merged model. In the same way, the Simulink Three-Way Merge Tool does not support resolving and merging code mappings. When you save the resolved model, the Three-Way Merge Tool copies the mappings of the model on the right pane into the merged model.
See Also
Comparison Tool | visdiff | Simulink.ID.getSID | Code Mappings Editor – C