Optimize Generated Code by Developing and Using Code Replacement Libraries - Simulink - MATLAB & Simulink (original) (raw)
Develop and use code replacement libraries to replace function and operators in generated code. Code replacement is a technique to change the code that the code generator produces for functions and operators to meet application code requirements. For example, you can replace generated code to meet requirements such as:
- Optimization for a specific run-time environment, including, but not limited to, specific target hardware
- Integration with existing application code
- Compliance with a standard, such as AUTOSAR
- Modification of code behavior, such as enabling or disabling nonfinite or inline support
- Application- or project-specific code requirements, such as use of BLAS or elimination of
math.h, system header files, or calls tomemcpyormemset.
You can configure a model such that the code generator uses a code replacement library that MathWorks® provides. If you have an Embedded Coder® license, you can develop your own code replacement library interactively with the Code Replacement Tool or programmatically.
This example uses models to show a variety of ways you can define code replacement mappings programmatically. Each model includes buttons that you can use to
- View the code replacement library table definitions from the Code Replacement Viewer
- Open the library table definition file in the editor
- Open the library registration file in the editor
- View the model configuration
- Generate code
For more information, see Define Code Replacement Library Optimizations and Register Code Replacement Library.
Steps for Developing a Code Replacement Library
- Identify your code replacement requirements with respect to function or operating mappings, build information, and registration information.
- Prepare for code replacement library development (for example, identify or develop models to test your library).
- Define code replacement mappings.
- Specify build information for replacement code.
- Register code replacement mappings.
- Verify code replacements.
- Deploy the library.
For more information, see Quick Start Code Replacement Library Development - Simulink.
Math Function Replacement
This example defines and registers code replacement mappings for math functions. You can define code replacement mappings for a variety of functions (see Code You Can Replace From Simulink Models).
Open the model CRLMath and use the buttons at the bottom of the model window to explore the files that define and register the code replacement library mappings.
For more information, see Math Function Code Replacement.

Addition and Subtraction Operator Replacement
This example shows how to define and register code replacement mappings for addition (+) and subtraction (-) operations. When defining entries for addition and subtraction operations, you can specify which of the following algorithms (EntryInfoAlgorithm) your library functions implement:
- Cast-before-operation (CBO) (
RTW_CAST_BEFORE_OP), the default - Cast-after-operation (CAO) (
RTW_CAST_AFTER_OP)
1. Open the model CRLAdditionSubtraction. The model shows how to define and register code replacement mappings for scalar addition (+) and subtraction (-) operations on two operands with the following pairings of built-in integer data types:
int8,uint8int16,uint16int32,uint32
CBO, the default algorithm, is assumed.
open_system("CRLAdditionSubtraction");

2. Use the buttons at the bottom of the model window to explore the files that define and register the code replacement library mappings.
3. Explore the differences between the CBO and CAO algorithms by opening the model CRLCastOperations. The model shows two SUM blocks, each demonstrating one of the algorithm settings to match a corresponding code replacement entry.
- For the
Cast_before_operation_Subblock, the code generator calculates the subtraction operation in the accumulator data type (int8), which is smaller than the input data type (int16). This is equivalent to a CBO because the code generator converts the input to the output data type before calculating the result. - For the
Cast_after_operation_Subblock, the code generator calculates the subtraction operation in the accumulator data type (int32), which is larger than the input data type (int16). This is equivalent to a CAO because the code generator produces the same result by calculating the result without loss of range or precision before converting to the output data type.
open_system("CRLCastOperations");

4. Use the buttons at the bottom of the model window to explore the files that define and register the code replacement library mappings.
For more information on addition and subtraction operator replacement, see Replace Addition and Subtraction Operator Code. For more information on the addition and subtraction algorithm (EntryInfoAlgorithm) options, see setTflCOperationEntryParameters.
Multiplication and Division Operator Replacement for Built-In Integers
This example defines and registers code replacement mappings for scalar multiplication (*) and division (/) operations. The operations take two operands with the following pairings of built-in integer data types:
int8,uint8int16,uint16int32,uint32
Open the model CRLMultiplicationDivision and use the buttons at the bottom of the model window to explore the files that define and register the code replacement library mappings.
open_system("CRLMultiplicationDivision");

Scalar Operator Replacement
This example defines and registers code replacement mappings for scalar operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, complex conjugate, cast, arithmetic shift right, and arithmetic shift left.
Supported types include:
- single, double
- int8, uint8
- int16, uint16
- int32, uint32
- csingle, cdouble
- cint8, cuint8
- cint16, cuint16
- cint32, cuint32
- fixed-point integers
- mixed types (different type on each input)
Open the model CRLScalarOperators and use the buttons at the bottom of the model window to explore the files that define and register the code replacement library mappings.
For more information on scalar operator replacement, Scalar Operator Code Replacement.
CBO, the default algorithm for addition and subtraction operations, is assumed.
open_system("CRLScalarOperators");

Matrix Operator Replacement
This example defines and registers code replacement mappings for matrix operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, transposition, conjugate, and Hermitian.
Supported types include:
single,doubleint8,uint8int16,uint16int32,uint32csingle,cdoublecint8,cuint8cint16,cuint16cint32,cuint32- fixed-point integers
- mixed types (different type on each input)
Open the model CRLMatrixOperators, which shows some of these replacements. Use the buttons at the bottom of the model window to explore the files that define and register the code replacement library mappings.
For more information on matrix operator replacement, see Small Matrix Operation to Processor Code Replacement.
CBO, the default algorithm for addition and subtraction operations, is assumed.
open_system("CRLMatrixOperators");

Matrix Multiplication Replacement for BLAS
This example defines and registers code replacement mappings for Basic Linear Algebra Subroutines (BLAS) subroutines xGEMM and xGEMV. You can map the following operations to a BLAS subroutine:
- Matrix multiplication
- Matrix multiplication with transpose on single or both inputs
- Matrix multiplication with Hermitian operation on single or both inputs
Open the model CRLBLASOperations and use the buttons at the bottom of the model window to explore the files that define and register the code replacement library mappings.
For more information on matrix multiplication replacement for BLAS, see Matrix Multiplication Operation to MathWorks BLAS Code Replacement.
open_system("CRLBLASOperations");

Fixed-Point Operator Replacement for Basic Operators
This example defines and registers code replacement mappings for scalar addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), and division (/) operations. The operations take two operands with fixed-point data types.
You can define code replacements as matching:
- Slope/bias scaling combination on the inputs and output
- Binary-point scaling combination on the inputs and output
- Relative scaling between the inputs and output
- Same slope value and a zero net bias across the inputs and output
Open the model CRLFixedPointOperators and use the buttons at the bottom of the model window to explore the files that define and register the code replacement library mappings.
- By default, for addition and subtraction operator code replacements, the code generator assumes that replacement code implements a cast-before-operation (CBO) algorithm.
- Using fixed-point data types in a model requires a Fixed-Point Designer™ license.
For more information about fixed-point operator code replacement, see Fixed-Point Operator Code Replacement.
open_system("CRLFixedPointOperators");

Match and Replacement Process Customization for Functions
This example defines and registers code replacement mappings for custom entries. You can create your own entry by subclassing from RTW.TflCFunctionEntryML or RTW.TflCOperationEntryML. Your entry class must implement a do_match method that customizes your matching logic or modifies the matched entry. The do_match method must have a fixed preset signature.
Open the model CRLCustomEntry. The model shows how to modify the matched entry by injecting constants as additional implementation function arguments. DTC1, Trigonometric Function, and Product show custom entry code replacement for:
- Cast operation that demonstrates how to extract the fraction lengths from types and pass them into the implementation function -
Out1 = custom_cast(In1, 2, 4). - Sine that demonstrates how to pass a constant value to the implementation function -
Out2=custom_sin(In2, 1). - Multiplication operation that demonstrates how to compute the net slope of an operation and pass that into the implementation function -
Out3=custom_multiply_shift_right(In3,In4,3).
Use the buttons at the bottom of the model window to explore the files that define and register the code replacement mappings.
For more information on custom entries, see Customize Match and Replacement Process.
open_system("CRLCustomEntry");

MATLAB Function Replacement
This example defines and registers code replacement mappings for MATLAB® functions specified in the MATLAB Function block. The function can be opted for replacement by specifying coder.replace within it. This feature supports replacement of MATLAB functions with the following:
- Single or multiple inputs
- Single or multiple outputs
- Scalar and matrix inputs and outputs
Open the model CRLMLFunctionReplacement. The model shows some of these requirements. Supported types include:
single,doubleint8,uint8int16,uint16int32,uint32csingle,cdoublecint8,cuint8cint16,cuint16cint32,cuint32- Fixed-point integers
- Mixed types (different type on each input)
Use the buttons at the bottom of the model window to explore the files that define and register the code replacement mappings.
For more information on MATLAB function replacement, see coder.replace.
open_system("CRLMLFunctionReplacement");
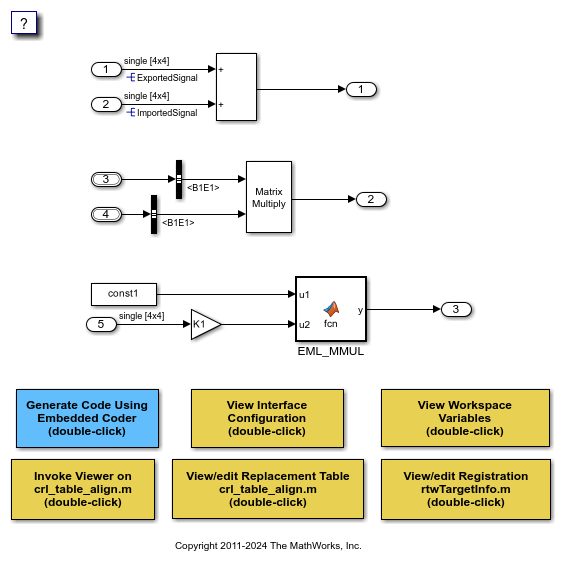
Data Alignment for Function Implementations
This example shows how to specify the alignment of matrix operands passed into a replacement function. Some target-specific function implementations require data to be aligned to optimize application performance. To configure data alignment for a function implementation:
- Specify the data alignment requirements in a table entry. You can specify alignment for implementation function arguments individually or collectively.
- Specify the data alignment capabilities and syntax for your compiler. Attach an
AlignmentSpecificationobject to theTargetCharacteristicsobject of the registry entry specified in yourrtwTargetInfo.mfile.
Open the model CRLDataAlignment. The model shows three data alignment code replacement scenarios:
Add- Alignment of exported and imported signals. You can specify an exact value for the alignment in the Signal Properties dialog box or allow the code generator to determine the best alignment based on usage by leaving the alignment value set to -1.Product- Alignment of virtual and nonvirtual bus types. You can specify an exact value for the alignment for the Alignment property of the Simulink.Bus object or allow the code generator to determine the best alignment based on usage by leaving the Alignment property set to -1.EML_MMUL- Alignment of local variables, global variables, and block parameters.
Use the buttons at the bottom of the model window to explore the files that define and register the code replacement mappings. Note that the model is configured to use a GCC, Clang, MSVC, or MinGW compiler.
For more information on specifying data alignment for code replacement, see Data Alignment for Code Replacement.
open_system("CRLDataAlignment");
Code Replacement Library Exploration and Verification
This example shows Code Replacement Viewer. You can use the Code Replacement Viewer to:
- Explore which code replacement library to use
- Verify the list of tables in a library and the entries in each table
- Review table entry specifications
- Troubleshoot code replacement misses
The following commands open the Code Replacement Viewer for code replacement table crl_table_muldiv:
crl = crl_table_muldiv; crviewer(crl);
For more information on the Code Replacement Viewer, see Verify Code Replacement Library.
Build Information
For each entry in a code replacement table, you can specify build information such as the following, for replacement functions:
- Header file dependencies
- Source file dependencies
- Additional include paths
- Additional source paths
- Additional link flags
Additionally, you can specify RTW.copyFileToBuildDir to copy header, source, or object files, which are required to generate replacement code, to the build folder before code generation. You can specify RTW.copyFileToBuildDir by setting it as the value of:
- Property
GenCallbackin a call tosetTflCFunctionEntryParameters,setTflCOperationEntryParameters, orsetTflCSemaphoreEntryParameters. - Argument
genCallbackin a call toregisterCFunctionEntry,registerCOperationEntry, orregisterCSemaphoreEntry.
Note: Models in this example are configured for code generation only because the implementations for the replacement functions are not provided.
For more information on specifying build information, see Specify build information in Define Code Replacement Library Optimizations.
Reserved Identifiers
Each function implementation name defined by a code replacement table entry is reserved as a unique identifier. You can specify other identifiers with a table on a per-header-file basis. Providing additional reserved identifiers can help prevent duplicate symbols and other identifier related compile and link issues.
For more information on specifying reserved identifiers, see Reserved Identifiers and Code Replacement.
Remove Example Code Replacement Libraries
When you finish using the example models, remove the example code replacement libraries and close the example models with these commands:
sl_refresh_customizations;
close_system("CRLMath",0) close_system("CRLAdditionSubtraction",0) close_system("CRLCastOperations",0) close_system("CRLMultiplicationDivision",0) close_system("CRLScalarOperators",0) close_system("CRLMatrixOperators",0) close_system("CRLBLASOperations",0) close_system("CRLFixedPointOperators",0) close_system("CRLCustomEntry",0) close_system("CRLMLFunctionReplacement",0) close_system("CRLDataAlignment",0)
drawnow; if exist("h","var") && ishghandle(h) close(h); end
clear h; clear isDaDemoSupported; clear crl;