Specify Fixed-Point Math Properties in MATLAB Function Block - MATLAB & Simulink (original) (raw)
Main Content
This example shows how to specify fixed-point math properties in a MATLAB Function block. You can specify fimath properties to add fixed-point numbers without bit growth. The same methods also apply to subtraction and multiplication.
Define Fixed-Point Variables with Attached fimath
Define fixed-point variables A and B with attached fimath.
clearvars
F = fimath(... 'RoundMode','Fix',... 'OverflowMode','Wrap',... 'ProductMode','SpecifyPrecision',... 'ProductWordLength',32,... 'ProductFractionLength',16,... 'SumMode','SpecifyPrecision',... 'SumWordLength',32,... 'SumFractionLength',16,... 'CastBeforeSum',true);
A = fi(1,true,32,16,F); B = fi(1,true,32,16,F);
Define a structure T containing prototypes of the variables A and B.
T.A = cast(0,'like',A); T.B = cast(0,'like',B);
The structure T functions as a types table. The values of the fields of T are not important. You will use the data types of the fields of T later in this example to specify fixed-point types that carry the fimath along with them.
Add the fixed-point variables A and B. In MATLAB®, the fimath attached to variables A and B specify that the sum is to be computed as 32-bit word length and 16-bit fraction length.
Y = 2
DataTypeMode: Fixed-point: binary point scaling
Signedness: Signed
WordLength: 32
FractionLength: 16
RoundingMethod: Zero
OverflowAction: Wrap
ProductMode: SpecifyPrecision
ProductWordLength: 32ProductFractionLength: 16 SumMode: SpecifyPrecision SumWordLength: 32 SumFractionLength: 16 CastBeforeSum: true
The fimath propagates to the variable Y.
Default MATLAB Function Block Behavior
In general, the Simulink software does not propagate fimath on fixed-point fi objects. This rule applies even if the fi objects have attached fimath in a Constant block or are passed in as a MATLAB Function block parameter. However, any attached fimath defined inside a MATLAB Function block are respected. One exception to the rule about parameters is described in the next section.
This function is defined in the block named MATLAB Function 1 in the mParameterFIMath model. If you execute this function in MATLAB, it returns the same 32-bit data type as the Y = A + B example.
function Y1 = default_behavior(A,B) Y1 = A + B; end
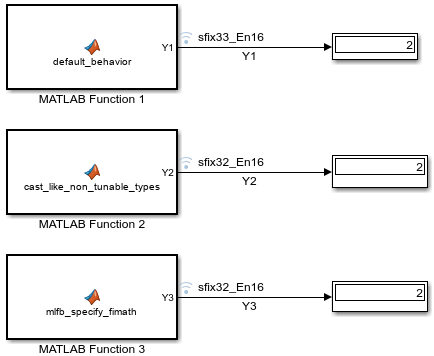
Simulate the mParameterFIMath model to see how the MATLAB Function block executes this code.
model = 'mParameterFIMath'; open_system(model); sim(model); Y1 = logsout.get('Y1').Values.Data
Y1 = 2
DataTypeMode: Fixed-point: binary point scaling
Signedness: Signed
WordLength: 33
FractionLength: 16The MATLAB Function 1 block returns Y1 with a 33-bit word length instead of the 32-bit word length returned in MATLAB. To see why, open the Property Inspector pane for the MATLAB Function 1 block.
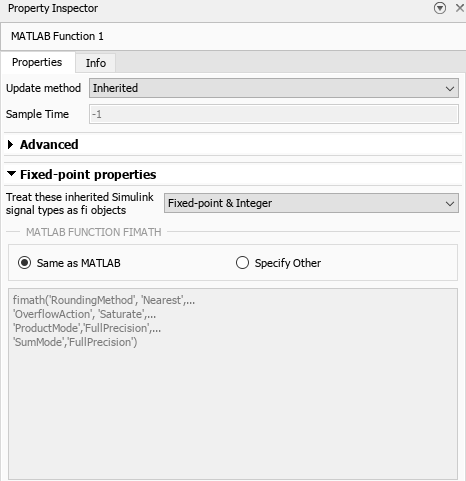
The MATLAB Function 1 block returns a 33-bit word length output because its MATLAB Function fimath setting has been set to Same as MATLAB. The input parameters A and B are stripped of their attached fimath and instead use the default fimath settings from MATLAB. The default fimath in MATLAB does full-precision sums. Therefore, the sum of two 32-bit variables return a 33-bit result.
To see the default fimath settings in MATLAB, first reset any global fimath settings, then enter fimath in the MATLAB Command Window.
ans = RoundingMethod: Nearest OverflowAction: Saturate ProductMode: FullPrecision SumMode: FullPrecision
You can also to change the value of globalfimath, but doing so changes the fixed-point math behavior globally. This method is not recommended.
Pass fimath into MATLAB Function Block from Parameter
In general, the MATLAB Function block strips fimath from fixed-point inputs. The exception to this rule is if an input parameter is a non-tunable structure, such as this one.
T.A = cast(0,'like',A); T.B = cast(0,'like',B);
In the mParameterFIMath model, the MATLAB Function 2 block has the structure T defined as a non-tunable input parameter.
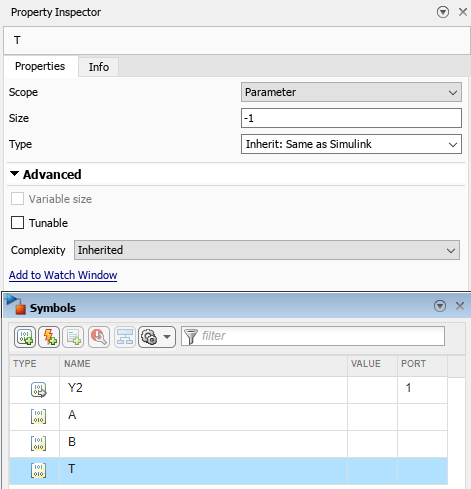
The fields T.A and T.B carry the data type and fimath of A and B. If you cast the inputs A and B like T.A and T.B, respectively, you recover the fimath that was defined in MATLAB.
function Y2 = cast_like_non_tunable_types(A, B, T) A = cast(A,'like',T.A); B = cast(B,'like',T.B); Y2 = A + B; end
The output of the MATLAB Function 2 block has the desired 32-bit word length.
Y2 = logsout.get('Y2').Values.Data
Y2 = 2
DataTypeMode: Fixed-point: binary point scaling
Signedness: Signed
WordLength: 32
FractionLength: 16This workflow provides a robust way of defining fixed-point data types in MATLAB Function blocks because it allows for the definition of different fimath and data type for each different variable. This method has these advantages:
- The algorithm and type specification can be separate, with the types controlled in a dictionary separate from the block. Changing the type does not change the algorithm or block.
- MATLAB and MATLAB Function blocks in Simulink have identical behavior.
- Each parameter can have its own
fimathand data type. - Each parameter can change to be types other than fixed-point. For instance,
T.A = single(0); T.B = single(0);would change all types in this example to single without having to use global data-type override settings.
Set fimath for All Input Parameters
An alternative way to define fimath in a MATLAB Function block is to declare the fimath in the Fixed-point properties of the MATLAB Function block.
In the mParameterFIMath model, the MATLAB Function 3 block contains this code.
function Y3 = mlfb_specify_fimath(A, B) Y3 = A + B; end
In the Property Inspector pane, under Fixed-point properties > MATLAB Function fimath, the option Specify Other is selected. The fimath is defined as the variable F from above.
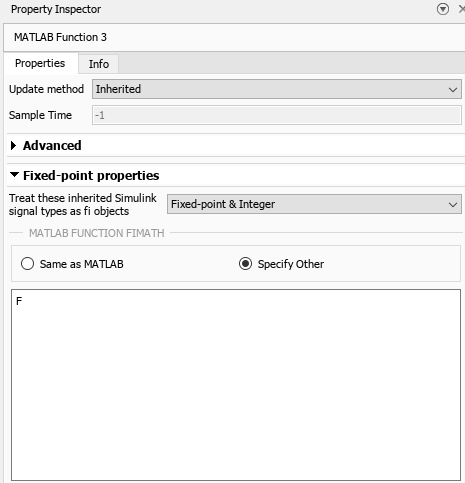
Alternatively, you can write the fimath definition directly in the MATLAB Function fimath box.
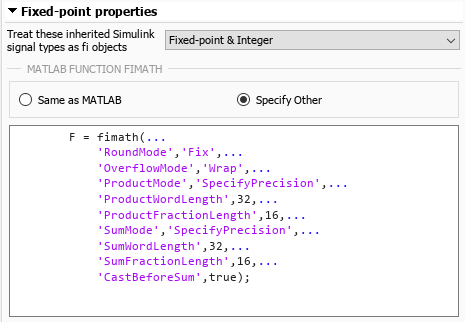
Confirm that the output of this block has the desired 32-bit word length.
Y3 = logsout.get('Y3').Values.Data
Y3 = 2
DataTypeMode: Fixed-point: binary point scaling
Signedness: Signed
WordLength: 32
FractionLength: 16This method has these limitations:
- All MATLAB Function block input parameters get the same
fimath. - Each MATLAB Function block must be modified to specify the
fimath.