hdlcoder.TimingGenerator - Base class to implement custom tool and device support for critical path
estimation reporting - MATLAB ([original](https://in.mathworks.com/help/hdlcoder/ref/hdlcoder.timinggenerator-class.html)) ([raw](?raw))Namespace: hdlcoder
Base class to implement custom tool and device support for critical path estimation reporting
Since R2024a
Description
The hdlcoder.TimingGenerator class is an abstract base class you can use to implement custom tool and device support for critical path estimation reporting. You can use instances of this class as the input to thegenhdltdb function.
Because the hdlcoder.TimingGenerator class is an abstract class, you cannot create an instance of this class directly. You use thehandle class to derive other classes, which can be concrete classes whose instances are handle objects.
To define a handle class, derive your class fromhdlcoder.TimingGenerator using the syntax in this classdef code.
classdef MyHandleClass < hdlcoder.TimingGenerator ... end
When you create a derived class object fromhdlcoder.TimingGenerator, HDL Coder™ generates a comma-separated file calledtiming_info.txt. The file contains timing details related to the operation undergoing a timing analysis.
The hdlcoder.TimingGenerator class is a handle class.
Class Attributes
| Abstract | true |
|---|---|
| HandleCompatible | true |
For information on class attributes, see Class Attributes.
Events
| Event Name | Trigger | Event Data | Event Attributes |
|---|---|---|---|
| ObjectBeingDestroyed | Triggered when the handle object is about to be destroyed, but before calling the delete method. | event.EventData | NotifyAccess=privateListenAccess=public |
Examples
In this example, you examine a custom timing generator subclass designed for Xilinx® Vivado® hardware. This class uses the synthesizeRTL method to run synthesis and timing analysis, and uses thehasDSPs method to characterize the DSPs on your device. If your device does not have DSPs or if you do not want to characterize them, sethasDSPs to false. After you create the class, you can pass the hdlcoder.TimingGenerator.XilinxVivado class as a name-value argument to the genhdltdb function to generate a timing database. To view the shipping custom class, at the MATLAB® Command Line, enter:
edit hdlcoder.TimingGenerator.XilinxVivado
XilinxVivado custom class definition.
classdef XilinxVivado < hdlcoder.TimingGenerator %
% Copyright 2023 The MathWorks, Inc.
The synthesizeRTL method calls the project creation, synthesis, and timing analysis TCL scripts.
function [status, logTxt] = synthesizeRTL(obj) % add code for project creation, synthesis and timing analysis end
The postProcessTimingInfo method further processes the timing information reported by the synthesis tool. For example, you can use this method to remove setup and clock-to-Q delays. Use this method when TCL scripts cannot handle removing setup and hold delays that are not required.
function timingInfo = postProcessTimingInfo(obj, timingInfo) % add code here for your custom timing information analysis end
These methods account for and characterize the DSPs on the device.:
- The
hasDSPsmethod is set totrueto characterize the DSPs on the device - The
countDSPsmethod counts and returns the number of DSPs during device synthesis - the
dspSynthesisAttributemethod uses name-value arguments in cell arrays to specify attributes to apply during HDL code generation - the
dontTouchSynthesisAttributemethod uses name-value arguments in cell arrays to specify attributes to apply during HDL code generation
function val = hasDSPs(~) val = true; end
function val = countDSPs(~, synthesisLogText)
val_str = regexp(synthesisLogText, '|DSP.\S*\s*\|\s*(\d+)', 'tokens', 'lineanchors');
assert(isscalar(val_str));
val = str2double(val_str{1}{1});
end
function val = dspSynthesisAttribute(~)
val = {'USE_DSP', 'yes'};
end
function val = dontTouchSynthesisAttribute(~)
val = {'DONT_TOUCH', 'TRUE'};
endGenerate a timing database by using the genhdltdb function and passing the XilinxVivado class as a name-value argument to the function.
tg = XilinxVivado; genhdltdb("SynthesisDeviceConfiguration",{"Zynq","xc7z020","clg484","-1"}, ... "TimingDatabaseDirectory","C:\Work\database", ... "TimingGenerator",tg);
In this example, you examine a custom timing generator subclass designed for Cadence® Genus hardware. This class uses the synthesizeRTL method to run synthesis and timing analysis and uses thehasDSPs method to characterize the DSPs on the device. If your device does not have DSPs or if you do not want to characterize them, sethasDSPs to false. If you set hasDSPs totrue, you must define the countDSPs,dspSynthesisAttribute, anddontTouchSynthesisAttribute methods. After you create the class, you can pass the hdlcoder.TimingGenerator.CadenceGenus class as a name-value argument to the genhdltdb function to generate a timing database. To examine the completed custom class, at the MATLAB command line, enter:
edit hdlcoder.TimingGenerator.CadenceGenus
CadenceGenus custom class definition.
classdef CadenceGenus < hdlcoder.TimingGenerator % % Copyright 2024 The MathWorks, Inc.
The synthesizeRTL method calls the project creation, synthesis, and timing analysis TCL scripts.
function [status, logTxt] = synthesizeRTL(obj)
% add code here for project creation, synthesis, and timing analysis
end
The useSynchronousReset method tells HDL Coder to specify what to set the global reset options to. For example, Cadence Genus supports asynchronous resets, souseSynchronousReset is set to false to perform asynchronous resets.
function val = useSynchronousReset(~) val = false; end
In this example, this class targets a device that does not have DSPs. ThehasDSPs method is set tofalse.
function val = hasDSPs(~) val = false; end
Generate a timing database by using the genhdltdb function. Pass the CadenceGenus class as a name-value argument to the function.
tg = CadenceGenus; genhdltdb("SynthesisDevicePart","tutorial.lib", ... "TimingDatabaseDirectory","C:\Work\database", ... "TimingGenerator",tg);
More About
When you create a custom hdlcoder.TimingGenerator object, you must create an abstract synthesizeRTL method that you call to run synthesis and create a timing analysis, and an abstracthasDSPs method to characterize the DSPs on your device. If your device does not have DSPs, or you do not want to characterize the DSPs on the device, set hasDSPs to false. ThesynthesizeRTL method includes calls to functions to generate TCL scripts that create projects, run synthesis, and perform a timing analysis on all input, output, and internal register paths. Because critical path estimation includes timing information in the presence of delay blocks, you must remove:
- Hold time from input-to-internal paths
- Setup time from internal-to-output paths
- Setup and hold times from input-to-output paths
When you set hasDSPs to true, you must define:
- A
countDSPsmethod to count and return the number of DSPs during device synthesis. - A
dspSynthesisAttributemethod and use name-value arguments in cell arrays to apply during HDL code generation. - A
dontTouchSynthesisAttributemethod and use name-value arguments in cell arrays to apply during HDL code generation.
You can also include an optionalpostProcessTimingInfo method to further process the timing info reported by the synthesis tool. Provide the name of the timing report generated by the synthesis tool by using the ReportFile property of the derived class object.
When you derive a hdlcoder.TimingGenerator object, these object parameters are pre-defined in the derived object and are copied from the basehdlcoder.TimingGenerator class:
- ReportFile — Name of file that stores the timing report generated by the synthesis tool. The
postprocessTimingInfomethod uses this file. The default value is'mathworks_report_timing_groups.log'. - CsvFile — Name of the comma-separated value (CSV) file that contains the timing information of the register-to-register paths used to build the timing database. The default value is
timing_info.txt. - RegSuffix — Wildcard option to query register names in the synthesis tool. This wildcard option includes all registers that have the same name and different numbers. The default value is
*.
The derived hdlcoder.TimingGenerator class object receives these inputs from the characterization infrastructure:
obj.TargetInfo.deviceFullName— You can populate this field with information from any of these values:SynthesisDevicePart,SynthesisDeviceConfiguration,SynthesisDeviceName,SynthesisDeviceSpeedGrade, orSynthesisDevicePackage.obj.ModelInfo— This field is a structure with these elements, which are populated by the characterization infrastructure:Field Name Description obj.ModelInfo.topSubsystem Name of design under test (DUT) subsystem obj.ModelInfo.blockSubsystem Name of subsystem that contains the block to be characterized obj.ModelInfo.portRegisters.in.values Cell array of DUT input register names obj.ModelInfo.portRegisters.out.values Cell array of DUT output register names
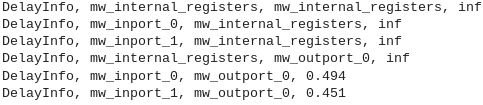
The output of the derived hdlcoder.TimingGenerator class is a CSV file named timing_info.txt. The file contains information in this format:DelayInfo, source_type, destination_type, propagation delay (ns).
The source_type or destination_type fields are of type:
mw_internal_registers— Any internal register inside the subsystem that contains the block to be characterized.mw_inport_#— Numbered input to the operator starting at index zero. For example,mw_inport_0,mw_inport_1, and so on.mw_outport_#— Numbered output from the operator starting at index zero. For example,mw_outport_0,mw_outport_1, and so on.
The propagation delay (ns) field is the value in nanoseconds for either internal-to-internal, input-to-internal, internal-to-output, or input-to-output propagation delays. If a timing path does not exist , this value isinf. This field contains the timing information for every path. This image shows the contents of an example timing_info.txt file:
Version History
Introduced in R2024a