HDL Counter - Free-running or count-limited hardware counter - Simulink (original) (raw)
Free-running or count-limited hardware counter
Libraries:
HDL Coder / Sources
Description
The HDL Counter block models a free-running, count-limited, or modulo hardware counter that supports signed and unsigned integer and fixed-point data types. The counter emits its value for the current sample time. During simulation, this block does not report warnings or errors due to wrap on overflow. To report these warnings, see Simulink.restoreDiagnostic.
By default, the counter does not have input ports. The counter counts up from an initial value to a threshold value based on the Counter type, theCount to value, and the Word length. The output data type of the counter depends on the Counter output data,Word length, and Fraction length.
Ports
Input
Local reset port for the counter that when high resets the count value.
Dependencies
To enable this port, set Local reset port.
Data Types: Boolean
Load port that when high sets the counter to the load value,load_val.
Dependencies
To enable this port, set Load ports.
Data Types: Boolean
Data value to load for setting the count value when high input is given to the load port.
Dependencies
To enable this port, set Load ports.
Data Types: Boolean
Enable signal that specifies whether the counter should count from the previous value. When this signal is high, the counter counts continues up or down depending on the direction. When this signal is low, the counter holds the previous value.
Dependencies
To enable this port, set Count enable port.
Data Types: Boolean
Count direction that specifies whether to count up or count down. This port interacts with Step value to determine count direction.
1: This value is the default that results in an up counter. The Step value is added to the current counter value to compute the next value.0: This value results in a down counter. The Step value is subtracted from the current counter value to compute the next value.
Dependencies
To enable this port, set Count direction port.
Data Types: Boolean
Output
This is the counter value. By default, if you do not enable the input ports, the counter counts up to a value that is determined based on theCounter type, the Count to value, and the Word length.
Data Types: int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | fixed point
Counter limit indicator, returned as a Boolean scalar.
1: indicates that the counter reached its limit.0: indicates that the counter did not reach its limit.
Dependencies
To enable this port, select the Count hit output port parameter.
Data Types: Boolean
Parameters
Counter behavior that determines whether to model a free running, count-limited, or module hardware counter.
Free running(default): The counter continues to increment or decrement by the Step value until reset.Count limited: The counter increments or decrements by the Step value until it is exactly equal to the Count to value. If the Step value value is such that the count value does not exactly equal theCount to value, then it can continue counting to a threshold value that is determined by the word length.Modulo: The counter increments or decrements by the Step value until it reaches the Count to value. If theStep value value is such that the count value does not exactly equal the Count to value, then the counter wraps to a value that is determined by the wrapping step value.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountType | |
|---|---|
| Type: character vector | |
| Value: 'Free running' | 'Count limited' | 'Modulo' |
| Default: 'Free running' |
The value to which the counter resets. The default value is0.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountInit |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: An integer greater than or equal to zero |
| Default: '0' |
Value added to counter at each sample time. The default value is1.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountStep |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: An integer greater than or equal to zero |
| Default: '1' |
When you use a Count limited counter, if the count is exactly equal to Count to value, the count restarts at the Initial value. If the count value exceeds the Count to value, the counter continues counting to a threshold value that depends on the Word length. The default is 25.
When you use a Modulo counter, if the count reaches theCount to value, the count restarts at a value that is determined by the wrapping step value.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Counter type toCount limited orModulo.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountMax |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: An integer greater than or equal to zero |
| Default: '25' |
Specifies the parameter that sets the start value after rollover when you use a Count limited or Free running counter. When you use aModulo counter, the counter can rollover to a wrapping step value that is different from the value to count from. When set to Specify, the Count from value parameter is the start value after rollover. The default is Initial value.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountFromType |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: 'Initial value' |'Specify' |
| Default: 'Initial value' |
Counter value after rollover when Count from is set to Specify. The default is 0.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountFrom |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: 'Initial value' |'Specify' |
| Default: 'Initial value' |
When selected, creates a local reset port, rst.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountResetPort |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: 'off' | 'on' |
| Default: 'off' |
When selected, creates a load data port, load_val, and load trigger port, load.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountLoadPort |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: 'off' | 'on' |
| Default: 'off' |
When selected, creates a count enable port, enb.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountEnbPort |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: 'off' | 'on' |
| Default: 'off' |
When selected, creates a count direction port, dir.
Enabling this parameter disables the Count hit output port parameter.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountDirPort |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: 'off' | 'on' |
| Default: 'off' |
Select this parameter to enable the count_hit output port.
Enabling this parameter clears the Count direction port parameter.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountHitOutputPort |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: 'off' | 'on' |
| Default: 'off' |
Output data type signedness. The default is Unsigned.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountDataType |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: 'Unsigned' | 'Signed' |
| Default: 'off' |
Bit width, including sign bit, for an integer counter; word length for a fixed-point data type counter. The minimum value if Output data type is Unsigned is1, 2 ifSigned. The maximum value is125. The default is 8.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountWordLen |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: An integer greater than or equal to one |
| Default: '8' |
Fixed-point data type fraction length. The default is0.
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountFracLen |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: An integer greater than or equal to zero |
| Default: '0' |
Sample time. The default is 1. This parameter is not available, and the block inherits its sample time from the input ports when any of these parameters is selected:
- Local reset port
- Load ports
- Count enable port
- Count direction port
Programmatic Use
| Block parameter: CountSampTime |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: An integer greater than or equal to one |
| Default: '1' |
Algorithms
By default, when you do not enable the control ports, the counter counts upwards from zero in free-running mode. In this mode, the counter increments in steps of one at each sample time unit until it reaches the threshold value. The count threshold value is calculated as 2^(Word length) - 1. When it reaches the count value, the counter resets to the initial value.
The counter behavior depends on control ports that you specify. This table shows the priority of the control signals and how the counter value is updated in relation to the control signals.
| Local reset, rst | Load trigger, load | Count enable, enb | Count direction, dir | Next Counter Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | – | – | – | Initial value |
| 0 | 1 | – | – | load_val value |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | – | Current value |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Current value + step value |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Current value - step value |
The Step value parameter and optional count direction port,dir, interact to determine the actual count direction.
| dir Signal Value | Step Value Sign | Actual Count Direction |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | + (positive) | Up |
| 1 | - (negative) | Down |
| 0 | + (positive) | Down |
| 0 | - (negative) | Up |
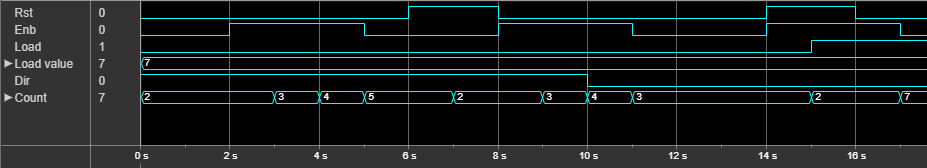
This figure illustrates the free running mode of operation. In this example, the counter has a Word length of 4. TheInitial value is 2, load value is7, and the Step value is1. When the Enb signal is high, the counter increments by steps of one. When Rst signal becomes high, the counter resets to the initial value, 2. When theDir port goes low, the counter decrements from4 to 3 at time step11s. The count value is tied to the load value when theLoad port becomes high.
You can use the Counter type parameter to specify the counter behavior. The Count limited mode of the counter wraps the count to the initial value when the counter exactly reaches the Count to value. If the counter does not exactly reach the Count to value, it can exceed this value. For an up counter, the count value can reach a threshold value that is calculated as 2^(Word length) - 1. For a down counter, the count value can reach the Initial value. When it reaches or exactly matches this threshold value, the counter resets to a value that is determined by the wrapping step value.
The Modulo mode of the counter wraps the count when it reaches or exactly matches the Count to value. Instead of restarting at the initial value, the counter wraps back to a value that is determined by a wrapping step value. For an up counter, the wrapping step value is calculated as step value - (count to value + 1) + count from value. For a down counter, the wrapping step value is calculated as_count from value - step value + (count to value + 1)_.
This figure illustrates the Count limited andModulo modes of operation. In this example, the counter has a Word length of 4,Initial value of 2, Step value of 3, and Count to value of 12.

In the Count limited mode, as the count value reaches11, it exceeds the Count to value and reaches 14. As the threshold value is 15 (2^4-1), the counter resets to a value that is determined by the wrapping step value. When counting down, the counter exceeds the Initial value and can reach zero. It then resets to a value that is determined by the wrapping step value.
In the Modulo mode, as the count value reaches11, the counter resets to a value that is determined by the wrapping step value. The wrapping step value is 3 - (12 + 1) + 2 = -8. Therefore, the counter resets to the value 3 (11 + (-8)). When counting down, as the count value reaches4, the counter resets to a value that is determined by the wrapping step value. The wrapping step value is 2 - 3 + (12 + 1) = 12. Therefore, the counter resets to the value12.
Extended Capabilities
HDL Coder™ provides additional configuration options that affect HDL implementation and synthesized logic.
HDL Architecture
This block has one default HDL architecture.
HDL Block Properties
| General | |
|---|---|
| ConstrainedOutputPipeline | Number of registers to place at the outputs by moving existing delays within your design. Distributed pipelining does not redistribute these registers. The default is0. For more details, see ConstrainedOutputPipeline. |
| InputPipeline | Number of input pipeline stages to insert in the generated code. Distributed pipelining and constrained output pipelining can move these registers. The default is0. For more details, see InputPipeline. |
| OutputPipeline | Number of output pipeline stages to insert in the generated code. Distributed pipelining and constrained output pipelining can move these registers. The default is0. For more details, see OutputPipeline. |
Restrictions
- If the bitwidth of the input signal to a HDL Counter exceeds the data type limit, the generated HDL code can produce incorrect simulation results. To accommodate the larger bit width, use a larger data type.
- The block does not support vectors. Only scalar types are supported for block inputs and outputs.
- Load value used in
Modulocounter mode must be within the range of the Count from andCount to value to avoid simulation mismatches.
Version History
Introduced in R2014a