arviz.plot_density — ArviZ 0.14.0 documentation (original) (raw)
arviz.plot_density(data, group='posterior', data_labels=None, var_names=None, filter_vars=None, combine_dims=None, transform=None, hdi_prob=None, point_estimate='auto', colors='cycle', outline=True, hdi_markers='', shade=0.0, bw='default', circular=False, grid=None, figsize=None, textsize=None, labeller=None, ax=None, backend=None, backend_kwargs=None, show=None)[source]#
Generate KDE plots for continuous variables and histograms for discrete ones.
Plots are truncated at their 100*(1-alpha)% highest density intervals. Plots are grouped per variable and colors assigned to models.
Parameters
dataUnion[Object, Iterator[Object]]
Any object that can be converted to an arviz.InferenceData object, or an Iterator returning a sequence of such objects. Refer to documentation of arviz.convert_to_dataset() for details about such objects.
group: Optional[str]
Specifies which arviz.InferenceData group should be plotted. Defaults to ‘posterior’. Alternative values include ‘prior’ and any other strings used as dataset keys in thearviz.InferenceData.
data_labelsOptional[List[str]]
List with names for the datasets passed as “data.” Useful when plotting more than one dataset. Must be the same shape as the data parameter. Defaults to None.
var_names: Optional[List[str]]
List of variables to plot. If multiple datasets are supplied and var_names is not None, will print the same set of variables for each dataset. Defaults to None, which results in all the variables being plotted.
filter_vars: {None, “like”, “regex”}, optional, default=None
If None (default), interpret var_names as the real variables names. If “like”, interpret var_names as substrings of the real variables names. If “regex”, interpret var_names as regular expressions on the real variables names. A lapandas.filter.
combine_dimsset_like of str, optional
List of dimensions to reduce. Defaults to reducing only the “chain” and “draw” dimensions. See the this section for usage examples.
transformcallable
Function to transform data (defaults to None i.e. the identity function)
hdi_probfloat
Probability for the highest density interval. Should be in the interval (0, 1]. Defaults to 0.94.
point_estimateOptional[str]
Plot point estimate per variable. Values should be ‘mean’, ‘median’, ‘mode’ or None. Defaults to ‘auto’ i.e. it falls back to default set in rcParams.
colorsOptional[Union[List[str],str]]
List with valid matplotlib colors, one color per model. Alternative a string can be passed. If the string is cycle, it will automatically choose a color per model from matplotlib’s cycle. If a single color is passed, e.g. ‘k’, ‘C2’ or ‘red’ this color will be used for all models. Defaults to cycle.
outlinebool
Use a line to draw KDEs and histograms. Default to True
hdi_markersstr
A valid matplotlib.markers like ‘v’, used to indicate the limits of the highest density interval. Defaults to empty string (no marker).
shadeOptional[float]
Alpha blending value for the shaded area under the curve, between 0 (no shade) and 1 (opaque). Defaults to 0.
bw: Optional[float or str]
If numeric, indicates the bandwidth and must be positive. If str, indicates the method to estimate the bandwidth and must be one of “scott”, “silverman”, “isj” or “experimental” when circular is False and “taylor” (for now) when circular is True. Defaults to “default” which means “experimental” when variable is not circular and “taylor” when it is.
circular: Optional[bool]
If True, it interprets the values passed are from a circular variable measured in radians and a circular KDE is used. Only valid for 1D KDE. Defaults to False.
gridtuple
Number of rows and columns. Defaults to None, the rows and columns are automatically inferred.
figsizeOptional[Tuple[int, int]]
Figure size. If None it will be defined automatically.
textsize: Optional[float]
Text size scaling factor for labels, titles and lines. If None it will be autoscaled based on figsize.
labellerlabeller instance, optional
Class providing the method make_label_vert to generate the labels in the plot titles. Read the Label guide for more details and usage examples.
ax: numpy array-like of matplotlib axes or bokeh figures, optional
A 2D array of locations into which to plot the densities. If not supplied, Arviz will create its own array of plot areas (and return it).
backend: str, optional
Select plotting backend {“matplotlib”,”bokeh”}. Default “matplotlib”.
backend_kwargs: bool, optional
These are kwargs specific to the backend being used, passed tomatplotlib.pyplot.subplots() or bokeh.plotting.figure(). For additional documentation check the plotting method of the backend.
showbool, optional
Call backend show function.
Returns
axesmatplotlib axes or bokeh figures
See also
Plot distribution as histogram or kernel density estimates.
Plot Posterior densities in the style of John K. Kruschke’s book.
Examples
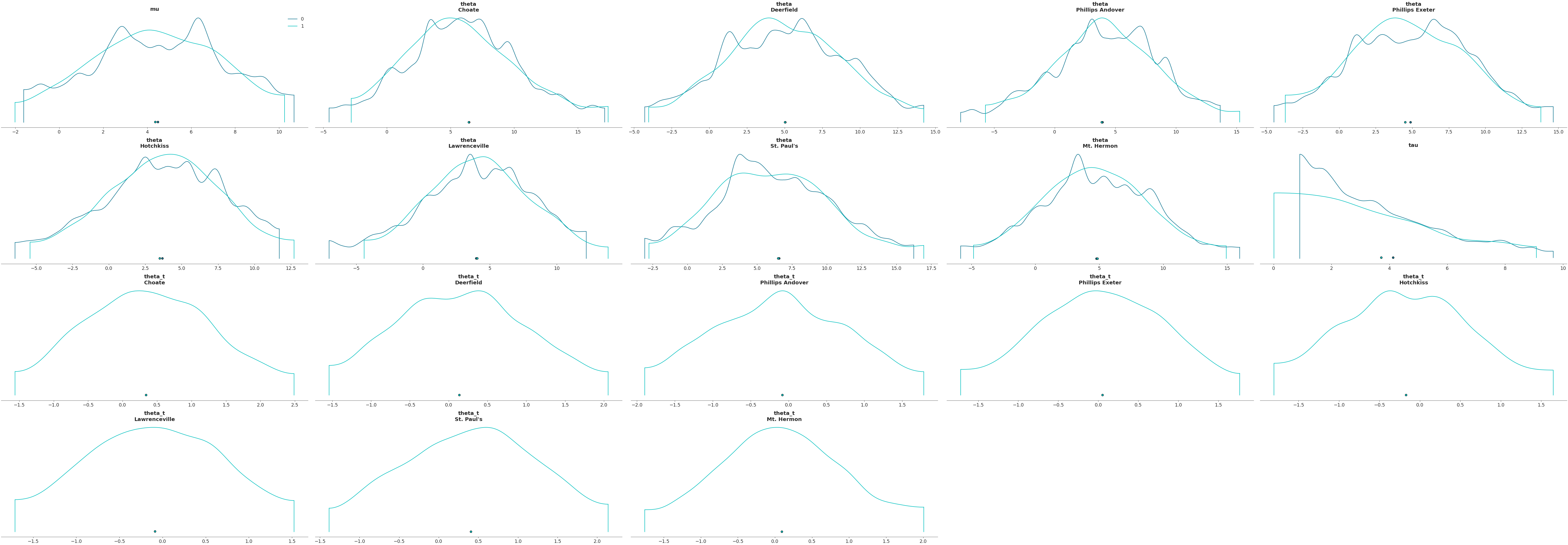
Plot default density plot
import arviz as az centered = az.load_arviz_data('centered_eight') non_centered = az.load_arviz_data('non_centered_eight') az.plot_density([centered, non_centered])
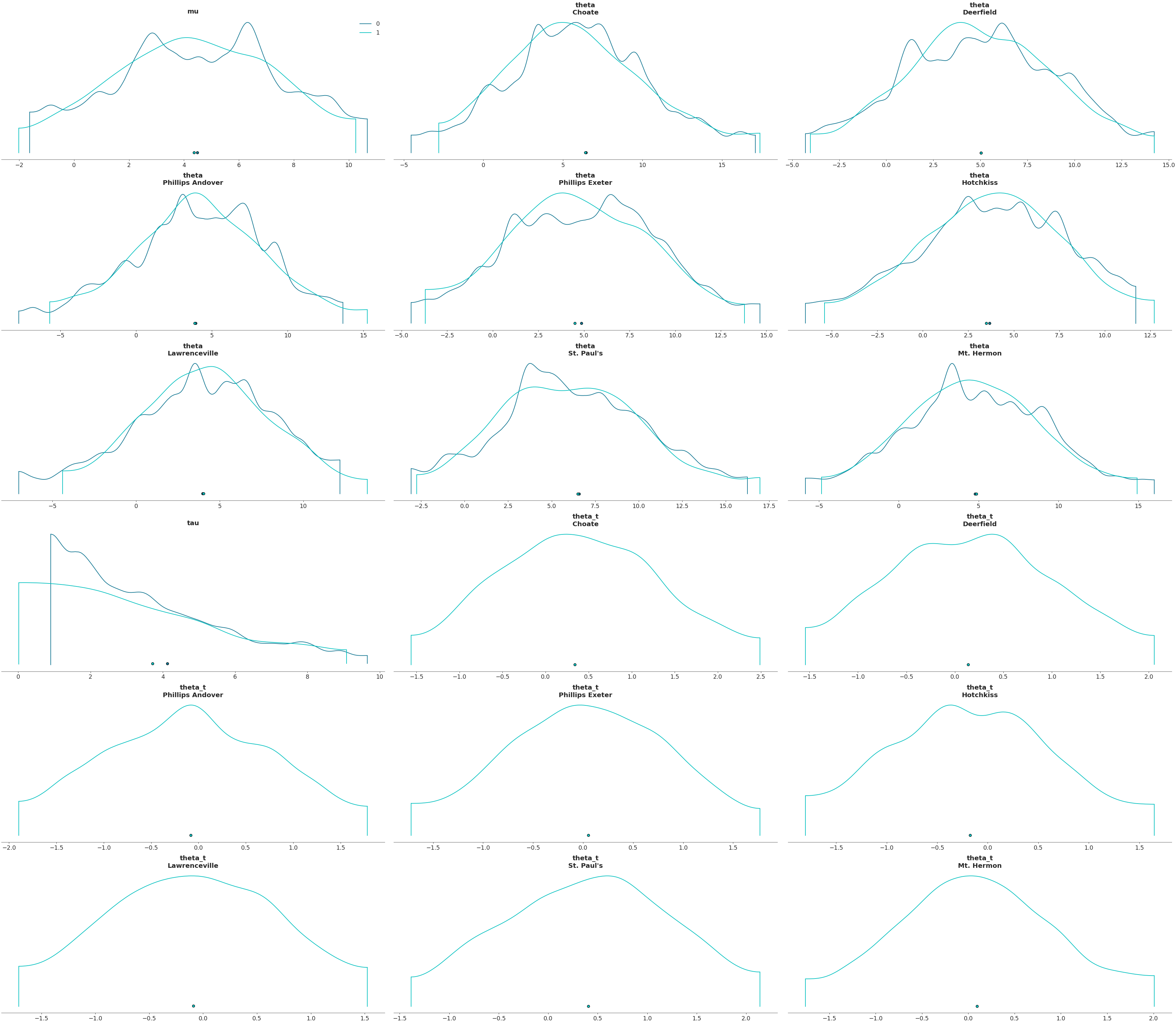
Plot variables in a 4x5 grid
az.plot_density([centered, non_centered], grid=(4, 5))
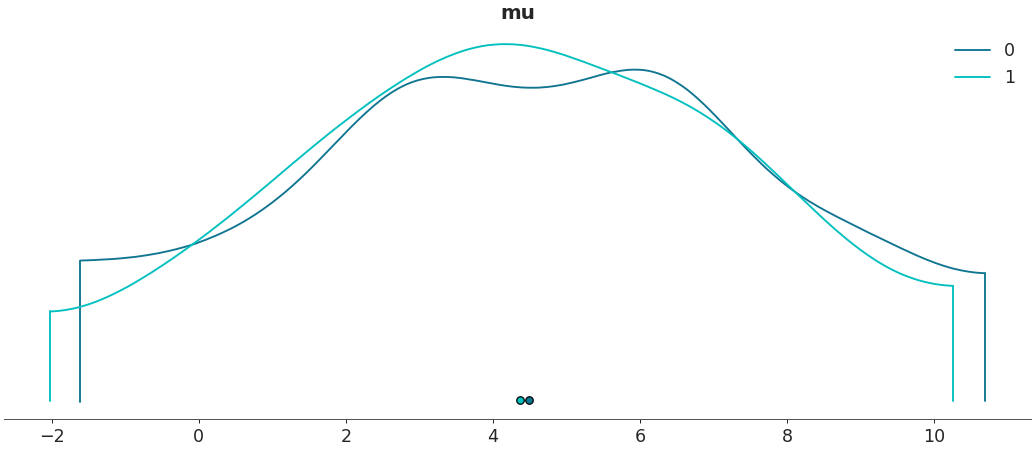
Plot subset variables by specifying variable name exactly
az.plot_density([centered, non_centered], var_names=["mu"])
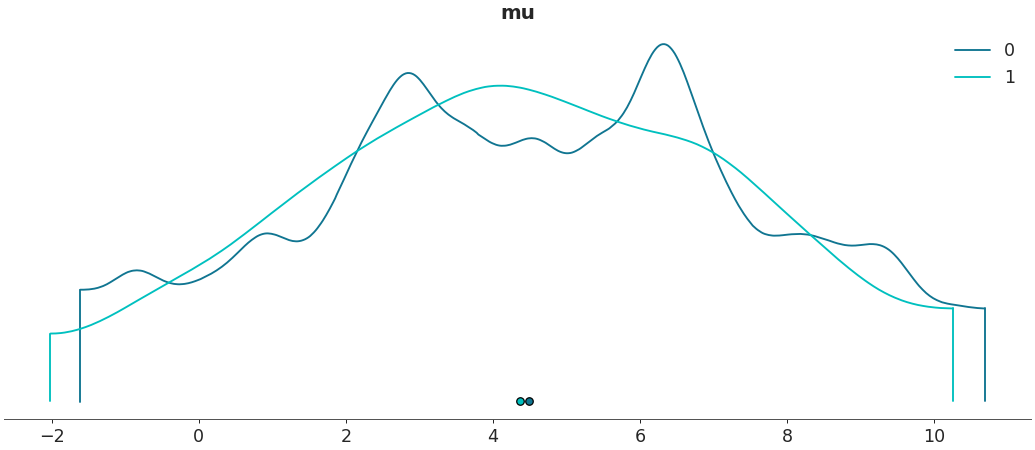
Plot a specific az.InferenceData group
az.plot_density([centered, non_centered], var_names=["mu"], group="prior")
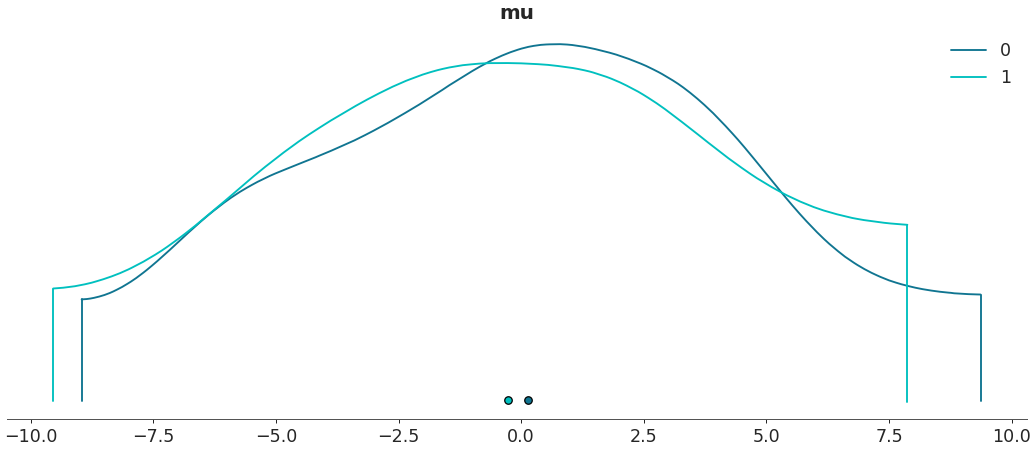
Specify highest density interval
az.plot_density([centered, non_centered], var_names=["mu"], hdi_prob=.5)
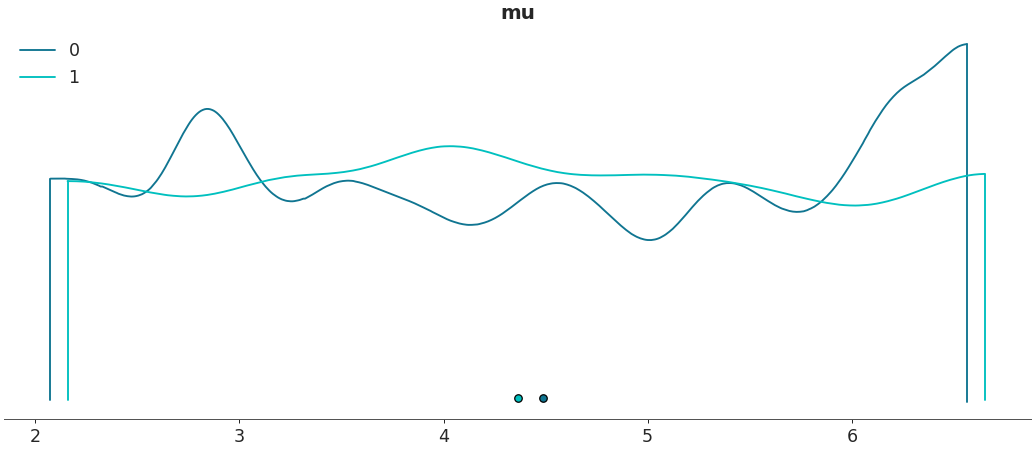
Shade plots and/or remove outlines
az.plot_density([centered, non_centered], var_names=["mu"], outline=False, shade=.8)
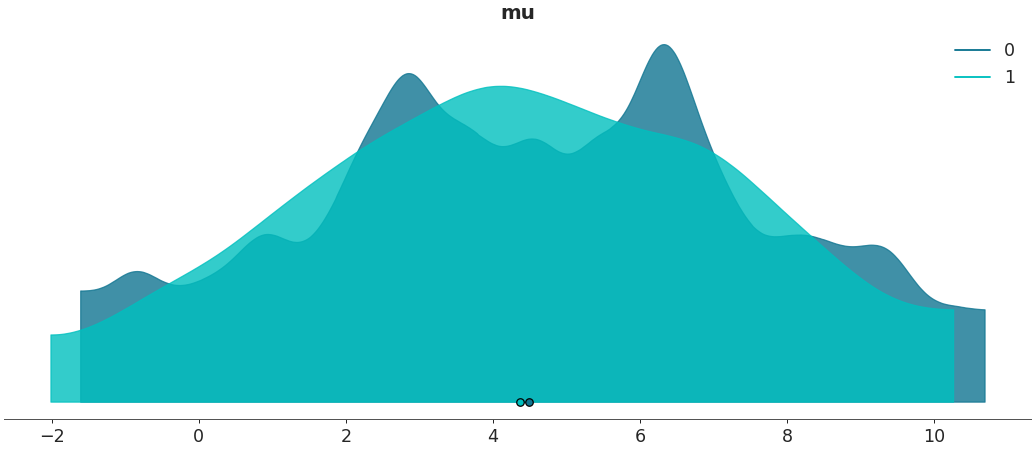
Specify binwidth for kernel density estimation
az.plot_density([centered, non_centered], var_names=["mu"], bw=.9)